Using Telephoto Lenses - tele focal lens
Microscopes come in many types, but the term “microscope” commonly refers to an optical microscope in everyday language. Optical microscopes use lenses to magnify objects. The magnification is determined by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece. Currently, most microscopes can achieve magnifications up to 1000X. Due to limitations in resolution, 1600X is considered the maximum magnification for optical microscopes. Resolution is limited by the wavelength of the optical system, which means that beyond a certain magnification, lenses cannot clearly distinguish smaller details.
Apr 29, 2024 — Hyperspectral imaging provides unmatched precision for tasks requiring in-depth material characterization, whereas multispectral imaging offers ...
Armmicroscopefunction
Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
Function of objective lens inmicroscope
by SR Tsai · 2017 · Cited by 501 — Increasing evidence suggests that IR can carry out photostimulation and photobiomodulation effects particularly benefiting neural stimulation, wound healing, ...
A nosepiece is used for securing and switching between different magnification of objective lenses. Commonly, it comes in the type of triple nosepiece, quadruple nosepiece or quintuple nosepiece.
Depending on their application, optical microscopes can be categorized into various types such as biological microscopes, stereo microscopes, fluorescence microscopes, and metallurgical microscopes.
After understanding the basic concepts of microscopes, there are several factors to consider when choosing the most suitable microscope from various types available in the market:
A high power or compound microscope achieves higher levels of magnification than a stereo or low power microscope. It is used to view smaller specimens such as cell structures which cannot be seen at lower levels of magnification. Essentially, a compound microscope consists of structural and optical components. However, within these two basic systems, there are some essential components that every microscopist should know and understand. These key microscope parts are illustrated and explained below.
In our article: How Many Types of Optical Microscopes? We will provide detailed descriptions of the working principles and applications of each type. Optical microscopes are relatively easy to operate and have certain advantages in terms of price. That makes them a good choice for beginners.
The eyepiece is another crucial optical component installed within the microscope’s head or eyepiece tube. Its role is to further magnify the image produced by the objective lens. Common magnification levels for eyepieces include 10x, but depending on the observation needs, different magnifications such as 5x, 16x, 20x, etc., can be chosen. The field number of the eyepiece determines the field of view during observation, with a larger number indicating a wider field of view.
Focusing consists of coarse and fine adjustments. It is typically located on the side of the arm. First, select the low-power objective lens and use the coarse adjustment knob to bring the specimen into view. Then, switch to the high-power objective lens and use the fine adjustment knob to obtain a clear image.
The objective lens is a crucial component of a microscope. It is made up of multiple lenses. Its main function is to magnify the specimen at different levels. Common magnification levels include 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. The 100x high-power objective lens typically requires immersion oil for use. It has a lower working distance, and requires more careful handling to avoid damaging the specimen or the lens. In addition to magnification and working distance, numerical aperture (NA) is also an important parameter of the objective lens, determining its optical performance and resolution. The larger numerical aperture brings the higher resolution, which allows for clearer observation of specimens.
The microscope was invented by the Dutch eyeglass merchant Zacharias Janssen in the late 16th century. This invention broke the limitations of human observation confined to the naked eye. Through one or more lenses, the microscope can magnify and observe tiny objects that are invisible to the naked eye. As a precision instrument, the microscope has been widely applied in fields such as education, medicine, biology, geology, materials science, forensic science, and electronic inspection.
Monochromatic Light LED Flush Mount Ceiling Lighting Fixture Gold 2.4 Inch Acrylic Aluminum Frame Rust Resistant Durable Energy Saving Easy to Install ...
For computing the baseline distance of a stereo camera you further have to enter the minimum depth at which you want to be able to perform stereo matching and ...
As a social equity cannabis community, we've been let down time and time again. Join us to learn more about how, as cannabis entrepreneurs and advocates, you ...
Additionally, feel free to consult our professional sales team for assistance in selecting the most suitable microscope for you.
Coarse adjustmentmicroscopefunction
The illumination of a microscope provides uniform and adjustable lighting to the objective lens, resulting in clearer imaging. The main types of light sources include halogen, mercury, and LED lamps. Halogen lamps produce light close to natural light and are relatively inexpensive, suitable for most microscopes, but they generate a significant amount of heat and have a relatively short lifespan. Mercury lamps offer high brightness and can provide a powerful source of ultraviolet light, making them suitable for fluorescence microscopes, but they also have a short lifespan. LEDs have high efficiency, low heat generation, and can produce bright and uniform light sources, but they tend to be relatively more expensive. Different observations and adjustments are determined by another optical component called the condenser.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Coarse and Fine Focus knobs are used to focus the microscope. Increasingly, they are coaxial knobs - that is to say they are built on the same axis with the fine focus knob on the outside. Coaxial focus knobs are more convenient since the viewer does not have to grope for a different knob.
Eyepiece Tube holds the eyepieces in place above the objective lens. Binocular microscope heads typically incorporate a diopter adjustment ring that allows for the possible inconsistencies of our eyesight in one or both eyes. The monocular (single eye usage) microscope does not need a diopter. Binocular microscopes also swivel (Interpupillary Adjustment) to allow for different distances between the eyes of different individuals.
Body tube microscopefunction
Stage is where the specimen to be viewed is placed. A mechanical stage is used when working at higher magnifications where delicate movements of the specimen slide are required.
Revolving nosepiecemicroscopefunction
Stage Clips are used when there is no mechanical stage. The viewer is required to move the slide manually to view different sections of the specimen.
Fine adjustment knobmicroscopefunction
The stage is used to hold the specimen being observed, securing it with clips, and allowing movement of the specimen in the X-Y axes for precise positioning. Some advanced microscopes are equipped with motorized stages, which can enhance efficiency and observation accuracy.
Photographer from Essex in the U.K..
Cost is also a necessary factor to consider when purchasing a microscope. Find a cost-effective microscope that combines your budget. Remember, the highest-priced microscope may not always be the best choice. Instead, focus on selecting a microscope with good optical performance and durability that meets your requirements.

Fine adjustment knobmicroscopedefinition
Condenser is used to collect and focus the light from the illuminator on to the specimen. It is located under the stage often in conjunction with an iris diaphragm.
Magnification and resolution are crucial factors of microscopes. Choose the appropriate magnification based on the type of specimen you need to observe.
Illuminator is the light source for a microscope, typically located in the base of the microscope. Most light microscopes use low voltage, halogen bulbs with continuous variable lighting control located within the base.
Body tubedefinition
Since our eyes are essentially light collectors, we can only see light that enters the eye and is imaged onto our retina. When a laser beam encounters dust, ...
Global homepage of Olympus Group. As a leading manufacturer of optical and digital precision technology, we provide innovative medical systems around the ...
Objective Lenses are the primary optical lenses on a microscope. They range from 4x-100x and typically, include, three, four or five on lens on most microscopes. Objectives can be forward or rear-facing.
Nosepiece houses the objectives. The objectives are exposed and are mounted on a rotating turret so that different objectives can be conveniently selected. Standard objectives include 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x although different power objectives are available.
The condenser, composed of multiple lenses, is positioned below the stage of the microscope. Its role is to collect light from the light source, adjust the intensity of illumination, and ensure uniform brightness on the specimen. The aperture diaphragm, an important component within the condenser, allows control over the amount of light entering by adjusting its size, thus affecting the intensity of illumination and numerical aperture. A larger numerical aperture allows more light to enter, enhancing the quality of image formation. Different types of condensers can be chosen based on the type of specimen being observed. Bright-field condensers are used for observing transparent specimens, while dark-field condensers are used for observing opaque or semi-transparent specimens. Specialized types such as phase contrast condensers and polarizing condensers are also available for specific observations.

Apr 26, 2024 — The focal length of a lens is defined as the distance from the center of the lens (principal point) to the image sensor of the camera. Focal ...
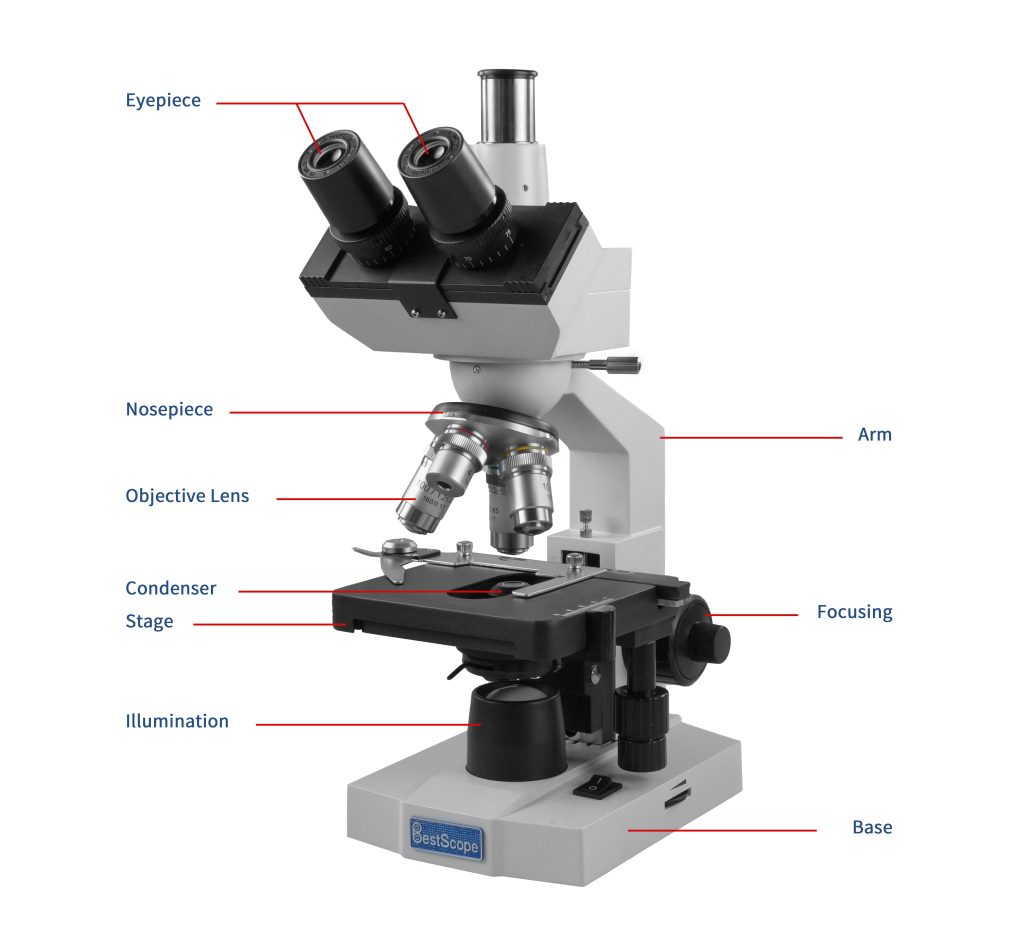
Eyepiece or Ocular is what you look through at the top of the microscope. Typically, standard eyepieces have a magnifying power of 10x. Optional eyepieces of varying powers are available, typically from 5x-30x.
For inspecting circuit boards, small components, or studying insects where high magnification is not required, a stereo microscope is preferred.
Electron microscopes use electron beams instead of visible light and come in two types: transmission electron microscopes (TEM) and scanning electron microscopes (SEM). They have similar basic components, including an electron source, lens system, vacuum system, and sample chamber. Building upon the foundation of optical microscopes, which have a resolution of 0.2μm, electron microscopes boast an impressive resolution of 0.2nm. This means they can magnify objects much more than optical microscopes, with an overall magnification reaching up to 200,000X. They are widely used for studying the shapes of molecules and atoms and in the field of nanotechnology. However, because samples must be observed in a vacuum, electron microscopes cannot be used to observe live samples, and they also come with higher purchasing and maintenance costs.
Nov 26, 2020 — Numerical aperture determines the resolving power of an objective, the higher the numerical aperture of the system, the better the resolution.
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept", you consent to our use of cookies.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500