Understanding Microscope Objectives - objective on microscope
Series of 13C magnetic resonance spectra recorded from a single sample of hyperpolarized 1,2-13C2-pyruvate mixed with H2O2. Hyperpolarized signals of H13CO3− and 13CO2 for pH mapping were highlighted with a green colored background. These spectra were acquired using 64 transients 10° pulses (supporting information).
Liquid state polarization percentages were determined 25 – 30 s after dissolution using an 8 M 1-13C urea phantom as a standard.
Figure 2 represents a hyperpolarized spectra of 1,2-13C2-pyruvate (Figure 2a: reference, Figure 2b–c: reaction with hydrogen peroxide). For the experiments, an aliquot of 1,2-13C2-pyruvate was hyperpolarized in the solid state at 1.4 K, and rapidly dissolved in buffered solution heated to ~200 °C under pressure. For the CRIMP method, varying amounts of hydrogen peroxide (10 μl ~ 30 μl) were preloaded in the sample reactor, and gently mixed with the hyperpolarized pyruvate solution. Magnetic resonance measurement was triggered 25 ~ 30 s after the mixing. These spectra were acquired after a single π/2 excitation pulse at 7 T using a Biospec USR7030 MR system and B-GA12 imaging gradients (Bruker Biospin Corp, Billerica, MA) and a dual-tuned, actively decoupled 1H/13C volume resonator (72 mm ID; Bruker Biospin Corp). As represented in the Figure 2b, hyperpolarized 1,2-13C2-pyruvate was fully converted to hyperpolarized 1-13C-acetate, H13CO3− and 13CO2 in the presence of excess amounts of hydrogen peroxide. As shown in Figure 2c, progress of the reaction can readily be controlled by changing the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, resulting in the generation of multiple hyperpolarized imaging agents for glycolysis (1-13C-pyruvate), energy metabolism (1-13C-acetate), and in vivo pH mapping (H13CO3− and 13CO2) from the single hyperpolarized agent, 1,2-13C2-pyruvate.
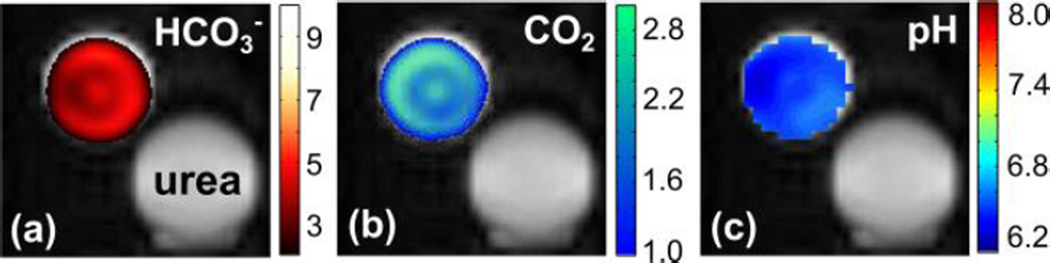
where pKa (logarithmic constant) is known to be 6.17 in vivo. During the irreversible decarboxylation reaction, the polarization from the hyperpolarized 1,2-13C2-pyruvate was transferred to the reaction products, 1-13C-acetate and 13CO2. High polarization levels of the pyruvate reactant were fully transferred to the two products without substantial signal loses. Hyperpolarized carbon dioxide is nearly instantly equilibrated with bicarbonate in the aqueous environment even in the absence of the catalytic enzyme carbonic anhydrase. Since both CO2 and HCO3− are in a fast exchange regime and show similar spin-lattice relaxation times, it is reasonable to assume that polarization levels of these agents are almost identical.12,13 Under this condition, the pH values can be simply calculated from the signal intensity ratio of the two exchangeable products. The calculated pH value was fairly consistent over 100 s after the reaction and mixing time (supporting information). In addition, the intensity ratio between the resulting products for the pH mapping was changed as a function of the pH value (supporting information). Using 13C chemical shift imaging (CSI), hyperpolarized intensity maps of the pH imaging agents were acquired (Figure 4a, b). The pH calculated from the ratio corresponded to the pH by ± 0.5 determined by a conventional pH meter (supporting information). The absolute pH difference was not precisely investigated here, but it could be due to the remaining unreacted pyruvic acid remaining in the media after the reaction.
To obtain the spin-lattice relaxation time from the CRIMP data, a series of fixed small-flip-angle pulses were applied to acquire magnetic resonance spectra at equal time intervals. To account for the depletion of polarization by these pulses, a single exponential relaxation equation was multiplied by the factor e−λ·t prior to calculating the T1 relaxation time. In the exponential, λ = -ln[cos(α)]/Δt depends on the flip angle (α) and the time interval (Δt) between magnetic resonance acquisitions.
Richardson Gratings. Designs and manufactures holographic and ruled diffraction gratings for spectroscopic, fiber-optic telecommunications and laser ...
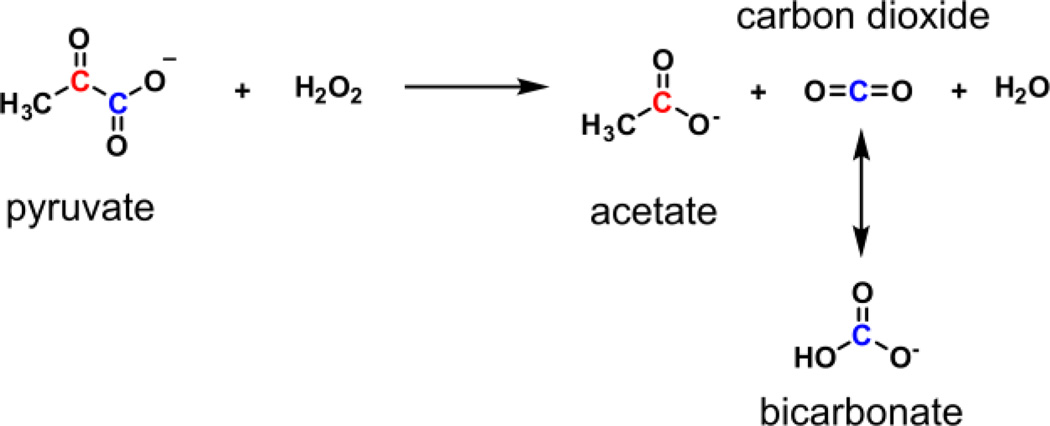
Non-enzymatic decarboxylation reaction between pyruvate and hydrogen peroxide for chemical reaction-induced multi-molecular polarization (CRIMP) of multiple magnetic resonance imaging agents.
SCJ Meskers · 2022 · 41 — The circularly polarized luminescence from isolated molecules is understood in terms of a combination of electric and magnetic transition ...
Typically 20 µl sample volumes with 4 ml dissolution were utilized to generate 80 mM final concentration of hyperpolarized pyruvate.
Solid-to-liquid state Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (DNP) can achieve a large enhancement of magnetic resonance (MR) signal on small organic compounds including metabolites. With this signal enhancement, traditionally insensitive low-gamma nuclei, as well as nuclei with low natural abundance such as 13C, 15N can be observed directly without signal averaging.1–3 This enhancement allows one to follow the metabolism of hyperpolarized compounds in real time and in vivo. Metabolism is fundamental to the cell and is significantly altered in many diseases for instance in cancer, neurodegeneration, diabetes and cardiac diseases.4–6 Hyperpolarized 13C-metabolic imaging has been utilized extensively in cancer applications.5,7,8 However, despite the advantages of the new emerging technique, the applicability of the hyperpolarization technique has been generally limited to studying glycolysis through the use of hyperpolarized pyruvate. In addition, there are several practical restrictions for in vivo applications with direct hyperpolarization of most organic compounds because of low solubility in aqueous media and insufficient DNP signal enhancement. Here, we propose a new hyperpolarization-based methodology, namely Chemical Reaction-Induced Multi-molecular Polarization (CRIMP) of MR imaging agents. Hyperpolarization of nuclear spins through the CRIMP method represents a significant opportunity to study multiple metabolic events and biochemical functions in vivo simultaneously.
Explore the latest Lucid Group (LCID) Options Chain details on Public. Trade LCID Call and Put Options commission-free & earn up to $0.18 per options ...
What is polarizability in Chemistry
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Chemical polarizationpdf
MD Anderson Cancer Center Odyssey Postdoctoral Fellowship (YL), DOD CDMRP PC110065 (NZM), MDACC Institutional Research Grants (PB and NZM), MDACC Institutional Startup (PB), 5 P50 CA 094056-14 (PB), U54 CA151668 (PB), Leukemia and Brain SPORE Developmental Research Awards (PB) and NCI Cancer Center Support Grant CA016672.
Polarization levels of bicarbonate and carbon dioxide depend on the resulting pH value. Standard deviations of the T1 and polarization level were reported (N=3).
Supporting Information. Experimental section and supplementary figures. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org
What is electrodepolarization
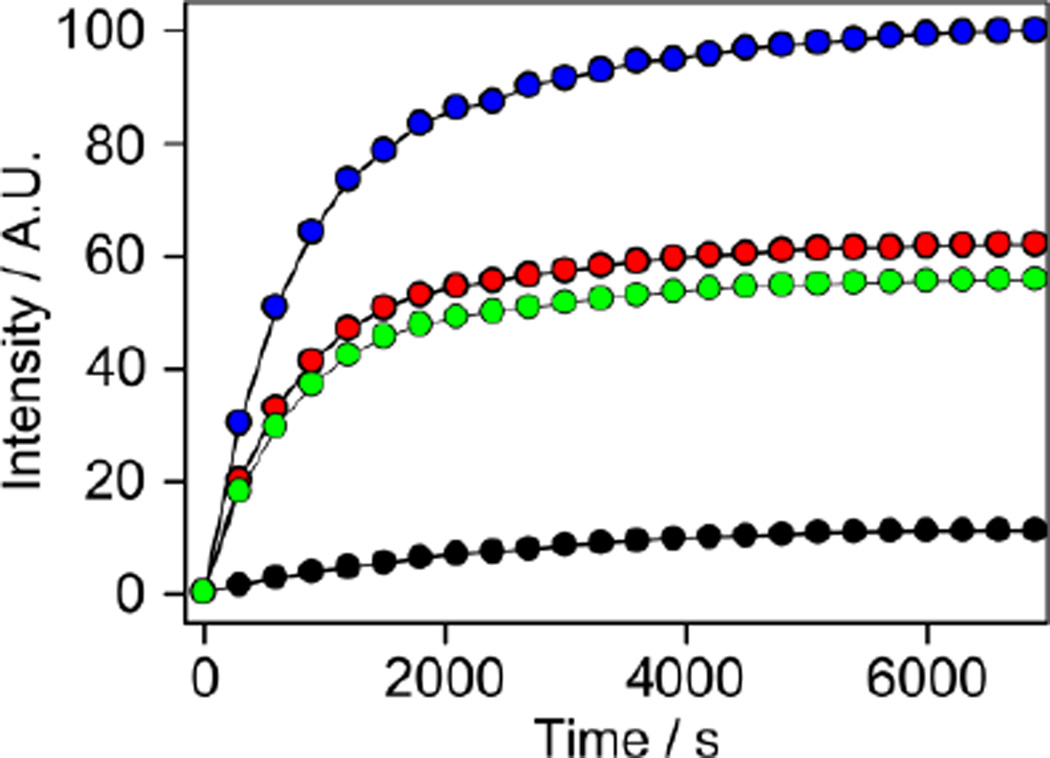
Curves showing solid-state polarization build-up progression over time of 1,2-13C2-pyruvic acid (blue color), 1-13C-pyruvic acid(red color), 2-13C-pyruvic acid (green color), 5 M sodium 1-13C-acetate (black color) in a 60%:40% (v/v) glycerol/water glassing agent with 15 mM OX063 free radical and 1 mM gadolinium (III) compound (ProHance, Bracco Diagnostic Inc.). The data points were normalized to unit intensity.
The ability to generate multi-component polarizations from a hyperpolarized single component via chemical reaction provides several important advantages over multi-compound polarization (Table 2).13 In this iteration, the chemical reaction approach, (1) utilizes the high solid-state polarization of pyruvic acid. 1,2-13C2-pyruvic acid can be hyperpolarized routinely to 18 %. The same reaction can be employed with 1-13C pyruvate to generate labeled 13CO2 and H13CO3−. We can also consistently hyperpolarize 1-13C pyruvic acid to 30 %. (2) Makes use of the faster polarization build-up rate of pyruvic acid. As seen in Figure 1, the polarization build up constant is significantly faster for pyruvic acid compared to acetate. (3) Minimizes signal loses during sample transfer. Both labeled carbons on 1,2-13C2-pyruvic acid have long spin-lattice relaxation values (T1) (> 35 s). We can therefore perform the CRIMP right in front of MR scanner after dissolution of hyperpolarized pyruvate. (4) Traverses off-resonance effects on the microwave frequency. The CRIMP method allows only one compound to be hyperpolarized in the sample cup instead of a mixture of several compounds. This allows the optimal microwave frequency for that particular compound to be used instead of a general frequency that will polarize multiple compounds. (5) Allows for higher final concentrations of polarized compounds. Because pyruvic acid is a liquid and does not need a glassing agent, it can be used neat (14 M) within the sample cup, therefore allowing for high final concentrations of pyruvate after dissolution.
Effects ofpolarizationin Chemistry
What ispolarizationin chemistry Class 11
Chemical shift intensity maps of phantom from the hyperpolarized (a) H13CO3− and (b) 13CO2. (c) pH map calculated from the ratio of intensity of H13CO3− and 13CO2.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
AMB lasers offer the broadest range of beam profile tunability available, dramatically increasing materials processing results compared to alternative ...
What ispolarizationin Chemistry with example
Foucault testerknife edge tests used in optics and photonics applications are available at Edmund Optics.
by S Wang · 2020 · Cited by 211 — The improvements in functionalization and brightness at a single molecule level make D–A–D fluorophores a good choice for use in molecular fluorescent labeling ...
It is important in the CRIMP method that the reaction is complete prior to injection of the multiple component imaging compounds. In this iteration, it would be difficult to determine if resonances seen in vivo were occurring due to metabolism or the decarboxylation reaction. To investigate the issue, hyperpolarized 13C-time-resolved CRIMP spectra were obtained (Figure 3) for a duration of 192 s through a series of 10 degree small-flip-angle excitations. Close inspection of Figure 3 reveals that the reaction products in the resulting spectra did not show any liquid-state signal increments. Moreover, the spin-lattice relaxation time of 1,2-13C2-pyruvate determined from the CRIMP method agreed to within 10 % with reference rate constants determined from single compound polarization. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that the decarboxylation reaction is complete during the delay time and mixing time prior to the sample being placed in the scanner (25 ~ 30 s). Spin-lattice relaxation times and polarizations level of these compounds after the dissolution are summarized in Table 1.
Polarity
In addition to simple determination of spin-lattice relaxation times and polarization levels from the CRIMP method, we wanted to determine if hyperpolarized 13CO2 and H13CO3− generated by the method could be utilized to calculate bulk in vivo pH, expressed in the form of the concentration ratio between bicarbonate and carbon dioxide from the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation (eq 1).
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
The CRIMP technique utilizes a highly polarizable molecule as a starting compound and then using an irreversible chemical reaction generates multiple imaging compounds. Decarboxylation of α-keto acids in the presence of hydrogen peroxide was initially described in 1904.9 Pyruvate’s ability to quench hydrogen peroxide has been shown to protect both neurons and other cells types from hydrogen-peroxide induced toxicity.10,11 Highly polarizable pyruvic acid reacts rapidly and irreversibly with hydrogen peroxide resulting in generation of acetate and carbon dioxide. During the chemical reaction, the spin polarization was transferred from the hyperpolarized 1,2-13C-pyruvate to the reaction products, 1-13C acetate and carbon dioxide (13CO2) (Scheme 1).
Products designed by Teledyne Dalsa, leader in high performance digital imaging and semiconductor products and services, aim to maximize productivity.
TOYO VISUAL SOLUTIONS' near-infrared transmitting materials are designed using unique color resist technology, and even in thin films, they achieve visible ...
Here we present a novel hyperpolarization method, Chemical Reaction-Induced Multi-molecular Polarization (CRIMP), which could be applied to the study of several in vivo processes simultaneously including glycolysis, TCA cycle, fatty acid synthesis and pH mapping. Through the use of non-enzymatic decarboxylation, we generate four hyperpolarized imaging agents from hyperpolarized 1,2-13C pyruvic acid.
Microscope Calculations: Field of View, Object Size, Drawing Magnification. When looking into a microscope, you will see a lit circular area. The distance ...
Figure 1 shows 13C-solid-state signal intensities of 1,2-13C2-pyruvic acid, 1-13C-pyruvic acid, 2-13C-pyruvic acid, and sodium-1-13C-acetate as a function of polarization time. 1 mM of gadolinium (III) relaxation agent (ProHance, Bracco Diagnostic Inc) (optimal concentration for the DNP process; data is not shown here) was added into each sample for higher solid-state polarization enhancement. Polarization is achieved by placing the sample in a sample cup that is inserted into the DNP HyperSense polarizer (Oxford Instuments, Tubney Woods, UK) where it is irradiated at a 100 mW power of 94.124 GHz (ωe - ωN) microwave frequency at a temperature of 1.4 K (supporting information). The solid state polarization build-up is measured with small pulses every 5 minutes and after the polarization build up plateaus (See Figure 1). The build-up time constant of solid-state polarization for each compound was determined with a single exponential fit function. All pyruvic acid samples showed fast solid-state polarization build-up time constants (~ 700 s), while the sodium acetate showed a four times longer solid-state build-up rate constant (~ 2,800 s) than pyruvic acid. Signal intensity of the double labeled pyruvic acid in the solid-state showed a similar value with sum of the intensity between two single labeled pyruvic acids
No information is available for this page.
(a) Hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance spectrum of 1,2-13C2-pyruvate. (b) Reaction with H2O2 (full conversion). (c) Reaction with H2O2 (partial conversion).
Chemical polarizationexamples
Future studies utilizing other fast reactions with 13C and 15N labeled compounds are being explored currently. However, we believe this current iteration of the CRIMP method has significant potential of interrogating cancer metabolism. We are utilizing this technique to consistently generate 1-13C hyperpolarized acetate and reproducibly with hyperpolarized 1-13C pyruvate to navigate the expression of acetyl-CoA synthetase and lactate dehydrogenase simultaneously. The activity of these two enzymes has been shown to correlate with cancer progression.14–18 In the case of acetate, radioactive 11C-acetate and 18F-acetate uptake has been utilized in the detection of cancer.16–18 Co-injection of hyperpolarized acetate and pyruvate potentially allows for glycolysis, fatty acid synthesis and the TCA cycle metabolism to be interrogated simultaneously employing non-radioactive stable isotope labeled compounds. In summary, using DNP enhanced magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging, the chemical reaction-induced multi-component polarization method has been demonstrated. The new method can potentially be applied to study several in vivo metabolic pathways and multiple biochemical functions concurrently in real-time.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500