Tool Sizes for Shaft Collar and Coupling Installation - hex size
More information: Ashish Jain et al, Selective and Tunable Absorption of Twisted Light in Achiral and Chiral Plasmonic Metasurfaces, ACS Nano (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c06983 Journal information: ACS Nano
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
A phase contrast microscope is an optical microscope designed to enhance the contrast of transparent and colorless specimens without the need for staining. It works by exploiting differences in the refractive index of different parts of the specimen, transforming these differences into variations in light intensity.
Typeof microscope
Shop for Handheld Magnifying Glass in Magnifying Glass. Buy products such as Magnifying Glass with 12 LED Lights 30X Magnifying Glass for Readingwork ...
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Lightpath overview · www.lightpathfiber.com · Long Island City, NY · 201 to 500 Employees · 1 Location · Type: Subsidiary or Business Segment · Founded in 1991 ...
Function ofstagein microscope
Nov 9, 2018 — The polarity depends upon the electronegativity of the bonding atoms; most electronegative atoms pull the electronic cloud towards itself.
Magnification is the process of enlarging the appearance of an object, making it look bigger than its actual size. In optics, it is the ratio of the size of the image produced by a lens or microscope to the actual size of the object being viewed.
Witness the microscopic world in stunning detail with our high-quality optics. Every slide comes to life with crystal-clear clarity, allowing you to delve into the intricacies of biology, chemistry, and beyond.
Navigate effortlessly through magnification levels and focus adjustments. Our microscopes feature intuitive controls, allowing you to concentrate on your research without the hassle of complicated settings.
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
Microscope objectives are vital lenses that determine the magnification, resolution, and quality of the images produced by a microscope. They come in various types and magnifications, each suited for different applications and levels of detail, making them indispensable in scientific research, medical diagnostics, and educational settings.
The relative aperture for a microscope is called the numerical aperture (NA) and is equal to the sine of half the angle subtended by the aperture at an object ...
What is a ghost image? In computing, ghost imaging, also called disk imaging, is a data backup process that creates an image of a computer's hard disk drive ( ...
AmScope exclusive ALL-IN-ONE 3D DIGITAL INSPECTION MICROSCOPE. View different angles and perspectives of objects with ease.
Researchers at the University of Ottawa have made a discovery that changes what we know about light and materials. They found that engineered achiral (symmetric) materials, called achiral plasmonic metasurfaces, can absorb light differently depending on the handedness of the wavefront of light. This was surprising because, for years, such materials were found to be indifferent to any optical probes and do not show such selective absorption.
Jun 29, 2021 — The main ranges for non-contact temperature measurement are the NIR, SWIR, MWIR and LWIR ranges covering wavelengths of 0.75 - 15 μm. It is ...
Commonly used in biological research, medical diagnostics, and educational settings for detailed examination of specimens.
A Compound Microscope is a type of optical microscope that uses multiple lenses to magnify small objects. It consists of two sets of lenses: the objective lens, which is closer to the specimen and provides the initial magnification, and the eyepiece lens, which further magnifies the image for the viewer's eye. Light passes through the specimen and is magnified by the objective lens, then further magnified by the eyepiece lens, resulting in a highly magnified image visible to the observer. Compound microscopes are commonly used in biology, medicine, and other scientific fields for viewing cells, tissues, and other small structures.
"For decades, we believed that these materials couldn't show any difference in how they absorb polarized light," says Professor Bhardwaj. "But our research shows that by using a special kind of twisted light, we can control and tune this absorption up to 50%."
What is the purposeofthe objective lensina lightmicroscope
Illuminate your subjects with brilliance. Our microscopes feature advanced lighting technologies, providing the perfect balance for optimal observation, even in low-light conditions.
A darkfield microscope is a type of optical microscope that provides high contrast images of unstained specimens by using scattered light. The specimen appears bright against a dark background
Magnification works by bending light through lenses or using digital technology to enlarge the appearance of an object, allowing for detailed observation and analysis.
Opticalmicroscope
The research, conducted over the past year at uOttawa's Advanced Research Complex (ARC), was led by Ravi Bhardwaj, Professor, Department of Physics at the University of Ottawa and Ph.D. student Ashish Jain.
A trinocular microscope head combines the benefits of binocular viewing with the capability to capture digital images or videos of specimens. It is particularly suited for advanced research, educational purposes, and industrial applications where precise imaging and documentation are essential.
Professor Bhardwaj explains, "Our research not only debunks the myth that dichroism doesn't exist in achiral structures but also opens doors to next-generation plasmonic-based spectroscopy and sensing via enhanced optical metrology." This work promises significant advancements in optical devices, such as sensors and switches.
Uses two separate optical paths with two objective lenses to provide a stereoscopic (3D) view of larger, opaque specimens.
Objective lens magnification
Used in fields like biology, geology, entomology, electronics assembly, and manufacturing for tasks requiring manipulation and examination of objects in three dimensions.
Collaborators include Howard Northfield, Research Engineer, and colleagues Ebrahim Karimi, Canada Research Chair in Structured Light and Associate Professor of Physics, and Pierre Berini, University Research Chair in Surface Plasmon Photonics and Professor of Electrical Engineering.
A binocular microscope head utilizes two eyepieces for simultaneous viewing with both eyes, providing enhanced comfort, depth perception, and superior image quality. Ideal for professional and research settings requiring detailed observation, its design minimizes eye strain and enhances ergonomic support compared to monocular microscopes.
The terms monocular, binocular, and trinocular refer to the different types of microscope heads, each offering a distinct way of viewing the specimen.
Compound Magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece.
A monocular microscope head is a basic type of microscope head with a single eyepiece, ideal for cost-effective and straightforward applications. It is particularly useful in educational settings and for beginners, but it can lead to eye strain over long periods and lacks the depth perception provided by more advanced binocular and trinocular heads.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form. For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines).
The Colors of Visible Radiation ¹ ; 559 - 571, Yellow green, Purple ; 571 - 576, Greenish yellow, Violet ; 576 - 580, Yellow, Blue ; 580 - 587, Yellowish orange ...
Provides high magnification (up to 1000x or more) and high resolution for viewing fine details of cells, tissues, and microorganisms.
Function ofeyepiecein microscope
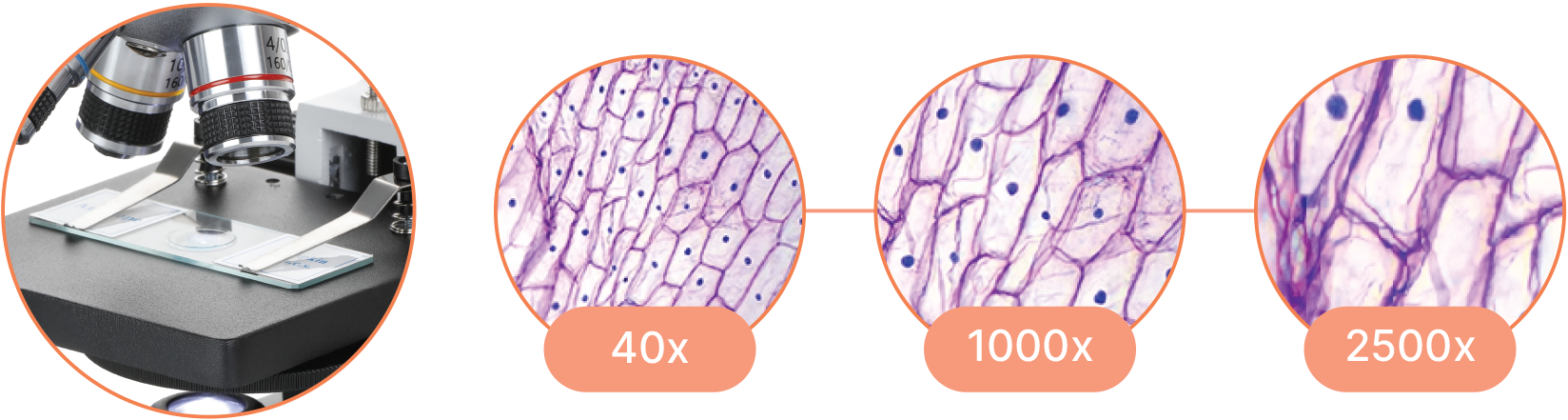
Capable of high magnification, which is achieved through the combination of the objective lens (typically 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x) and the eyepiece (usually 10x).

A specimen is a sample or example used for scientific study. It can be anything from biological tissues to materials, examined under a microscope or other instruments for analysis.
Which partofthemicroscopesupports the slide that you are viewing
Objective lensmicroscope function
A microscope is a scientific instrument used to magnify and observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. It works by focusing light or electrons to create an enlarged image of the specimen.
In addition, "this discovery is important because it shows that even symmetrical materials can have special light-absorbing properties, opening up new possibilities for advanced sensing and measurement technologies," adds Jain.
Table of Contents · Objective Identification · M = L / F . · NA = ni × sinθ · FN = Field of View Diameter × Magnification · Magnification · Using an Objective with a ...
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
Knight Optical offers a range of stock and custom precision Fresnel Lenses made from PMMA Acrylic in two grade for fast global delivery ...
We're excited to offer fans an exclusive chance to dive into the vibrant, imaginative worlds of our beloved Achromatic Chronicles series. Penned by the ...
A stereo microscope, also known as a stereoscopic or dissecting microscope, provides three-dimensional viewing of larger, opaque specimens through dual optical paths with objective lenses. It offers lower magnification (typically 5x to 40x) than compound microscopes but enhances depth perception. Ideal for tasks in biology, geology, and manufacturing, it allows comfortable, extended viewing with ergonomic adjustments.
Compound microscopes are suited for detailed examination of microscopic structures, while stereo microscopes are more appropriate for observing larger objects in three dimensions and for tasks that involve manipulation and dissection.
The team used a special light tool developed by Professor Karimi's Structural Quantum Optics (SQO) group and fabricated the necessary structures with the help of Howard Northfield and Professor Berini. Their findings showed that this selective absorption happens because of interactions between different parts of the light and the material.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500