The Imaging Source - Hersteller von Industriekameras - industrielle kameras
Types ofoptics in physics
Infrared: Infrared light lies between the visible and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum and has a range of wavelengths, just like visible light has wavelengths that range from red light to violet. "Near infrared" light is closest in wavelength to visible light and "far infrared" is closer to the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The longer, far infrared wavelengths are about the size of a pin head and the shorter, near infrared ones are the size of microscopic cells. We experience far-infrared radiation every day in the form of heat that we feel from sunlight, a fire, or a warm sidewalk. Shorter. near infrared waves are not hot and cannot be felt. These shorter wavelengths are the ones used by your TV's remote control.
Q2: The critical angle θc in an optical fiber is given by ________ Where n1 is the refractive index of medium 1 and n2 is the refractive index of medium 2. [ISRO Scientist EC 2011 Paper]a) sin-1 (n2/n1)b) sin-1 (n1/n2)c) sin-1 (n1*n2)d) sin-1 n2
Types of opticallenses
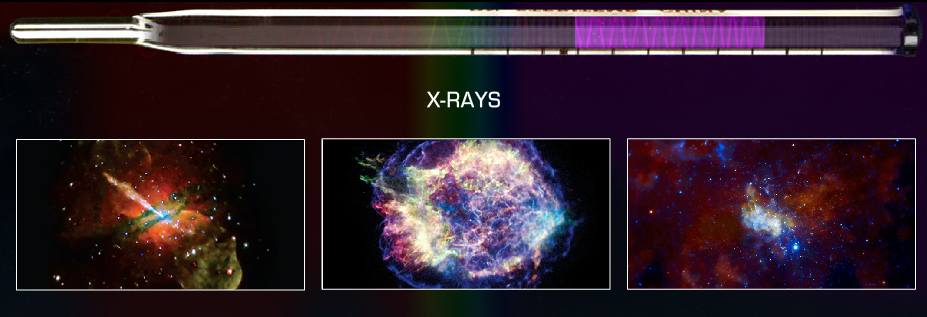
X-ray: Light is the by-product of the constant jiggling, vibrating, hurly-burly of all matter. A new form of radiation was discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen, a German physicist. He called it X-radiation to denote its unknown nature. This mysterious radiation had the ability to pass through many materials that absorb visible light. Very high temperatures (millions of degrees Celsius) produce X-rays. The energies of X-ray photons range from hundreds to thousands of times higher than that of optical photons. The Earth's atmosphere is thick enough that virtually no X-rays are able to penetrate from outer space all the way to the Earth's surface.
How manytypes of optical
Radio: Radio waves have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. These waves can range from less than one centimeter to greater than 100 meters (this is bigger than the size of a football field). The energy of radio waves is much lower than the energy of other types of electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves can bring music to a radio, and carry signals for a television and cellular phone.
Visible: The word light usually makes one think of the colors of the rainbow or light from the Sun or a lamp. This light, however, is only one type of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation comes in a range of energies, known as the electromagnetic spectrum. The spectrum consists of radiation such as gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet, visible. infrared and radio.
Types of opticalglasses
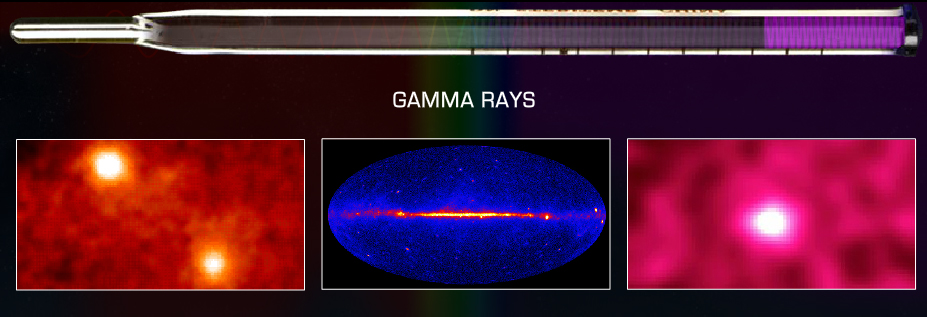
Gamma Ray: Electromagnetic radiation travels in waves, just like waves in an ocean.The energy of the radiation depends on the distance be.een the crests (the highest points) of the waves. or the wavelength. In general the smaller the wavelength. the higher the energy of the radiation. Gamma rays have wavelengths less than ten trillionths of a meter which is about the size of the nucleus of an atom. This means that gamma rays have very high-energy.
Types of opticalfibre
Microwave: Microwaves have wavelengths that can be measured in centimeters. The longer microwaves, those closer to a foot in length, are the waves which can heat food in a microwave oven. Microwaves are good for transmitting information from one place to another because microwave energy can penetrate haze, light rain and snow, clouds, and smoke. Shorter microwaves, those just a few inches long, can be used for radar like the doppler radar in weather forecasts.
Fiber Optics has the work of transmission of light particles, or photons. Fiber optics transmit data as light through thin sheets of glass or plastic. Each fiber consists of a core, where the light travels through it, and a surrounding cladding that reflects the light back into the core part. Data is converted into light using a laser or LED, and these light pulses travel through the core, bouncing off the cladding to stay contained in it. At the receiving end, a photodetector converts the light back into the electrical signals. This technology allows for fast, high-capacity data transmission with minimal signal loss, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and therefore the security is enhanced. Fiber optics are generally used for high-speed internet, telecommunications, medical devices, and many more industrial applications.
Types of opticaldevices
Fiber Optics or Optical Fiber is a technology that transmits data as a light pulse along a glass or plastic fiber. An Optical Fiber is a cylindrical fiber of glass that is hair-thin in size or any transparent dielectric medium. The fiber which is used for optical communication is waveguides made of transparent dielectrics. In this article, we will discuss Optical Fiber/Fiber Optics in detail.

Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet (UV) light has shorter wavelengths than visible light. Though these waves are invisible to the human eye. some insects, like bumblebees, can see them. Our Sun emits light at all the different wavelengths in electromagnetic spectrum. but it is ultraviolet waves that are responsible for causing our sunburns.
what are the 3types ofoptics?
Fiber optics refers to the technology and method of transmitting data as light pulses along a glass or plastic strand or fiber. Fiber optic cables are used for long-distance and high-performance data networking. They are capable of transmitting data over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than electrical cables, making them a critical component in modern telecommunications, internet, and computer networking.
(a) Fiber optic cable is much lighter than copper cable(b) Fiber optic cable is not affected by power surges or electromagnetic interference(c) Optical transmission is inherently bidirectional.
Though some ultraviolet waves from the Sun penetrate Earth's atmosphere, most of them are blocked from entering by various gases like Ozone. Some days. more ultraviolet waves get through our atmosphere. Scientists have developed a UV index to help people protect themselves from these harmful ultraviolet waves.
Fibre optics technology uses light pulses through glass or plastic fibres to transmit data at fast speeds and over long distances. Fibre optics, with its high bandwidth, low electromagnetic interference, and resilience, is critical for modern telecommunications, internet, medical, and military applications. Despite greater costs and installation issues, its advantages make it the best option for effective data communication.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500