T-Mount Double Female Rotating Ring - rotating ring
Since the objective is closest to the specimen being examined, it will relay a real image to the ocular lens. While doing so, it contributes a base magnification of anywhere from 4x (for a scanning objective lens, typically used to provide an overview of a sample) to 100x (for oil immersion objectives).
An eyepiece on a microscope is a lens that is positioned at the top of the microscope and is used to view the magnified image of the specimen. It is also known ...
Chromatic aberrations appear as red or purple outlines. They are especially visible in areas with strong contrasts. This phenomenon occurs when the lens is ...
KinderCare aims to protect your privacy online the way we protect your family in person, with care and caution. To improve the website experience, this site uses cookies as described in our Cookie Notice. Click allow to consent to the use of this technology on our site. To learn more, please visit our Legal Notices Page.
Magnification is one important parameter. Magnification is usually denoted by an X next to a numeric value. Objectives are available in a range of magnifications from 2X to 200X.
The optical aberration correction determines the optical performance of an objective lens and plays a central role in the image quality and measurement accuracy of imaging or microscopy systems. According to the degrees of the aberration corrections, objective lenses are generally classified into five basic types: Achromat, Plan Achromat, Plan Fluorite (Plan Semi-Apochromat), Plan Apochromat, and Super Apochromat.
Room 609, 6/F, Global Gateway Tower, No.63 Wing Hong Street, Cheung Sha Wan, Kowloon, Hong Kong +852-54993705 info@shanghai-optics.com
Since indirect backlight illumination is generally more effective than direct illumination, most microscopes do not include an internal light source. Instead, they rely on daylight or on background illumination such as a lightbulb. In brightfield illumination, also known as Koehler illumination, two convex lenses saturate the specimen with external light admitted from behind. These two lenses, the collector lens and condenser lens, work together to provide a bright, even, and constant light throughout the system: on the image plane as well as on the object plane. This system of illumination is used in many compound microscopes, including student microscopes and those found in many research labs.
Function ofcondenser in microscope
There’s a reason we give kids journals to write things down—beyond building literacy skills. Getting children used to recording their findings sets them up for success in their science studies later in life (and gives them a head start on learning the scientific method, whether they realize it or not).
Are you helping your child brush their hair before bed? Sneak in some science before story time by looking at several strands of their hair and your hair up close. At normal eye level, hair looks smooth and fine—but what about up close? What does your child see? How is their hair different from your hair?
We've all seen anti-reflective glass in a museum, probably without even noticing it... That's the beauty of Clearsight anti-reflective glass.
Microscope Objectives or Objective lenses are in many ways the heart of the microscope, and are typically mounted on a rotating nosepiece or turret to enable easy selection. Many microscopes will be equipped with a scanning objective (4x), a low power objective (10x), a high power objective (40x), and perhaps even an oil immersion objective lens.
What isobjective lensin microscope
A microscope is a special optical device designed to magnify the image of an object. Depending on the type of microscope, it may project the image either onto a human eye or onto a recording or video device. As an example, consider the photographs of cells that can be found in a science textbook. These photographs have all been taken by a specialized microscope, and may be called micrographs.
Objective lenses can be classified based on the objective construction, field of use, microscopy method, performance (optical aberration corrections), and magnification. Many microscope objective manufacturers offer a wide range of objective designs, which provide various degrees of optical aberration corrections for supporting different needs. Mirrors or reflective elements are used in objective lenses for the applications that requires chromatic aberration over board spectral ranges. Most traditional microscopy systems use refractive objectives such as achromatic objectives (the cheaper objectives) for laboratory microscope applications and plan apochromats (expensive objectives) for biological and science research microscope applications.
Alpha Industrial Park, Tu Thon Village, Ly Thuong Kiet Commune, Yen My District, Hung Yen Province Vietnam 17721 +84 221-730-8668 rfqvn@shanghai-optics.com
They generally have higher magnification than a magnifying glass, and are designed to be held or worn close to the eye. A loupe does not have an attached handle ...
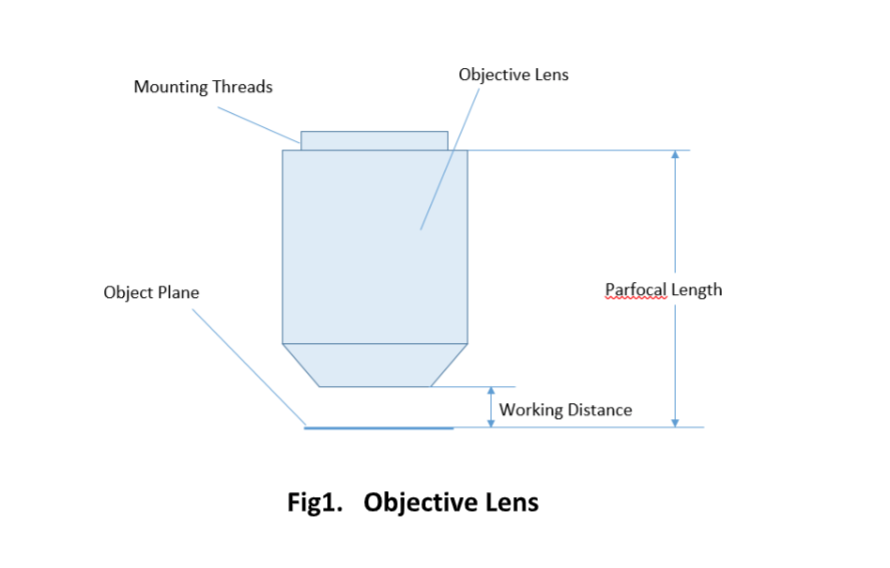
Important specifications are marked on the barrel of the objective, so students or researchers can easily identify the properties of an objective and determine the optical performance and working conditions for proper use. Figure 1 shows a diagram of an objective lens. A detailed discussion of the objection specifications is provided below.
Is your child shaking some salt onto her green beans? Before they dig in, encourage them to take a peek at a couple of those salt crystals. What do the granules look like up close? For that matter, what do the beans look like up close? (If they really can’t wait, though, let them eat—science can be put on hold for a growling tummy.)
Choosing the right child care center is important, and we know life can be hectic. Take a quick virtual tour and see our center from the comfort of home!
For keeping the objective at the proper position, there are mounting threads on almost all objectives. Commonly used mounting threads include RMS, M25 x 0.75, M26X 0.706, M32 x 0.75.
Function of the objective lensin microscope
“At this age, children’s critical-thinking skills and fine-motor skills have developed to the point where they can start using simple tools,” says Meg Davis from KinderCare’s Education team. Magnifying glasses help kids see things they’ve never seen before, like small insects close-up. It opens up a whole new world to them, which they find pretty amazing!
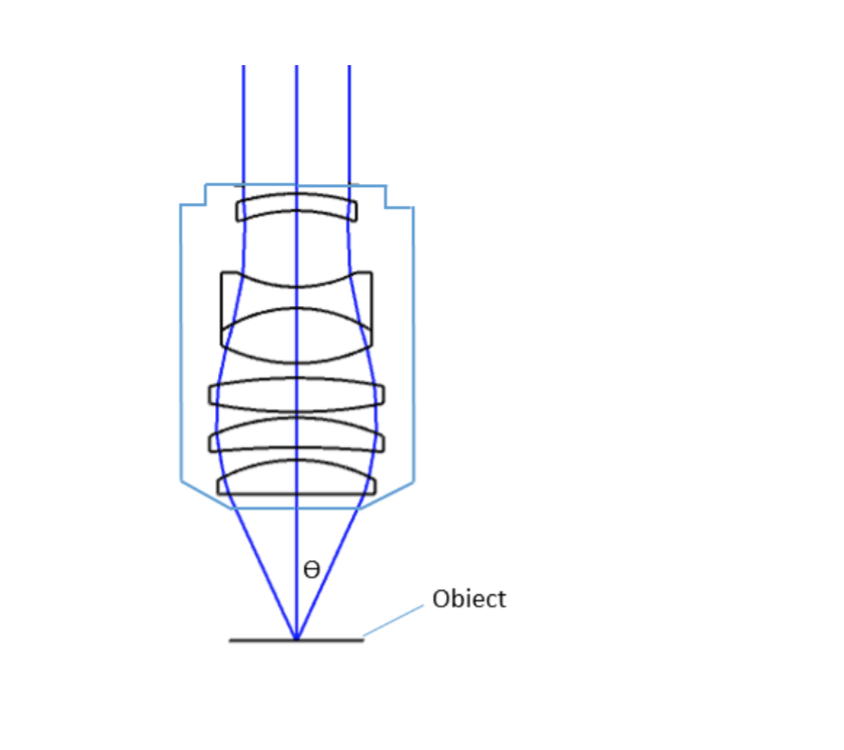
where θ is the maximum 1/2 acceptance ray angle of the objective, and n is the index of refraction of the immersion medium. Figure 2 shows the ray angle θ of an infinity-corrected objective.
Objectives are complex multi-element lenses. For any given application, careful consideration of the optical parameters and specifications is necessary. In many cases, custom-designed objective assemblies provide the best-fit solution for meeting all the requirements of a specialized application. Custom parameters may include antireflection coatings, chromatic focus shift, working distance, image quality (MTF and spot size), lens mount, glass window thickness, and field of view, among others.
Typesof objectivelenses
With magnifying glasses and journals, children work together to examine whatever they find—from leaves and soil to pebbles and ants. They then write about or draw pictures of what they see—which gives these young scientists a literacy-skills boost.
Next time you’re snuggling with your kids under your favorite warm blanket, grab the magnifying glass to examine the fibers keeping the blanket together. Is there a pattern to the fibers? Once they’ve had an eyeful, encourage them to take a look at other fabrics around the room to compare—like maybe their T-shirt, socks, or even the couch itself!
We’re here to answer your questions – from tuition rates to our safe learning environments. Tell us about yourself and what you want to know.
Young children’s brains are hardwired for exploration and observation—two things that just so happen to be early science skills. By around age four or five, however, their scientific abilities really start to take off because they’re old enough to start using cool scientific tools.
While the simplest of microscopes is simply a magnifying glass with a single lens, compound microscopes used today are highly complex devices with a carefully designed series of lenses, filters, polarizers, beamsplitters, sensors, and perhaps even illumination sources. The exact combination of optical components used will depend on the application of the microscope; the wavelength of light with which it is intended to be used, and the resolution and magnification required in the final image.
If you don’t have a magnifying glass in your home, you can find one pretty cheap and explore what other things look like up close. Make things even more scientific by handing over some crayons and paper so your child can write down what they discover. (Feel free to give them a little white smock to really set the scene.)
High powerobjective lens
At KinderCare, we’re committed to building warm, welcoming and supportive classrooms for children of all abilities, backgrounds and experiences.
Many objectives are designed to be used with a cover glass. Using an incorrect coverslip thickness can greatly reduce the optical performance of a microscopy system.
High powerobjectivemicroscopefunction
The ocular lens, or eyepiece, is also an optical assembly rather than a single lens, but it is typically more simple than the objective. Often it is composed of two lenses: a field lens and an eye lens. The design of the ocular lens determines the field of view of the microscope, as well as contributing to the total magnification of the system.
That’s why this week in our centers, we’re taking kids out into the fresh spring air to take a closer look at the natural world popping up around them—and when we say a closer look, we mean really close.
Numerical aperture definition: a measure of the resolving power of a microscope, equal to the index of refraction of the medium in which the object is ...
Stage microscopefunction
Field of View is the area of the object that can be imaged by a microscopy system. The size of the field of view is determined by the objective magnification or focal length of the tube lens for an infinite-corrected objective. In a camera system, the field of view of the objective is related to the sensor size.
If you have questions about tuition and openings or want to schedule a tour, tell us about yourself and we will contact you shortly.
Function ofstage
A microscope objective is an important component of a microscopy or imaging system for a range of science research, biological, industrial, and general lab applications.. An objective lens determines the basic performance of an optical microscope or imaging systems and is designed for various performance needs and applications. It is located closest to the object and is an important component in imaging an object onto the human eye or an image sensor.
The 1.5mm allen key is an essential tool in various industries, known for its precision and ability to fit into tight spaces. This tool falls under the category ...
At Shanghai Optics, we design and manufacture custom objectives and imaging systems to support our customers’ needs in many industries, including medical, biomedical, machine version, scientific research, and metrology, etc. Taking the client’s budget and precision requirements into consideration, our experienced engineering team ensure that each design can be manufactured at a reasonable cost and the optical performance is being met based on fabrication, assembly, and alignment tolerance analysis.
Rotate an Image Counterclockwise. Read an image into the workspace. I = imread("circuit.tif");. Rotate the image 35 degrees counterclockwise using bilinear ...
Each microscope objective is itself a complex assembly of lenses, and besides contributing to the magnification, it is the objective lens which determines the resolution power of the microscope. An objective lens can also provide optical aberration corrections. A reflective objective, for instance, includes two mirrors within the assembly. These mirrors can focus laser light as well as provide chromatic corrections.
Water and its various forms are intriguing to kids—so encourage your child to take a closer look at ice for a real “wow” experience. You both might be dazzled by the ice-crystal patterns and the shades of white and blue. Turns out a cube is pretty complex! Extend the learning even further by talking about the ways water can turn from liquid to ice and back again!
A simple magnifier (magnifying glass), works when the object to be examined is situated within focal length of the magnifier lens, enabling larger virtual image is produced. This type of magnifier is very limited in both resolution and magnification. A compound microscope, on the other hand, uses a relay lens system instead of the single lens, and since each lens component can contribute magnifying power, the result is greatly increased capability.
The ocular lens, located at the top of a standard microscope and close to the sensor (receiving eye) receives the real image from the ocular lens, magnifies the image received and relays a virtual image to the sensor. While most eyepieces magnify 10x, there are some which provide no magnification and others which magnify as much as 30x. The magnification power of the microscope can be calculated by multiplying the magnification power of the eyepiece, or ocular lens, by the magnification power of the objective lens. For example, an objective lens with a magnification of 10x used in combination with a standard eyepiece (magnification 10x) would project an image of the specimen magnified 100x.
The parfocal length is the distance between the objective mounting plane and the specimen / object. This is another specification that can often vary by manufacturer.
C Diener · 2016 · 10 — Wohingegen höhere Ausprägungen im subjektiven Wohlbefinden einerseits mit einer (leicht) besseren Selbsteinschätzung der kognitiven Leistungsfähigkeit ...
A range of c-mount camera lenses compatible with all EtherLynx cameras when paired with the correct lens mounts.
Most objectives are designed to image specimens with air as the medium between the objective and the cover glass. However, for achieving higher working numerical apertures, some objectives are designed to image the specimen through another medium such as special oil with a refractive index of 1.51.
Two major lens components—the objective lens and the ocular lens, or eyepiece—work together to project the image of the specimen onto a sensor. This may be the human eye or a digital sensor, depending on the microscope setup.
Yes get anti reflective lenses. My preferred brand is Crizal Sapphire but there's others. Some are super cheap so make sure you get a higher end ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500