Understanding & Using Polarizing Filters - how does polarizer work
Materialdispersion
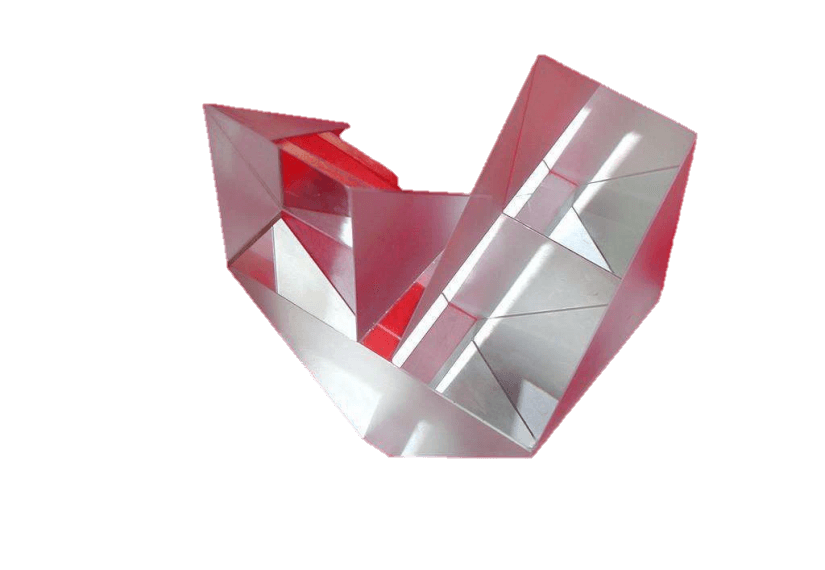
The two common types of the Micro-prism are PentaPrism and Right-angle Prism. These two prisms are widely used in the field of optical fiber communication, especially in the core field of optical switches. Examples of such applications include circulator interleaver and MEMS.
Dispersion opticalpdf
This has several consequences. One is that the different color components of white light will possess different angles of refraction when the white light is incident, with a non-zero angle of incidence, on an interface between two media. Prisms and rain drops both create rainbows because of this effect.
Dove prism is a reflective prism used to invert an image.It is made up of a truncated right angle prism.A beam of light enters an inclined surface of the prism, undergoing complete internal reflection from the interior of the longest (bottom) surface and exiting from the opposite inclined surface. The image through the prism is flipped, because only one reflection occurs, so the image is inverted instead of transposed horizontally.
Dispersion opticalwavelength
The pentagonal prism has a stable light deviation, which is always 90 degrees regardless of the optical axis and light, and is used for measurement, laser scanning, alignment and other optical tools.
Specification for standard Roof Prism:Material: BK7 Grade A optical glassDimension Tolerance:+0,-0.2mmFlatness: λ/4 at 632.8 nmSurface Quality: 60-40 scratch and digClear Aperture: >80%Bevel: 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm x 45oAngle Tolerance: ± 3arcmin
Waveguidedispersion
There are four main types of prisms based on the function: dispersion prism, deflection or reflection prism, rotating prism and offset prism. Deflection, offset and rotating prisms are commonly used in imaging applications; diffusion prisms are designed for dispersive light sources and are not suitable for any application that requires high quality images.
Lens systems in sensitive equipment must be carefully designed to reduce the magnitude of chromatic dispersion and other aberrations (more on aberrations later). One way to correct for chromatic aberrations is to form a compound lens called an achromat. This doublet is made up of a positive lens that is made from crown glass, and a negative lens that is made from flint glass. Crown glass has moderate dispersion and flint glass has higher dispersion. The positive crown glass is made into a positive lens, and the flint glass is made into a negative lens. The powers of two lenses in contact add: P = P1 + P2 so it is possible for the doublet to have positive power if the power of the positive lens is greater than the power of the negative lens. The different dispersions of the two glasses, combined with a careful adjustment of the curvatures of the two lenses can result in a compound lens that is corrected for chromatic aberrations.
If youve ever seen a rainbow or a prism split what appears to be white light into its rainbow of color components, youve seen chromatic dispersion. (White light comes from a source that emits many wavelenths of EM Rad. Sunlight is white light.) In a dispersive material, different wavelengths travel at different speeds, which is the same as saying that each wavelength of EM Rad has a different refractive index in the material! The practical result of this, as predicted by Fermats Principle, is that no one path is the shortest for all wavelengths in most optical systems. Different wavelengths of EM Rad always follows their own fastest route though an optical system.
Dispersionin Physics
Dispersioninopticalfiber
Room 609, 6/F, Global Gateway Tower, No.63 Wing Hong Street, Cheung Sha Wan, Kowloon, Hong Kong +852-54993705 info@shanghai-optics.com
The semi-pentagon prisms’ main function is to deflect the light by 45°, and the image is dextrorotatory. Mainly used in the Pecan mirror assembly.
Deviating the prism of the ray path or shifting the image from its original axis, is helpful in many imaging systems. Light is typically deflected at 45, 60, 90 and 180 degrees. This helps to aggregate system size or adjust the ray path without affecting the rest of the system settings. The polygonal prism can be set to different angles of deflection according to customer needs.
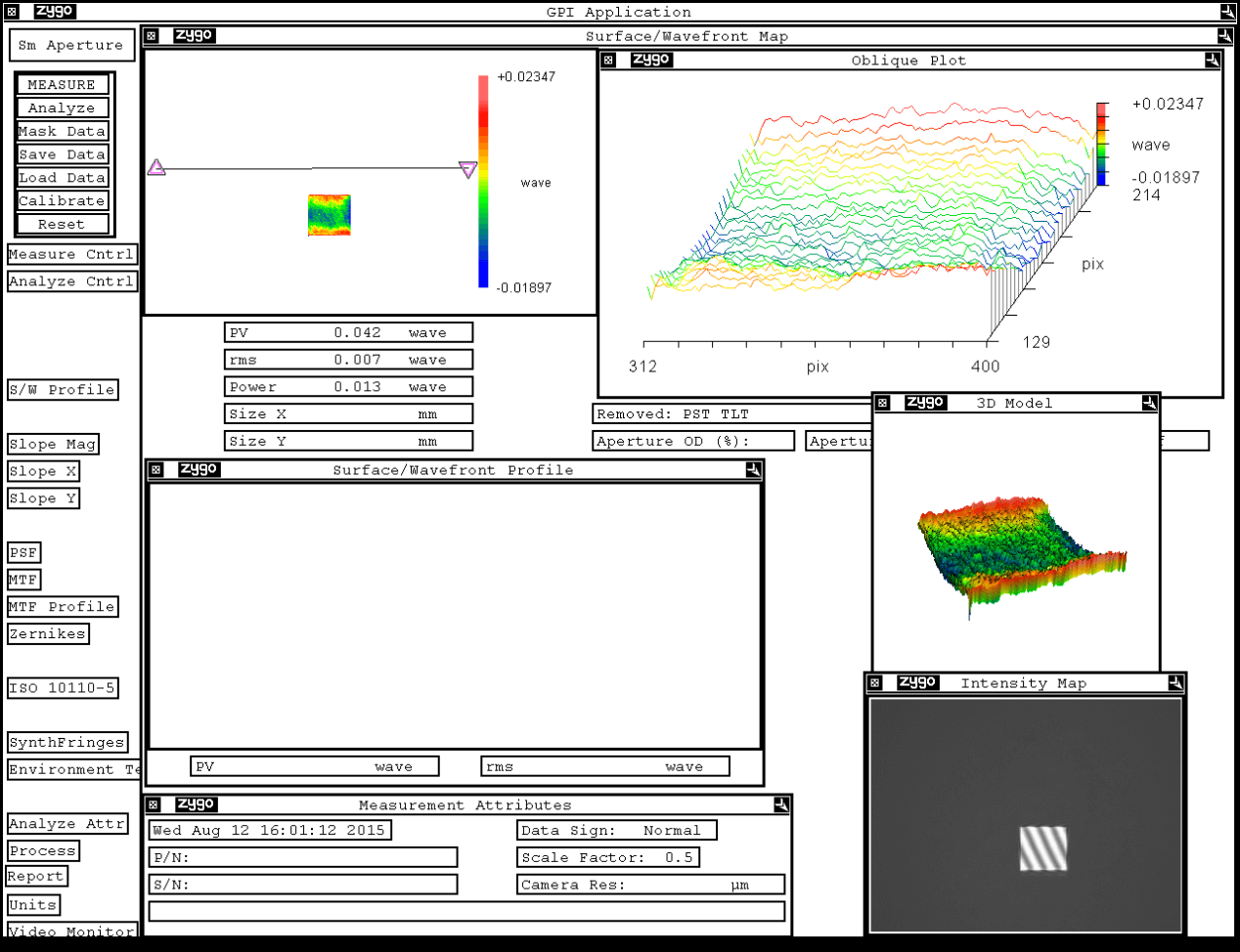
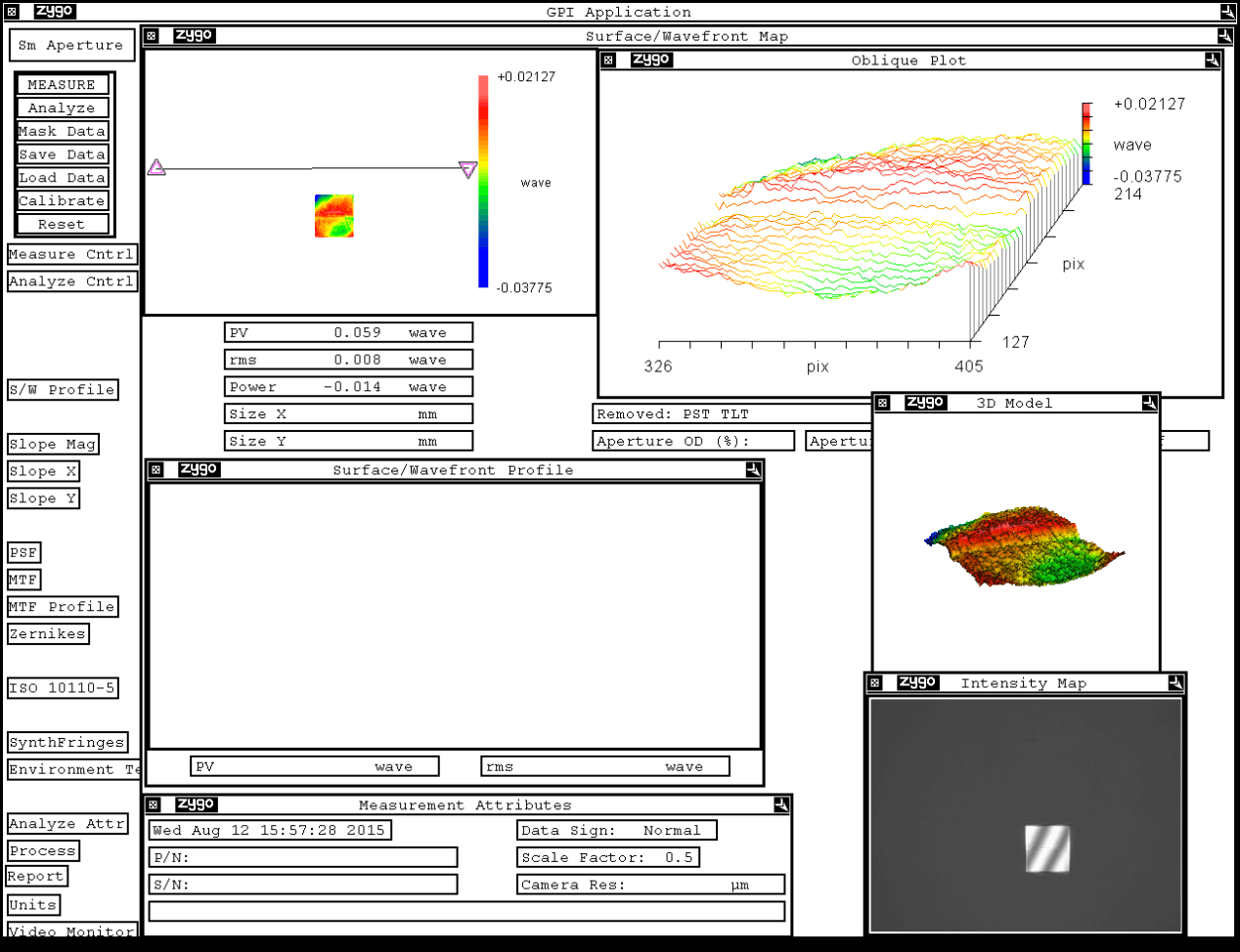
A prism is a transparent object surrounded by two planes that intersect but are not parallel to each other. The most important parameters of a prism are the angle and material. Prisms are widely used in splitting, depolarization, polarization, image orientation, dual channel instruments, etc.
Chromaticdispersion optical
Shanghai Optics can provide high-precision prisms with arbitrary angles, sizes below 300mm and angular accuracy of 1 second. Customized coatings are available for different UV, visible and infrared wavelengths according to customer requirements.
Alpha Industrial Park, Tu Thon Village, Ly Thuong Kiet Commune, Yen My District, Hung Yen Province Vietnam 17721 +84 221-730-8668 rfqvn@shanghai-optics.com
Dispersion opticalformula
The effect of chromatic dispersion is also important to people who send short pulses, which are made up of many different wavelengths, through optical waveguides, like optical fiber. Short pulses of EM Rad are used as a way of encoding data, like voices during a telephone call and the information on this website, so that the data can be sent from one place to another. As the pulse travels in the waveguide, some wavelengths of light travel faster than others. As the pulses travel down the waveguide, they increase in width and overlap with one another. If they spread too much, it is difficult to tell where one pulse begins and the other ends, and this results in information being lost. Researchers who work in the Communications and Fiber Optics fields of optics are developing devices to combat the effects of dispersion. (Visit the Optoelectronics, Communications, and Fiber Optics branch to learn more.)
An interesting feature of a Dove Prism is as it rotates along its longitudinal axis, the emitted image rotates at twice the speed of the prism. Meaning, it can rotate the beam at any angle, which makes them useful in beam rotators, which are used in areas such as interferometry, astronomy and pattern recognition.
When the exit surface is incident at a right angle, a 90 degree deflection can occur. The oblique side is the incident exit surface, and the light is deflected by 180 degrees.
Chromatic dispersion is especially important to researchers who are designing optical equipment like cameras, optical microscopes, and telescopes. When a lens system is not carefully designed, the system will focus different colors of light at different spots and this doesnt give a very good image! By planning the system carefully and using a combination of lenses made out of different materials with different indices of refraction, these chromatic aberrations can be greatly minimized.
Right-angle prisms are used as mirrors to deflect light by 90 degrees or as retroreflectors, allowing light to pass through 180 degrees of total internal reflection. Right-angle prisms can also be used for applications such as stitching and beam shifting. In addition, using the critical angle characteristic, efficient internal total reflection of incident light is one of the basic functions of a right-angle prism.
An important characteristic of a pyramid is that the reflected light is always parallel to the incident light, regardless of the angle of incidence. Corner cubes are used for target determination and quick alignment.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500