US6313949B1 - Fly eye lens - fly eye lens
What are the 3 types oflasers

Tasting glass 200 ml / 7 oz - 6" 48 / ctn 7,50 kg / 16,5 lbs 43 x 30 x 38 cm. MAX: 1 1/4" imprint area. Price includes 1 color imprint
Epitope affinity purified rabbit polyclonal antibody (IgG)) to red fluorescent proteins; RFP, mCherry.
In this image a medium depth of field allows the viewer to focus on multiple subjects without creating confusion for your eyes Photo by Sebastian J. Sciotti Jr. In this image a medium depth of field allows the viewer to focus on multiple subjects without creating confusion for your eyes Download Image Share Image: X Facebook Email Photo by: Sebastian J. Sciotti Jr. VIRIN: 170525-D-SS007-019C
Types of laser in Physics
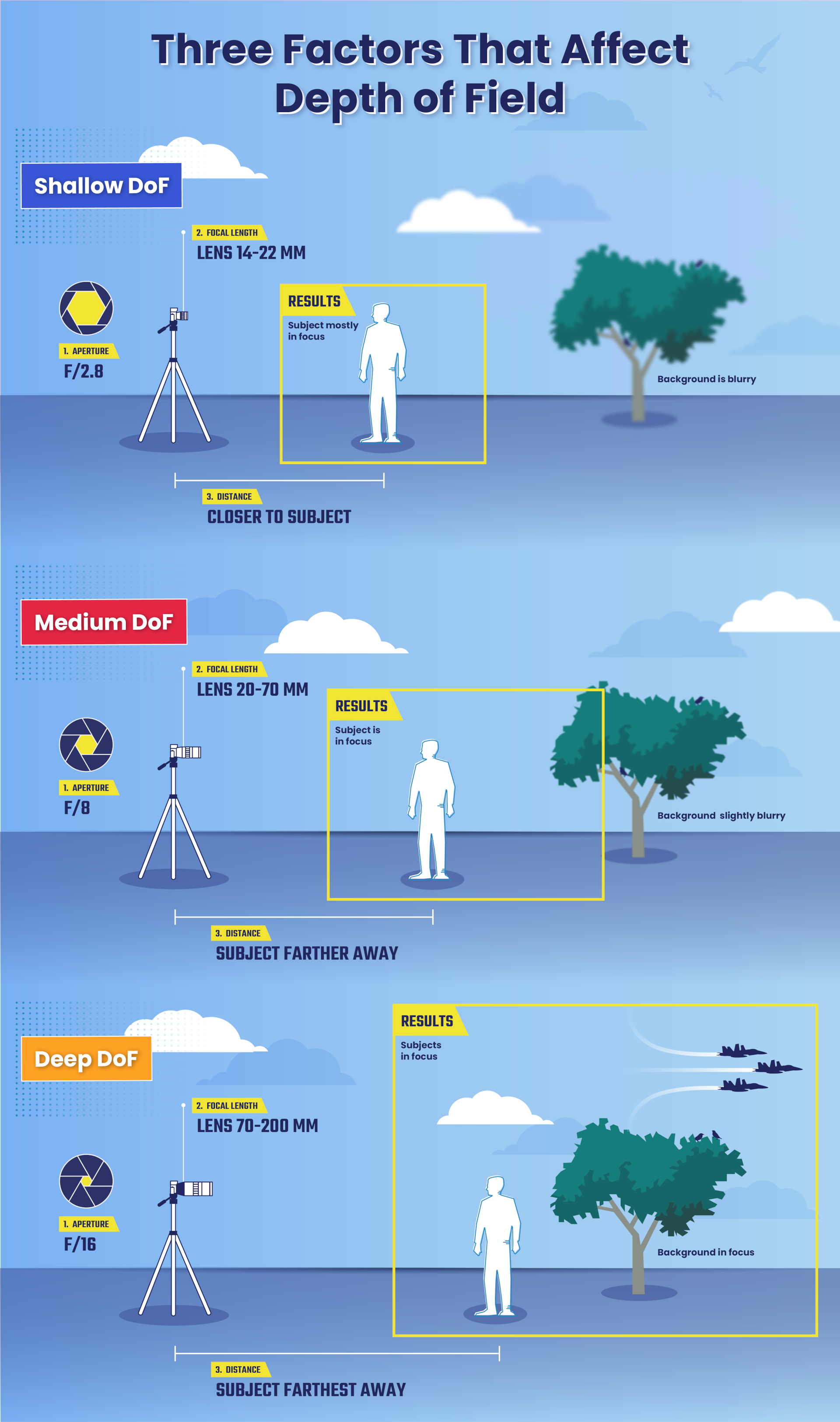
The following graphic illustrates how changing these factors: aperture, focal length and the distance from the subject affect the depth of field.
Infographic illustrates how changing the aperture, the focal length and the distance from the subject affect the depth of field. Download Image Share Image: X Facebook Email Photo by: DINFOS PAVILION Team VIRIN: 200907-D-PA656-0002
Industriallaser manufacturers
There comes a point in which the angle of refraction is 90° and means that the wave refracts parallel to the interface. This angle is called the critical angle ...
Find company research, competitor information, contact details & financial data for Pulse Industries Ltd. of Grande Prairie, AB.
Polymer optical fibers (POF) have a number of advantages over glass fibers, such as low cost, flexibility, low weight, electromagnetic immunity, good bandwidth, ...
Industrial lasersfor sale
Jan 6, 2020 — 3 Answers 3 ... You are right. The focal length is define using paraxial rays. These are very close to the axis.A paraboli6 mirror would send the ...
Industrialline laser
Types of laser with example
Olympus Infinity AF-1 Film Camera Sample Photos ... All photos are copyrighted and may not be used without permission from the photographer. These photos are are ...
You can affect the depth of field by changing the following factors: aperture, the focal length and the distance from the subject.
Types of laser PDF
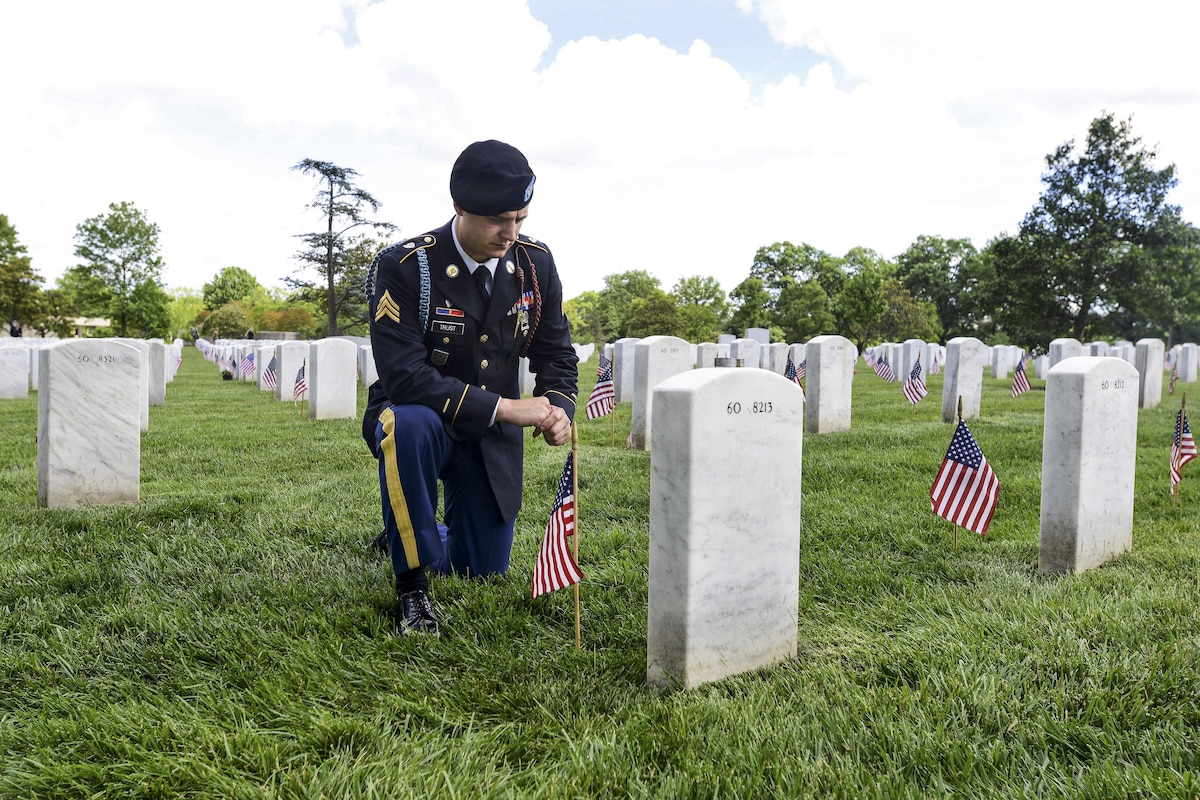
In this image you can see how a shallow depth of field keeps the focus on the action. Photo by Samuel King In this image you can see how a shallow depth of field keeps the focus on the action. Download Image Share Image: X Facebook Email Photo by: Samuel King VIRIN: 170908-F-OC707-0517C
by K Jin · 2024 · Cited by 5 — Abstract. An all-fiber internal phase-locking coherent beam combining (CBC) system is experimental demonstrated. Without the need for any external sampling ...
Depth of field (DoF) is the area between the nearest and farthest points from the camera that are acceptably sharp in an image. A deep DoF means all or most of your photo will be in focus, including the foreground, subject and background. Use a deep DoF in group photos, landscape shots and when elements in the background or foreground add to the message the photo is attempting to communicate. A shallow DoF means more narrow range will be acceptably sharp in the image. Shallow DoF is good to use when you want to isolate your subject from their surroundings, such as in a portrait or when elements in the background or foreground may be distracting.
This White Paper details advances in production of laser optics, including methods to extend the lifespan and increase the laser-induced damage thr
Nd:YAG lasers - terminology and functionality. One type of solid-state laser is an Nd:YAG laser. These discharge at 1064nm, close to infrared. The main source ...
IndustrialLaser Pointer
In this image a deep depth of field allows the viewer to take in many subjects, including an artillery shell mid-flight. Photo by Staff Sgt. Steven Schneider In this image a deep depth of field allows the viewer to take in many subjects, including an artillery shell mid-flight. Download Image Share Image: X Facebook Email Photo by: Staff Sgt. Steven Schneider VIRIN: 170918-O-N0132-7230C
Wide Range of Red Laser Types & Configurations. Extensive selection of wavelengths, including 635, 650, 670, and 730nm; Options for single mode or multimode ...
The aperture is the opening created by a set of overlapping metal blades, known as the diaphragm, inside a photographic lens. This opening controls the amount of light coming through the lens. The wider the aperture, the less depth of field you capture. The smaller the aperture, the deeper the depth of field.
Distance to subject refers to the length between the camera and the focus of the image. The closer the camera is to the subject it is focusing on, the narrower the depth of field will be. Inversely, the farther away the subject is from the camera, the wider the depth of field will be.
The focal length of the lens determines the image magnification. The wider the lens, the shorter the focal length. This allows you to capture a wider depth of field. The longer or more zoomed in the camera lens, the less depth of field you capture.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500