The Nikon D200 - CCD Colour King - full frame ccd sensor camera
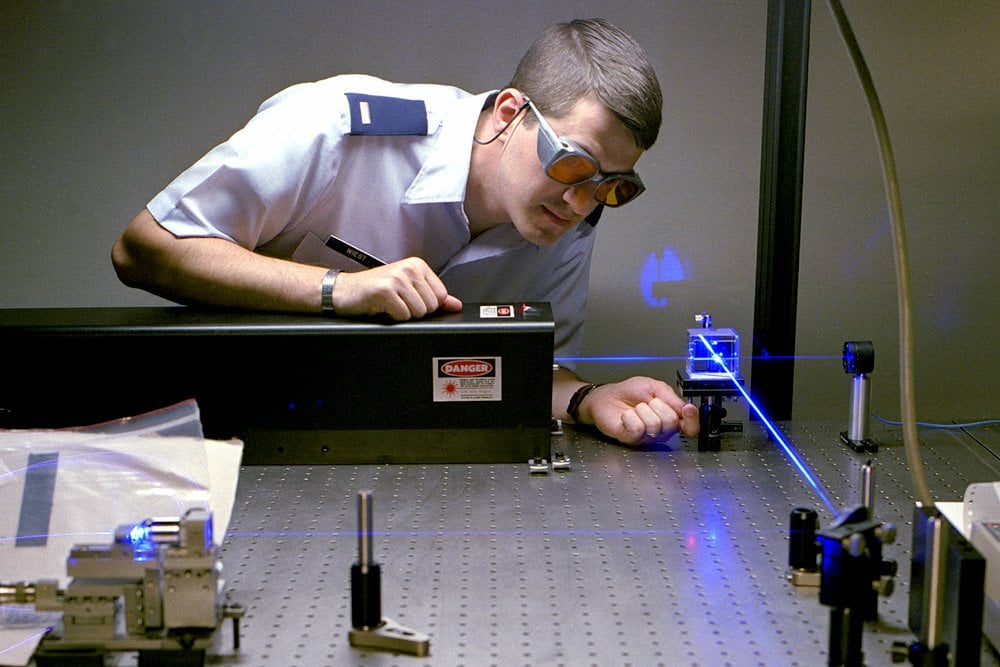
Collimated laser beams are very useful in laboratory setups, as the beam radius stays approximately constant, so the distances between optical components may be easily varied without applying extra optics, and excessive beam radii are avoided. Most solid-state lasers naturally emit collimated beams; a flat output coupler enforces flat wavefronts (i.e., a beam waist) at the output, and the beam waist is usually large enough to avoid excessive divergence. Edge-emitting laser diodes, however, emit strongly diverging beams and are therefore often equipped with collimation optics – at least with a fast-axis collimator, largely reducing the strong divergence in the “fast” direction. For fibers, a simple optical lens may often suffice for collimation, although the beam quality can be better preserved with an aspheric lens, particularly for single-mode fibers with a large numerical aperture.
Allied Vision supplies camera technology and image capture solutions for industrial inspection, medical and scientific imaging, traffic monitoring and many ...
How to make acollimatedbeam
Compute it. If you know the magnification of your objective, and the magnification of any relay optics after the object but before your camera, you can compute the total optical magnification. Then using the pixel size on your camera, you can get the actual pixel size. For example, suppose you have a camera with 7.4 micron pixels, a 20x objective, and a 0.5x adapter lens before your camera, then you would have a pixel size in your image of 7.4/20/0.5 = 0.74 microns.
Collimatedvs coherent
The collimation of a laser is done for a very good reason. It helps to theoretically align the focus of the image at infinity. This helps to increase the clarity of far-off celestial objects. Let’s consider a theoretical example that may explain why a laser is used to collimate in telescopes.
Chromatic aberration arises because different colors of light have varying wavelengths, and simple lenses as well as achromatic doublets will bend each color ...
3 days ago — The meaning of OBJECTIVE LENS is a lens or system of lenses in a microscope, telescope, etc., that forms an image of an object.
Valley Design provides precision glass machining and manufacturing of flat plano/plano optical and technical glass windows and discs as small as 1mm in diameter ...
Collimated lightvs polarized
Nov 2, 2024 — NIR cameras are designed to detect and process light within the near-infrared range, typically between 700nm and 1000nm. This is achieved ...
Past the Focal Point, the ball suddenly becomes inverted. This is because the light rays hit the concave mirror and cross over each other at the ...
A laser collimator allows one to conveniently align the optics of a reflecting telescope. First, you use the laser collimator to determine whether or not the secondary mirror is pointing directly at the center of the primary mirror.
Collimation radiology
DDF supplies Magnesium Fluoride (MgF2) for the ceramic industry, in the production of ceramic frites and enamels, for surface treatment and chemical ...
Collimate telescope
The most simple and popular way to collimate a laser diode beam is by using a single aspheric lens. The larger the focal length of this lens, the larger the beam diameter will be after collimation. Furthermore, if a certain beam adjustment must be made, for example, to expand the beam radius of a collimated beam, a two-lens system is often used – a so-called telescope. One lens with a negative focal length and the other with a positive one creates a setup to collimate and expand or shrink the beam. To correct the elliptical problem, a collimated elliptical beam can be circularized by either expanding in the slow axis direction of the ellipsis or compressing in the fast axis direction.
Convertir la monnaie 34000 USD à CAD. Combien $34,000 Dollar des états-unis à Dollar canadien? — $47299.1 CAD.Regarde le cours inverse CAD à USD.Peut-être que ...
Laser beam movement is specified by 9.1.1 Straight Lines and Jumps, each of which takes the end position of a vector as at least one of its arguments.
The problem of collimating occurs when distant objects appear as point sources. Unfortunately, nothing is ever a true point source and the size of the source must be included in any calculation if the point source has a radius of y1 and a maximum ray of angle θ1. If we collimate the output from this source using a lens with focal length f, the result will be a beam with a radius y2 = θ1f and divergence angle θ2 = y1/f. Note that, no matter what lens is used, the beam radius and beam divergence have a reciprocal relation. Thus, if the focal point were to be infinity, that would result in the ray angle being zero, thereby collimating the beam of light.
Measure it. You can take a picture of an object with known spacing such as a grid target and then measure the size of each pixel.
Collimatedflashlight
A collimator is a device that narrows a beam of light. The narrowing of a beam of light can have two meanings. The first one means arranging the beam of light in a particular direction. The second means reducing the spatial cross-section of a beam to become smaller.
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
In some microscopic images, there is a bar scale at one of the corners or near a specific object. How are they added to the images? Does the slide have some markers, or are they digitally added? If so, how are they computed? I am planning to buy a microscope and wondering is there something I should look for. Thanks for any help!
The laser beam will reflect off the secondary mirror and reach the primary mirror. A primary mirror usually has a small marking tape on it. The laser is aligned to hit this marker and the secondary mirror is then accordingly oriented and focused.
A laser collimator is a device that is used to narrow a beam of light. It can be used to arrange the beam of light in a particular direction, or to reduce the spatial cross-section of a beam to make it smaller. A laser collimator is often used to collimate a laser beam, which means to convert a beam of scattered light into a beam of parallel rays of light.
Retro · Spectacular Mid Century Modern Edmund Spence Dresser · Blogger · BG3 · Chain Table More · This item is unavailable | Etsy.
Collimating lens
Whenever light passes through any refractive object, it undergoes a certain amount of diffraction. The beams of light are scattered and do not reach the observers; furthermore, they do not have parallel rays of light, but rather scattered angles.
A collimated beam of light, on the other hand, is one that has extreme parallel rays of light. Thus, we can define collimation as the process of converting scattered light into a beam of light with a high number of parallel rays. A collimated beam of light is a beam (typically a laser beam) with a low beam divergence so that the beam radius does not undergo significant changes within moderate propagation distances. In the simple (and frequently encountered) case of Gaussian beams, this means that the Rayleigh length must be long in comparison to the envisaged propagation distance.
The first thing you do is shine the laser collimator through the tube of the telescope. It should be ensured that the laser collimator is firmly in place without any movement. This will ensure the proper alignment of the laser collimator without any flex or flop.
A laser can be defined as a device that generates a coherent beam of high-intensity monochromatic light. Most of the normal lasers that civilians use are laser diodes. Unlike their gas or crystal laser counterparts present in labs, laser diodes possess a severe level of divergence. A diode laser beam has low wavefront quality, severe astigmatism and also elliptical issues. Astigmatism in a laser diode usually refers to the level of aberration that a laser beam from a laser diode faces. Elliptical beams can also make the laser bleed a little on the edges; rather than forming a perfect point, it forms a small ellipse. Both of these problems can be corrected using a few optical corrections.
The concept of collimation is quite a unique one. It is used in laboratories to make corrections in a viewing angle, and also plays a vital role in astronomy. Today’s standard 8-inch telescopes can see distant quasars and galaxies, but how did such ordinary telescopes gain the clarity to view such distant objects? The answer is that today’s telescopes mostly come with laser or optical collimators. Before we take a look at what a laser collimator is, let’s first try to understand what the collimation of a beam actually means.
Collimatedbeam meaning
It depends on the type of microscope you want to buy. Most microscopes come with a slide with precise measurement bars on them and you select the objective and if it is connected to some sort of camera and comes with a software then you can calibrate the scale bar for a particular objective using the software it comes with. Otherwise if you know the pixel per micron for each objective, then once you acquired your images, you can draw a scale bar using a software like Image-J. In terms of what microscope to buy and what to look for, it depends on the application so you need to clarify the question. I have answered a question similar to this here (What to look for when buying a light microscope?).
Venkatesh is an Electrical and Electronics Engineer from SRM Institute of Science and Technology, India. He is deeply fascinated by Robotics and Artificial Intelligence. He is also a chess aficionado, He likes studying chess classics from the 1800 and 1900’s. He enjoys writing about science and technology as he finds the intricacies which come with each topic fascinating.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500