The Best Pocket Microscope for You - hand held microscopes
But with so many microscope objective types available, it can be difficult to find the right one for your application. Where do you start?
There are a few different ways to get UV light at home. One way is to use a sunlamp and purchase Sun lamps at most stores. Another way to get UV light at home is to use a tanning bed. Moreover, one can find tanning beds at some 9yms and some salons. A third way is to use sunscreen and go outside in the sun without too much protection.
The sun has three types of ultraviolet rays: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVA and UVB rays can damage the skin and lead to sunburns and skin cancer. The UVC rays are the shortest of the three and are the safest because they do not cause any harm to the skin. They can, however, cause eye damage when exposure is prolonged. The intensity of UV rays depends on the time of day, the sun’s location, and its strength.
Whatdoesthe objectivelens doon a microscope
If you work with samples that emit a weak fluorescence signal, then we recommend high NA objectives since they gather more light. Olympus has a wide range of microscope objectives that offer fluorescence excitation from ultraviolet (UV) to near-infrared (NIR).
What is thestageon a microscope
The most common immersion media are air, water, oil, and silicone. Choosing the appropriate objective for your media will result in better image quality.
The resolution of the microscope objective determines the smallest distance between two objects that can be observed. It is directly proportional to the illumination wavelength of light and inversely proportional to the NA.
We all know the importance of UV light for our health, and it’s even more critical during the winter months when we can’t get outside as much. But getting good UV light sources at home can be challenging, as most sources are too expensive or difficult to find. Fortunately, there are some great options to get the UV light you need to stay healthy and happy all year long!
The objective is perhaps the most important part of an optical microscope because it’s responsible for primary image formation and plays a central role in determining image quality.
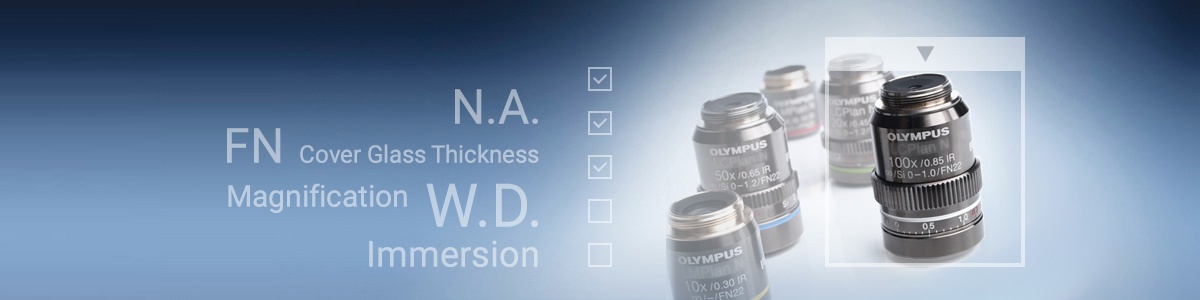
Working distance (WD) is the distance from the objective’s front lens to the closest surface of the coverslip when the specimen is in focus. WD is inversely proportional to the NA, which means that higher NA objectives typically have low working distances.
What is objectivelens inmicroscope
Ultraviolet (UV) light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength between 100 and 400 nanometers. It has beneficial and harmful effects on the human body, and it is essential to understand the potential risks before exposing yourself to this type of light. While UV light can provide several health benefits, it can cause skin damage, eye problems, and other health conditions if misused.
Many microscope objectives are designed to image specimens with air as the medium, while others use an immersion medium that contains a higher refractive index to enable a high NA and resolution.
Opticalmicroscope
A sunlamp is a machine with a light bulb that emits ultraviolet light, allowing you to tan your skin. Since the sun emits different amounts of UV rays at different parts of the year, you can use the sunlamp all year long to get a tan whenever you want. However, the light from the sun varies in intensity and power depending on where it is in the sky. There is the risk that you will get burned if you go outside when the sun is high in the sky. It is safer to use a sunlamp indoors than it is to go out into the sun.
Olympus’ microscope objectives feature a range of magnifications from 1.25x to 150x. This is the first parameter to consider when finding the best objective for your application. Combined with the magnification from the eyepieces, it determines the microscope’s overall magnification.
Olympus offers dedicated objectives for advanced optical systems such as confocal, spinning disk confocal, multi-photon excitation, and total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy. If you work with these systems, then choosing the correct objective for your application is crucial.
Excessive exposure to UV light can cause damage to the eyes, such as cataracts, and increases the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Whatdoestheeyepiece lens doon a microscope
Rebecca holds a bachelor's degree in journalism from Endicott College and writes about trends and technologies in science and industry. She works closely with Evident engineers and scientists to write pieces about the latest laser scanning, super-resolution, multiphoton, upright, stereo, and inverted microscope systems, as well as leading-edge optics, cameras, and software. Follow her work to learn about Evident's latest for numerous applications, including cytology, pathology, education, and more.
To compensate for chromatic correction, you can use different types of objectives: achromat, semi-apochromat, and apochromat. Achromat objectives provide the least amount of correction, semi-apochromats (or fluorites) have additional spherical corrections, and apochromats offer the highest chromatic correction.
Whatdoesthestage doon a microscope
Ultraviolet (UV) light has many advantages in sterilization and disinfection but is not without risks. Exposure to UV light can damage the skin and the eyes and even lead to skin cancer. It is essential to be aware of UV light’s potential hazards and understand how to protect yourself and others from its dangers.
Choosing the right objective can improve your microscope’s imaging performance and produce more reliable results for quantification and analysis. To help you make this important decision, we compiled some helpful resources:
Objectivelens and eyepiece lens magnification
Getting enough natural sunlight is essential for our overall health, but finding the time to get outside can take time and effort. Fortunately, there are several ways to get your daily dose of UV light without leaving the house. From desk lamps to special light boxes, there are plenty of options to get the Vitamin D your body needs. You can Call Us for UV Light in Canton.
If your application demands multichannel fluorescence, then we recommend Olympus UPLXAPO extended apochromat objectives.
Sunlight has both visible and invisible rays. Ultraviolet light is one of the invisible rays of sunlight. Ultraviolet radiation is part of the electromagnetic spectrum and consists of wavelengths shorter than visible light. It ranges from about 100 to 400 nanometers in length and cannot be seen by the naked eye. UV radiation can have harmful effects on the human body if it is exposed to it for too long a period. Excessive exposure to Ultraviolet can cause skin cancer and other skin diseases. It may also damage your eyes. Therefore, it is essential to protect your eyes when you go outdoors for long periods. Always wear sunglasses with UV filters to protect your eyes from the sun’s harmful rays.
Sun Lamps are designed to emit specific wavelengths of light absorbed by the skin to produce a tan. There are three main types of light produced by sunlamps: UVA, UVB, and Uv-C. It is essential to make sure that your sunlamp uses the proper wavelength for you to get the best tan possible. The intensity or power of the sunlamp is also essential. If you have sensitive skin, use a lower-powered lamp to minimize the risk of getting burned. Sun lamps come in many different sizes and designs. Some may be small enough to fit on your desk or work table, while others can be as large as a bed.
The higher the NA, the smaller the distance between two objects. As we mentioned previously, choosing the right NA for your application is crucial in determining the resolution of your microscope system.
In today’s blog post, we compiled a series of questions to help you weigh your options and choose the right objective for your application. Let’s dive in.
NA is also important to observe very fine structures or detect dim signals during fluorescence observation. When determining which microscope objective will resolve the smallest feature in your specimen, think about the NA. As you weigh your options, keep in mind that numerical aperture ranges between 0.04 to 1.7.
What is thepurpose ofthe objectivelens inalightmicroscope
If your application demands non-coverslip applications that require an increased distance between the focal plane and the objective’s tip (i.e. samples with irregular topography, delicate structures, or mechanical constraints of the overall optical assembly), then you may find Olympus’ LMPLFLN or SLMPLN long-working distance objectives well-suited to your application.
For instance, using immersion oil instead of air as the imaging medium can increase the resolution by a factor of approximately 1.5.
When dealing with samples that are too thick, too thin, or birefringent, researchers will apply different observation methods other than brightfield. Common techniques are darkfield, differential interference contrast (DIC), phase contrast, and polarization. Olympus offers dedicated objectives associated with these different observation methods.
The second most important parameter of a microscope objective is the numerical aperture (NA). NA measures its ability to gather light. It’s an important factor to determine resolution, depth of focus, and the brightness of images. Objectives with a larger NA gather a wider range of light, resulting in brighter, higher resolution images.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500