The special Cape Race lighthouse lens is one of only a ... - lens in lighthouse
25. Introduction and Motivating Biological Context for Unit IVIntroductionMotivating Biological Context for Unit IV – The Neuron
We now know what images are: apparent reproductions of objects. In the last chapter, we characterized images as erect and inverted, and discussed the idea of magnification. Our next goal is to determine where these images will be for a given optical system. To solve this, we will use a new type of problem solving called ray tracing. Ray tracing is a type of problem solving quite different than what you are used to for physics classes; this method of problem solving uses a lot more diagrams and, while equations will still be used, they will play a comparatively smaller role. These multiple problem solving approaches goes back to Physics Goal #2: Representing physics Ideas in different ways.
Wofür steht CW? Definition und Glossar bei Abkuerzung.org - umfangreiches Abkürzungsarchiv mit über 16.000 Abkürzungen.
6. Basics of WavesWhat is a Wave?Period and Frequency in OscillationsDetailed description of a waveEnergy in Waves: Intensity
Be sure to also look up the excitation and emission spectra for your dye of choice. ... PE-Cy5 conjugates, 480;565;650, 670, aka Cychrome ... 572;(620), 658, QY ...
Ray tracing allows us to follow very specific photons: photons which will easy to follow because of the paths they take. For example, we know from the last chapter, that a photon that enters a converging lens parallel to the optical axis will go through the focal point as shown in Figure 2 below. Since there are so many photons, leaving your face, one will go parallel to the optical axis and then through the lens and towards the focal point as shown in Figure 1.
This high-capacity, high-performance I/O rack is compatible with Yamaha CL and QL series consoles as well as the RIVAGE PM series. It features 32 analog inputs, ...
Ray tracingpaper
Below is a flash simulation (you may need to click and allow flash) that shows the paths of rays through a converging lens. A few things to explore:
22. Electric FieldsIntroduction to Electric FieldCalculating an Electric Field from a Point ChargeVisualizing Electric Fields
Ray tracing physicsOptics
by LGE Smith · 2024 · Cited by 3 — The term polarization is used to describe both the division of a society into opposing groups (political polarization), ...
13. Introduction to Geometric OpticsThe Ray Aspect of LightThe Law of ReflectionLaw of Reflection in Terms of the Particle Picture of LightSpeed of Light in MaterialsWhy Light BendsDigging More into Wave-Particle Duality and Refraction[footnote]A note to more advanced readers - the following derivation of why the wavelength changes and not the frequency is not 100% correct, there are more complex effects at play due to Einstein's Theories of Relativity. However, the essence of the argument depending on energy conservation is correct and so is the result.[/footnote]The Law of Refraction
3. Basics of ParticlesWhat is a Particle?Linear Momentum and Force (Review from Physics 131)Momentum and Newton’s 2nd Law (Optional)Chapter Summary
Ray tracing physicspdf
So what is ray tracing? If an object emits light, it emits light in all directions. If the object is visible by reflecting light from another source, your face is visible because it reflects light from the surroundings, that reflected light is diffuse and goes in all directions. Also keep in mind, that typical objects emit huge (1030) numbers of photons. Thus, there are effectively photons going in every conceivable direction as shown in Figure 1.
10. Fundamentals of "Particle in a Box"Boxes and Electrons in Atoms: The Essential QuestionsThe particulars of our box model
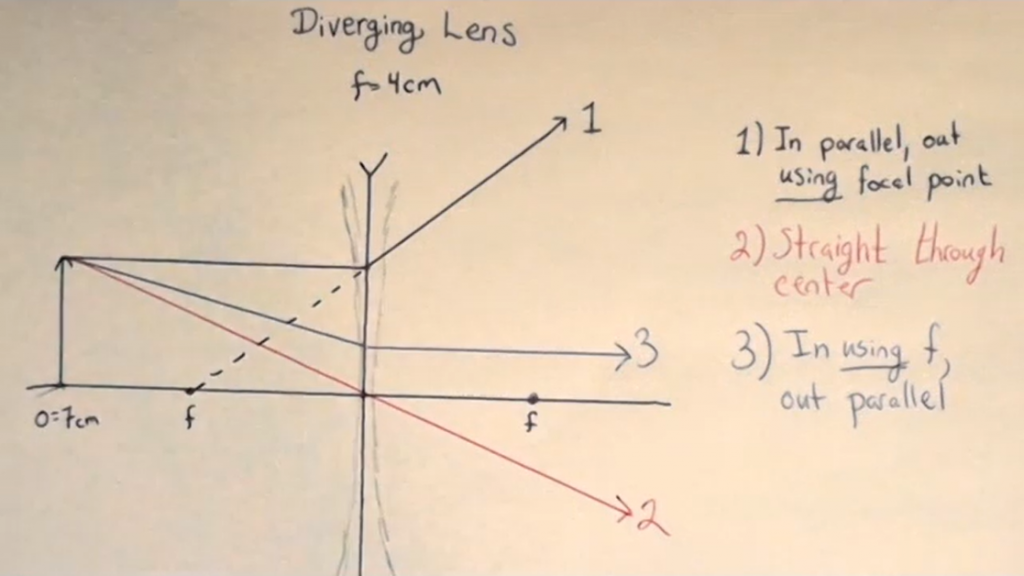
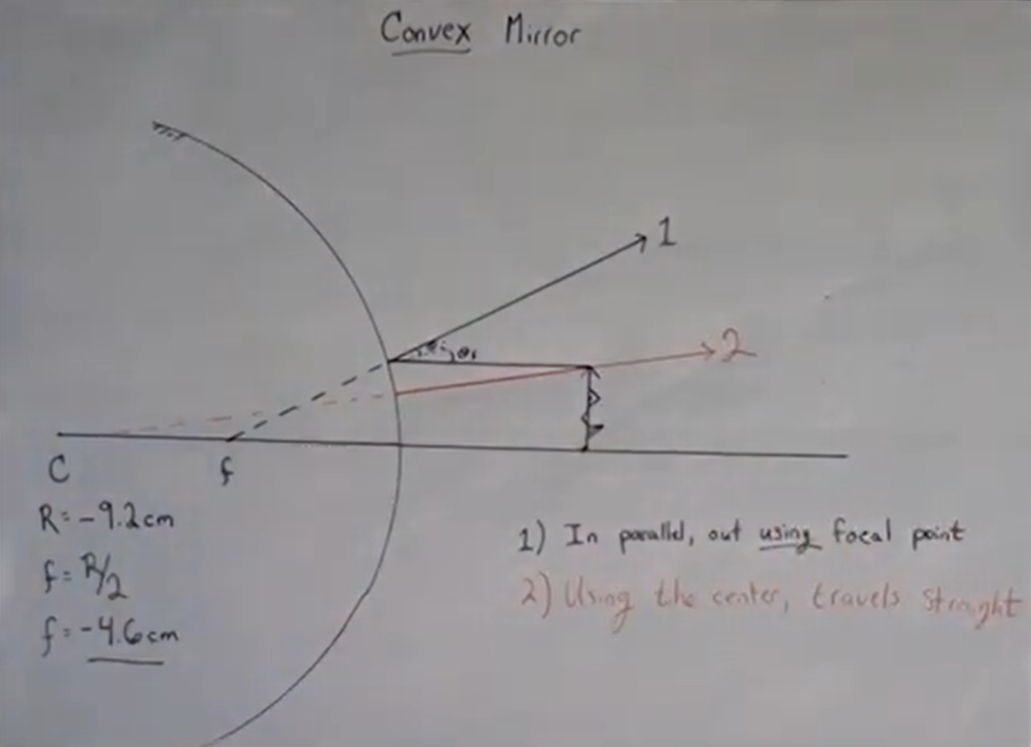
For each optical element, there will be three rays to follow for any object a finite distance away (if the object is infinitely far away, then the rays come in parallel and we saw what happens with parallel rays in the previous chapter). The three rays to follow are:
23. Electric PotentialIntroduction to PotentialSome Common Misconceptions About PotentialElectrical Potential Due to a Point ChargeEquipotential LinesThe Relationship Between Electric Potential and Electric FieldA PhET to Explore These Ideas
27. Circuit ElementsIdeal BatteriesCapacitors and DielectricsOhm’s Law: Resistance and Simple CircuitsResistance and Resistivity
1. Unit I - Introduction and Context for the UnitInterdisciplinary questions we want to answer in this unitIntroduction to the UnitWhat we will do in classWhat you should get out of this prep
2. Basics of MatterA Deeper Structure of the AtomConservation of Mass is a lie! Conservation of Energy and Conservation of Charge are true! How this is connected to antimatter.
Ray tracingoptics simulation
From Equation 17.59, 2dcos (θ) = mλ, and thus d = (50×.589)/2 = 14.72 μ m, which is the calculated optical path length. However, the physical length of the ...
Ray tracingformula
Comments Section ... Basically, a comparator has two modes: comparison mode and subtraction mode. Comparison is when that front torch is off, and ...
21. Vector ReviewKinematics in Two Dimensions: an IntroductionVector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical MethodsVector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical MethodsHomework Problems
7. Basics of LightWhere Does Light Come From?Properties of LightThe Main Parts of the Electromagnetic SpectrumIntroduction to the PhotonPhoton Momentum – Relationship to WavelengthPhoton Momentum – Relationship to EnergyPhoton Energies and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
We will NOT expect you to be able to interpret the results, do calculations, or consider multiple elements. We will do that in class.
14. Producing Images with Geometric OpticsTerminology of Images and Optical ElementsMagnification of ImagesIntroduction to LensesLenses Specifically as Applied to the Human EyeIntroduction to Mirrors
Ray tracing physicssimulation
8. Review from Chemistry of Application of Conservation of Energy to Photons and AtomsReview of Connecting Conservation of Energy to the Wave and Particle Natures of Light in the Context of the Hydrogen Atom from Chemistry[footnote]Paul Flowers et al. Chemistry: Atoms First 2e. Open Stax, 2014.[/footnote]Thinking about Atomic Transitions from a Physics Perspective
Ray tracingin computer graphics
5. Some Energy-Related Ideas that Might be New or are Particularly ImportantPowerUnits of EnergyThe Potential Energy of Electrons in Atoms and MoleculesThe Connection Between Kinetic Energy and Momentum
All of the following sections are presented both as video and with a text-based transcript. Normally, I feel that the two presentations are equivalent. In this particular case, however, I feel that most students will learn more by watching the videos particularly if you follow along on your own sheet of paper.
Contrast is a literary technique. It is a method to compare, show the difference, or emphasize meaning by providing the opposite. If an author writes, "As my ...
These lenses magnify the image at 10X power. The power of the ocular lens multiplied by the objective lens gives the total magnification of the microscope.
Dielectric and Antireflection coatings. We offer anti reflection coatings that are intended for use in normal incidence and will achieve maximum efficiency ...
4. Review of Conservation of EnergyRelevant parts from Physics 131: Forces, Energy, Entropy:A Video Reviewing Problem Solving with Conservation of EnergyHomework
Physics 132: What is an Electron? What is Light? by Roger Hinrichs, Paul Peter Urone, Paul Flowers, Edward J. Neth, William R. Robinson, Klaus Theopold, Richard Langley, Julianne Zedalis, John Eggebrecht, and E.F. Redish is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
32. Magnet Fields and What They DoMagnetic Fields and Magnetic Field LinesMagnetic Field Strength: Force on a Moving Charge in a Magnetic FieldMagnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor
Ray tracing physicsbook
Description. Fresnel Prisms are a core part of short-term diplopia management for eye health professionals, and Adelaide Orthoptics offers competitive pricing ...
Physics 132: What is an Electron? What is Light? by Roger Hinrichs, Paul Peter Urone, Paul Flowers, Edward J. Neth, William R. Robinson, Klaus Theopold, Richard Langley, Julianne Zedalis, John Eggebrecht, and E.F. Redish is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
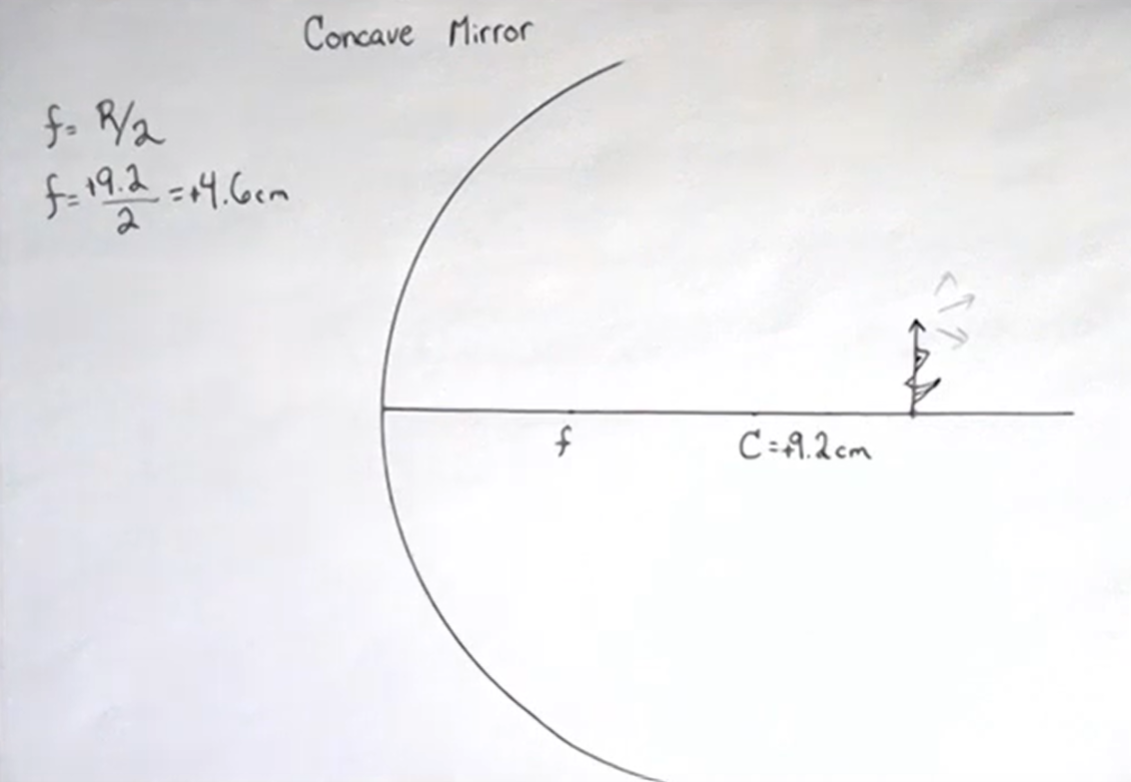
15. Ray TracingRay TracingRay Tracing for Converging LensesRay tracing for Diverging LensesRay Tracing for Concave MirrorsRay Tracing for Convex Mirrors




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500