Understanding Clearly the Magnification of Microscopy - magnification meaning
Analog (film) photographers use loupes to review, edit or analyze negatives and slides on a light table. Typical magnifications for viewing slides full-frame depend on image format; 35 mm frames (24×36 mm slides to 38×38 mm superslides) are best viewed at ca. 5×, while ca. 3× is optimal for viewing medium format slides (6×4.5 cm / 6×6 cm / 6×7 cm). Often, a 10× loupe is used to examine critical sharpness. Photographers using large format cameras may use a loupe to view the ground glass image to aid in focusing. Users of digital single-lens reflex cameras use loupes to help to identify dust and other particles on the sensor, in preparation for sensor cleaning.[citation needed]
Jewellers typically use a monocular, handheld loupe to magnify gemstones and other jewelry that they wish to inspect.[4] A 10× magnification is good to use for inspecting jewelry and hallmarks[4] and is the Gemological Institute of America's standard for grading diamond clarity. Stones will sometimes be inspected at higher magnifications than 10×, although the depth of field and field of view become too small to be instructive.[5] The accepted standard for grading diamonds is therefore that inclusions and blemishes visible at 10× impact the clarity grade.[6] The inclusions in VVS diamonds are hard to find even at 10×.[7]
Newtechnologyproduct
Treatment of periodontal disease is achieved by removing calculus deposits, plaque and therefore bacteria which causes inflammation and subsequently bone destruction. In severe cases, surgery to reduce pocket depth is indicated. Periodontists and hygienists must visualize plaque and calculus to remove it. Magnification can assist dentists and hygienists with identification and removal of plaque and calculus in addition to improving visualization for periodontal surgery.[13]
Terrain-relative navigation helped Perseverance land – and Ingenuity fly – autonomously on Mars. Now it’s time to test a similar…
Space-qualified computing technology is designed to address the most computationally-intensive part of a mission. But for the future, NASA is going to need more power and more processing capabilities. We also work on modeling and simulation tech, software, and unique electronics and computing hardware for flight systems, whether in space or the atmosphere.
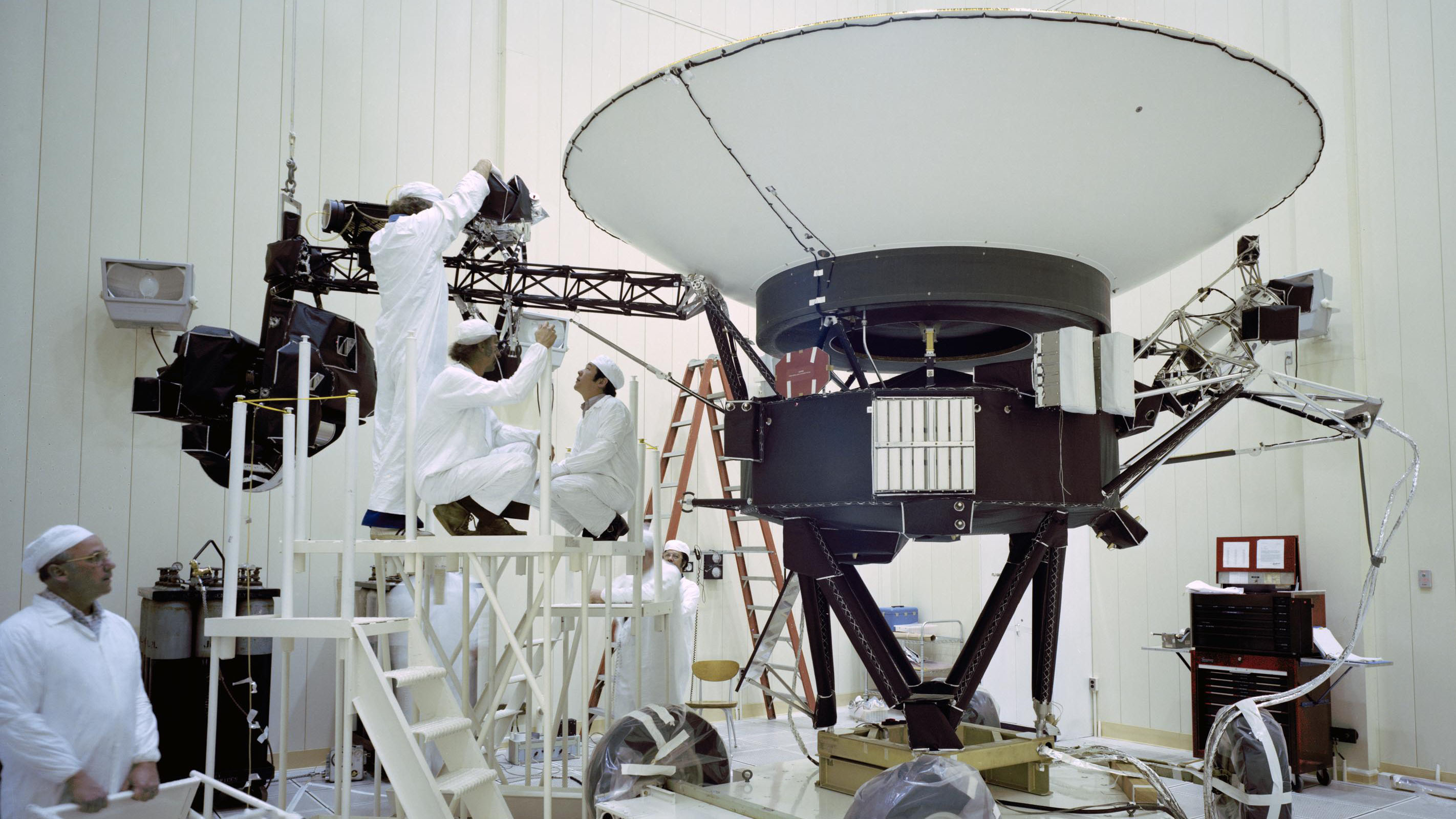

NASA technology development supports the nation’s innovation economy by creating solutions for space exploration that also generate tangible benefits for life on Earth. NASA is investing in the future of innovation.
Newtechnology
The dental specialty of endodontics has performed the vast majority of research regarding magnification in dentistry. Because the identification of accessory canals in addition to the primary pulp canals is essential to complete nonsurgical root canal therapy, magnification provides dentists enhanced visualization to locate and treat more obscured canals.
emerging technologies中文
Science instruments are state-of-the-art tools for acquiring information about planetary geology, atmosphere, and environmental conditions. This includes technologies for remote sensing, mapping and observation capabilities, analyzing light from the universe, and even searching for signs of life.
Loupes are an essential tool in both numismatics, the study of currency, and the related practice of coin collection. Coin collectors frequently employ loupes for better evaluation of the quality of their coins, since identifying surface wear is vital when attempting to classify the grade of a coin. Uncirculated coins (coins without wear) can command a substantial premium over coins with slight wear. This wear cannot always be seen with the naked eye. Numismatists can also employ loupes to identify some counterfeit coins that would pass a naked-eye visual inspection.[citation needed] Loupes are similarly used for evaluating other collectable objects, such as trading cards and antiques.
Technologies for living in space enable our robotic and human explorers to achieve their mission goals. This means everything from having power to do their work, to the habitats or spacecraft they’ll call home. Our astronauts also need technologies to make food and eat, exercise, sleep and maintain their overall wellbeing.
Dentists, hygienists, and dental therapists typically use binocular loupe glasses since they need both hands free when performing dental procedures. The magnification helps with accurate diagnoses of oral conditions and enhances surgical precision when completing treatment. Additionally, loupes can improve dentists' posture which can decrease occupational strain.[8] Some dental loupes are flip-type, which take the form of two small cylinders, one in front of each lens of the glasses. Other types are inset within the lens of the glasses.
NASA selected 60 winning teams for the second TechRise Student Challenge, a nationwide contest designed to engage students in technology, science, and space exploration. These teams will work together to build science and technology experiments in preparation for a suborbital flight test.
STMD is refining its strategy for prioritizing technology investments, with the goal of evolving into a stronger and more resilient national tech base for civil space.
Since the first crew’s arrival aboard more than twenty years ago, the International Space Station has evolved into a state-of-the-art scientific lab.
Futuretechnology
NASA uses robotic systems to explore other planets and objects in our solar system as precursors to crewed missions, assist astronauts on the International Space Station, study the universe, and much more. This also includes autonomous systems that enable robotics, spacecraft and aircraft to operate in a dynamic environment independent of external control.
mittechnologyreview是什么
NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System could advance future space travel and expand our understanding of our Sun and Solar System.
Fictional astronaut Callie Rodriguez continues exploring space as the first woman to walk on the Moon in a new issue of NASA’s First Woman graphic novel series!
Reliable space communication systems are critical to every NASA mission. Spacecraft commands, never-before-seen images, and scientific data are sent and received daily by NASA's giant antennas on Earth. From the Voyager mission exploring beyond our solar system, to astronauts onboard the International Space Station, space communications provide the crucial connection to our home planet.
Emerging technologies
Conservators often use hand held loupes or head-mounted binocular magnifiers such as the Optivisor to examine artifacts and documents requiring cleaning or repair.
The path to the Moon, Mars, and beyond requires technologies to get us where we need to go quickly, safely and efficiently. Space travel includes launch and in-space propulsion systems, cryogenic fluid management, and thermal management, as well as navigation and landing systems to get our supplies, equipment, and robotic or human explorers to diverse surface destinations.
A typical magnification for use in dentistry is 2.5×, but dental loupes can be anywhere in the range from 2× to 8×.[15] Optimal magnification is a function of the type of work the doctor does - namely, how much detail he or she needs to see, taking into consideration that when magnification increases, the field of view decreases. As a tool that sits on the face and is used for hours at a time, weight is also a significant factor in considering the type of loupes to use.
Loupes are used in many professions where magnification enables precision work to be done with greater efficiency and ease. Examples include surgery, dentistry, ophthalmology, the jewelry trade, gemology, questioned document examination and watchmaking.[3] Loupes are also sometimes used in photography and printing.
Surgeons in many specialties commonly use loupes when doing surgery on delicate structures. The loupes used by surgeons are mounted in the lenses of glasses and are custom made for the individual surgeon, taking into account their corrected vision, interpupillary distance and desired focal distance. Multiple magnification powers are available. They are most commonly used in otolaryngology, neurosurgery, ophthalmology, plastic surgery, cardiac surgery, orthopedic surgery, and vascular surgery.
inventions中文
The NASA Technology Transfer program ensures that innovations developed for exploration and discovery are broadly available to the public, maximizing the benefit to the nation. NASA ensures inventions for space find practical uses closer to home. They often become solutions to different challenges – ones we didn’t set out to solve. Called NASA spinoffs, these technologies benefit life on Earth in the form of commercial products.
Advanced manufacturing technologies for both terrestrial and in-space purposes will make commercial and exploration missions more efficient and affordable. We’re developing new materials with improved or combined properties, learning how to build infrastructure and innovating on manufacturing processes.
technologyadvancement意思
A loupe (/ˈluːp/ LOOP) is a simple, small magnification device used to see small details more closely.[1] They generally have higher magnification than a magnifying glass, and are designed to be held or worn close to the eye. A loupe does not have an attached handle, and its focusing lens(es) are contained in an opaque cylinder or cone. On some loupes this cylinder folds into an enclosing housing that protects the lenses when not in use.
Loupes are employed to assist watchmakers in assembling mechanical watches. Many aspects require the use of the loupe, in particular the assembly of the watch mechanism itself, the assembly and details of the watch dial, as well as the formation of the watch strap and installation of precious stones onto the watch face.
Together with proper access to the oral cavity, light is an important part of performing precision dentistry. Because a dentist's head often eclipses the overhead dental lamp, loupes may be fitted with a light source. Loupe-mounted lights used to be fed by fiber optic cables that connected to either a wall-mounted or table-top light source. Newer models feature a more convenient LED lamp within the loupe-mounted light and an electric cord coming from either the conventional wall-mounted or table-top light source or a belt clip rechargeable battery pack. Options for loupe-mounted cameras and video recorders are also available.[16]
NASA explores the unknown in air and space, innovates for the benefit of humanity, and inspires the world through discovery.
Ergonomics have long been a pain point for doctors who need to physically strain, bending over and looking down, to treat their patients. Over time this posture results in discomfort, pain, and even neuromuscular disease.[14] Some modern loupes address this by incorporating refractive prisms which alter the course of the light through the telescopes, so that the dentist can maintain a neutral, upright position with eyes relaxed and looking straight ahead.
Dental caries, also known as cavities, are most accurately identified by visual and tactile examination of a clean, dry tooth.[9] Magnification enables dentists to improve their ability to differentiate between a stain and a cavity. Cavities are rated and scored based on their visual presentation.[10] If magnification is too high diagnosis becomes difficult due to the small field of view. Ideal magnification for diagnostic purposes is up to 2×.[11][12] Treatment of dental caries, periodontal disease, and pulpal disease are all aided by magnification.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500