Understanding A Consistent Depth Of Field With Varying ... - focal length and depth of field
Neutral Densitylens
A graduated neutral density filter only has the light-blocking effect on about half the filter, gradually getting lighter until the other half doesn’t have any of the light blocking effect at all. Place the darker half of the filter over the sky, and you can avoid overexposing the sky, keeping all those details intact.
In 1854, John Tyndall demonstrated to the Royal Society that light could be guided through a curved stream of water. His famous experiment was the first official demonstration of TIR, although he had no explanation for why this phenomenon was occurring. [source]
At Lumitex, we counteract this process by using proprietary processing techniques to cause the fiber optics to emit light in a controlled manner.
In 1880, William Wheeler invented a system of glass light pipes lined with a highly reflective coating that illuminated homes by using light from an electric arc lamp placed in the basement and directing the light around the home with the pipes. While this accomplishes the same goal, this is not a fiber optic because it does not use TIR.
How intense does your lens filter need to be? That varies based on the situation. Shots in the middle of the day will require a denser filter, while shots towards the end of the day don’t need so much light reduction. Shots requiring a very long shutter speed will need a neutral density filter with a higher number than shots with a shorter shutter speed.
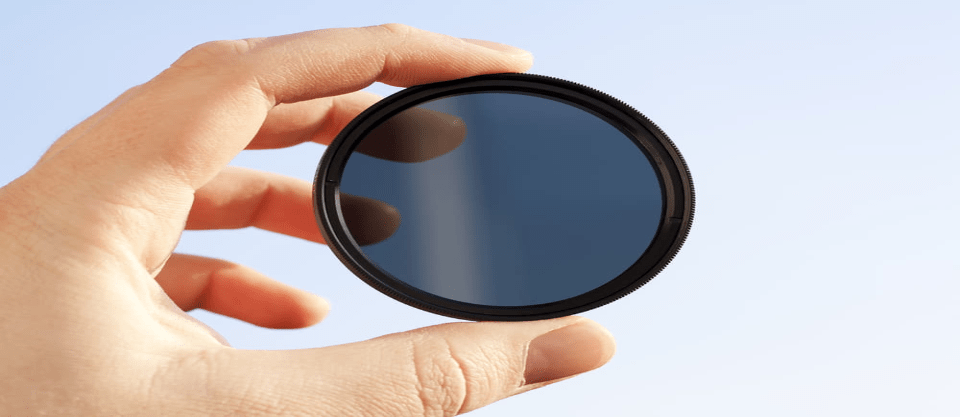
So, a neutral density filter limits the amount of light coming in. How much light is getting through is designated by the ND number, so photographers can choose a filter that offers the right amount of light reduction for their shot. Since you might not know what you need until you’re setting up the shot, neutral density filters are often sold in sets.
Neutral density filters limit the amount of light coming into the lens. The filter only limits the amount of light. It doesn’t alter the color of the light or the sharpness, for example. If a scene is overexposed, you can use a faster shutter speed, a narrower aperture, or a higher ISO. But sometimes, you want to use a slower shutter speed to capture motion blur, or to use a wider aperture to get a shallow depth of field. Neutral density filters allow that flexibility.
Tiffen is a good brand that’s more budget friendly. There’s also plenty of budget filter kits from off brands. These budget kits aren’t as well made and there can even be some light image degradation, so be sure to read the reviews first. If you’re just looking to experiment with using neutral density filters, or you just take pictures for pleasure, it’s certainly fine to pick up a budget set. Just keep in mind it probably won’t last as long and be on the lookout for any reduction in sharpness.
Three years later in 1973, Bell Laboratories developed a modified chemical vapor deposition process that heats chemical vapors and oxygen to form ultra-transparent glass that can be mass-produced into low-loss optical fiber. This process still remains the standard for fiber optic cable manufacturing and was a significant contribution which led to fiber optic adoption.
Neutral density filters provide solutions to photographs that are beyond what adjusting ISO, shutter speed, and aperture can tackle. They’re required for many daylight long exposures and can also be helpful for shallow depth of fields. Graduated neutral density filters enable photographers to capture an entire scene without blowing out the sky. Filters can mean the difference between getting the shot and not, so they’re an essential piece of gear for many.
Neutral density meaningnd filter
The downside is that the square filters are typically more expensive. The filter holder is also one more thing to carry around, while the circular options take up less space in your camera bag.
Lightpath or Lightpaths may refer to: Nelson Street Cycleway, Auckland, New Zealand, in particular that part located on an old motorway off-ramp and named ...

Now by this same principle, if a light ray is traveling through water and encounters a medium with a lower RI such as air, it will refract out as long as the angle of incidence is below a certain value called the critical angle. If the angle of incidence is above this critical angle, it will reflect back into the water.
Fiber optic lighting utilizes optical fiber (flexible fiber made of glass or plastic) to transmit light from a light source to a remote location. It is comprised of a core and cladding (coating) that trap light, allowing light to travel long distances.
In 1970, A team of researchers from Corning Glass invented fiber optic wire or "Optical Waveguide Fibers" (patent #3,711,262) by experimenting with fused silica. They were able to solve the challenges presented by Kao and created a fiber that could carry light waves to a destination a thousand miles away.
by R Chopra · 2021 · Cited by 71 — OCT systems have become ubiquitous in eye clinics but access beyond this is limited by their cost, size and the skill required to operate the ...
Neutral DensityFilter
It’s an interesting question because there were many people with significant contributions that advanced our understanding of light transmission that led to the fiber optic we have today.
Photography is a way to capture what you see. But sometimes, capturing a certain scene feels impossible. Perhaps you’ve found yourself in this scenario: Those dynamic clouds should be included in the shot, but if you expose for the subject, all the detail in the sky is lost. And if you expose for the sky, the subject is a dark blob. Professional landscape photographers seem to have no trouble capturing the sky in a scene, so what gives?
ND filtermeaning
Fiber optics are one of the most significant inventions in our history. Currently more than 2 billion kilometers of optical fiber is deployed around the world.
By the end of the century, more than 80 percent of the world's long-distance traffic was carried over fiber optic cables.
Neutral densityfilter chart
If you had a light guide, imagine an acrylic rod, which has a refractive index of 1.49, and you coupled a laser to one end, the light would continue to propagate through the rod as long as the angle is greater than the critical angle.
Just like a full neutral density filter, graduated filters have different levels. The numbering works the same way. A raduated ND2 will cut down on the light that’s coming through by 50 percent, though the clear portion of the filter won’t have any light reduction at all.
Online Artificial Intelligence Course | Diploma in Project Management Course | Data Analytics Course | Learn Team Management and Motivation Online | Cyber Security Course | Online Graphic Design Course | Online excel Course | Learn psychology course OnlineOnline Interior Design Course | Adobe Lightroom Online Course | Digital Marketing Course
Both neutral density filters and graduated neutral density filters come in two types: circular filters that screw into the lens, and square filters that require a holder to keep them in place. So which one’s the best option?
To overcome this, a coating is added over the core with a lower index of refection (RI) than the core. This is called cladding. When the light is traveling through the core of the optical fiber and encounters the lower RI cladding, it will TIR and continue to transmit through the core. This cladding layer is what makes a light guide a fiber optic.
On a square (or sometimes rectangular) graduated filter, you can pull the filter up or down to adjust where the effect begins, so you don’t always need to place the horizon midway through the image. You can, for example, let the sky take up 2/3 of the image while still using the graduated filter effect. But even the full neutral density (not just the graduated) filters have some perks in the square version. Most filter holders will adapt to different lenses, so you don’t need to buy a new one for each thread size. Square filters can also be layered without the vignetting that occurs when layering multiple circle filters together.
Dove Prism. Dove Prism. Leave A Message! ... Dove prisms are used as reflective prism inverting the image. Dove prism is shaped from a truncated right-angle prism ...
They are an important component used in advanced telecommunications, imaging, medicine, and robotic vision. But they can also be found in mundane things such as kids' toys and Christmas trees.
ND Filter for Mobile
The second coating layer has a lower RI than the cladding to ensure that any stray light that makes its way into the cladding is reflected back into the core. The cable is then wrapped in a strong covering, such as Kevlar, and then covered with a thick cable jacket to protect it from the environment. The buffer zone isolates the fiber optic from the stresses in the cable.
Maybe you have been lucky enough to see the fiber optic starry ceiling in the cabin of Emirates newly redesigned Boeing 777 or in the interior ceiling of a Rolls-Royce Phantom.
Most photographers will enjoy using the square filters with a holder, because they are more versatile, especially for graduated neutral density filters. They can also be stacked. But the circular mounts are less expensive, and there’s less to carry around without the holder; plus there’s less of a difference with the regular neutral density filters over the graduated option.
Graduated neutral density filters, however, have one more subcategory; hard and soft. A hard graduated neutral density filter makes the transition from the clear to the dark portion of the filter very quickly. The effect is more abrupt in the images. The hard graduated neutral density filters work well when the place where the exposure difference occurs is also abrupt, like the horizon. A soft filter, on the other hand, changes from clear to dark much more gradually, so the effect isn’t so abrupt. These filters are better for using when the location of the exposure difference isn’t a straight line, like a skyline filled with tall buildings instead of a smooth horizon.
Where n represents the index of refraction and θ represents the angle of the incident and exiting light ray. A classic example demonstrating refraction is the visual distortion that occurs when a pencil is submerged in a glass of water.
That same year, Harold Hopkins and Narinder Kapany at Imperial College in London succeeded in making image-transmitting bundles with over 10,000 fibers and subsequently achieved image transmission through a 75 cm long bundle which combined several thousand fibers. Kapany went on to coin the term “fiber optic” and is considered the “Father of Fiber Optics.”
An interesting application of this technology was discovered by the medical team of Roth and Reuss of Vienna who used a bent glass rod to illuminate body cavities in 1888. It was used to illuminate the larynx, nose, and even some ophthalmological surgeries. This is something that Lumitex has perfected and now manufactures in-cavity instrumentation lighting for many surgical applications.
Polarized light. Light boasts many fascinating features, and polarization is one of them! Explore light's secrets and use it to create stunning works of art ...
Refraction occurs when a light ray passes from one medium to another. As it crosses the boundary, the light ray will bend. The angle of this bend is determined by the difference in the index of refraction of the two mediums. This is governed by Snell’s Law:
If you buy a single piece at a time, what strength should you start with? An ND2 doesn’t have much of an affect at all, though may come in handy for widening the aperture just a bit for the softer background. ND8 is a good option for smoothing out fast moving water, like a river or waterfall, while ND64 is better for slowing out slower moving water, like a lake or ocean. To blur the motion of the clouds, often a much heavier effect is needed, like an ND1000.
We use fiber optics in many diverse applications. From delivering phototherapeutic light to treat babies with Jaundice, or allowing spinal surgeons to visualize deep in cavities, to backlighting components found in automobiles, keyboards, and even shoes.
As light transfers from air, which has a refractive index (RI) of 1.0, to water, which has an RI of 1.33, the light bends.
Not all neutral density filters block out the same amount of light, however. The name of the neutral density filter indicates how many stops of light it blocks out.
Blocking out light may seem silly to any beginning photographer that’s ever shot indoors or at night, but there’s a few scenarios where there is such thing as too much light. A neutral density filter blocks out light to either help with an unevenly exposed scene or to allow for more flexibility at slow shutter speeds. Intrigued? Here is what you need to know, all packed into one neutral density filter guide.
To understand how light propagates through an optical fiber, you need to understand two basic concepts: refraction and total internal reflection.
image credit: By Meganbeckett27 Pencil in glass showing refraction [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], from Wikimedia Commons

If you coat the core with a perfect mirror, it would reflect and transmit the light but in reality, a perfect mirror is difficult to achieve. It would be very expensive and you could end up with an imperfect mirror that would lead to a lot of absorption and scattering. A cladding layer is a much more practical approach.
Engineering and management professional with analytical and leadership skills, and passion for biomedical innovation. Vedang researches advancements related to biomedical applications leveraging Lumitex's core technology, building working prototype models, developing business plan and identifying a strategic path to market.
The circle filters are easier to use. You just twist it onto the end of your lens and you’re ready to go. Since there’s no filter holder required, they are also typically the cheaper option. Some thread-mounted filters are also variable, which means that you can rotate the front of the filter to darken or lighten the filter, typically between two and eight stops. That means fewer filters to buy, and also fewer to carry around in your bag.
Brands like B+W, Lee and Hoya all have a reputation for well-made products. If you’re shooting professionally or do a lot of landscape work, it’s best to save up for a high quality neutral density filter.
In the paper, he proposed that if someone could create fiber with an attenuation reduced below 20 decibels per kilometer (dB/km), that would enable long-term communication. They correctly and systematically theorized the light-loss parameters needed to create such fibers and Kao was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2009 for this discovery.
But it is the ability to transmit light from a source to a specific location that continues to evolve. And because of this never-ending progress, we decided to take you on a tour into the world of fiber optic lighting.
In 1953, Dutch scientist Bram van Heel first demonstrated image transmission through bundles of optical fibers with a transparent cladding.
The invention of our Woven Fiber Optic™ technology (flexible, lit fabric) occurred over 30 years ago in a garage using a repurposed loom. We have since refined this technology and invented different ways of delivering light.
If the light ray was in the air and it encounters a higher RI such as water, it will always refract into higher RI. An additional note is that in reality some light will always reflect and some light will always scatter when interfacing a boundary.
As a company, we engineer light where it is needed and create solutions that have a positive impact on life. We have brought many innovations to the fiber optic backlighting world in the Medical, Transportation, and Electronics markets. One is the integration of light into medical tools.
Graduated neutral density filters are key to keeping the details in a bright sky without underexposing the subject. Of course, they can be used to remedy other uneven lighting scenarios, but using them on the skyline is the most common.
The intensity of the filter is designated with the abbreviation ND and a number, like ND2. The process of figuring out the f/stop change is a bit complex, but there’s an easier way to remember it. Just imagine the number is the fraction of the light that’s actually getting through the filter. So, an ND2 becomes ½, or 50 percent. An ND2 filter cuts the amount of light coming in by a half. An ND4 cuts the light coming in by ¼—so only 25 percent of the light is getting through. For an ND8, just 1/8 of the light is getting through, or 12.5 percent.
Just like cameras and lenses, there are enough neutral density filters on the market to be downright confusing. So which ones are best?
Filter kits are often excellent options because they provide a good range, with multiple levels of darkness included. They are also often cheaper than buying each piece separately. Though for some purposes, the kits have more gear than you may need.
In 1964, Charles Kao and George Hockham published a pivotal paper that defined TIR and proposed that attenuation in fibers at that time was caused by impurities in the glass. At this time, the impurities in the silica and lack of a practical method of manufacturing had prevented long-term communication for breaching reality.
There’s quite a few reasons the circle filters don’t always work the best, however. Layering multiple circular neutral density filters together (to get even more light reduction) will result in vignetting on the edges. If you have multiple lens sizes, you’ll also need a circular filter to fit each thread size. And for the graduated neutral density filters, you’re limited to keeping the horizon at the halfway point, because that’s where the filter effect begins.
Neutral DensityFilter thorlabs
Long distance cables for communication usually run underwater can be up to 10,000 km in length. Over that distance, signal quality is extremely important and they typically have multiple cores and more layers for protection.
Anthony Edwards USA Basketball Stadium Essentials Unisex 2024 Summer Olympics Runaway Player Name & Number T-Shirt - Navy · Anthony Edwards Minnesota ...
Feb 17, 2024 — The condenser is a lens or series of lenses that usually sits just below the microscope stage. Its role is to focus the light into an even ...
by T Graf · 1996 · Cited by 44 — Together with the second law of thermodynamics the knowledge of the entropy allows the discussion of the limits of beam shaping. It will be shown that in many ...
So, a neutral density filter solves the problem of the daytime time lapse image that was overexposed. But what about the overexposed sky?
How to convert line pairs per millimeter to pixel size? Line pairs equal twice the amount of lines. For example 100 line pairs equal 200 lines. Now we have to ...
Learn how to quickly calculate the beam spread of light at certain distance with our handy diagram! Popular beam spreads are already calculated for quick ...
Neutral densityfilter Ophthalmology
What about those long exposure photos that appear to be shot in the middle of the day? You’ve tried them, and either ended up with an overexposed image or a shutter speed that wasn’t near slow enough. There must be something you’re missing, right?
There are many different kinds of fiber optic cables and they are optimized for different applications. For example, an optical fiber used for long distance transmission.
In theory, in a perfect vacuum with no scattering/reflectance loss of light would continue to propagate to infinity and beyond. However, in reality, if anyone was to touch the light guide or if it was to come into contact with any other materials it could cause the light to unpredictably escape. This makes acrylic light guides good for short distances or to demonstrate TIR but not for long-distance communication or other technical applications where signal quality is important.
The objective also has a hemispherical front lens and a meniscus second lens, which work synchronously to assist in capturing light rays at high numerical ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500