Stolen Camera Finder - find your photos, find your camera - cam finder
Define polarizationin physics
Define polarizationin communication
If you have any questions about using immersion oil with your microscope, contact Microscope World. Shop microscope immersion oil here.
Define polarizationin chemistry
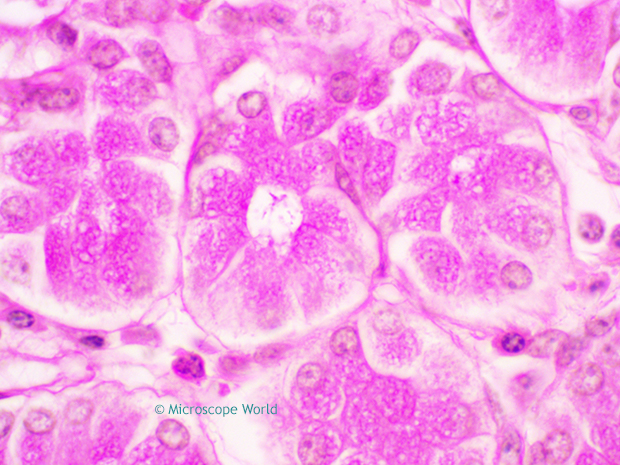
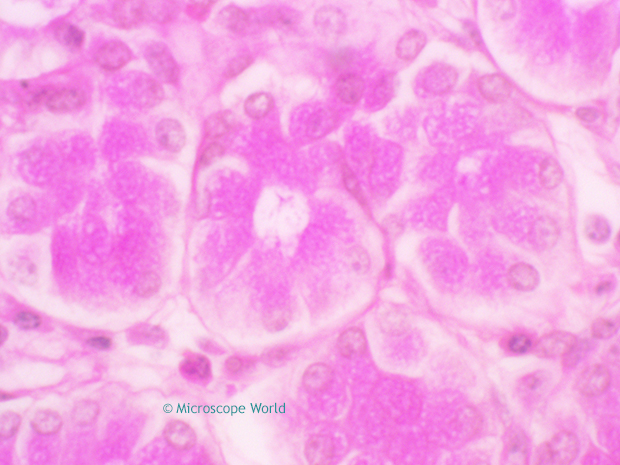
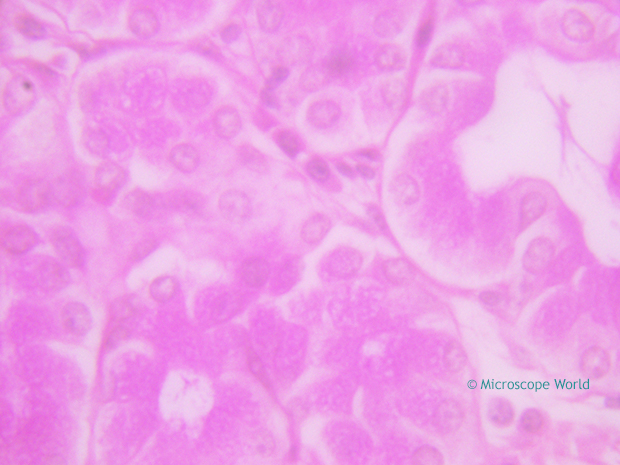
Basically when using lower magnification microscope objective lenses (4x, 10x, 40x) the light refraction is not usually noticeable. However, once you use the 100x objective lens, the light refraction when using a dry lens is noticeable. If you can reduce the amount of light refraction, more light passing through the microscope slide will be directed through the very narrow diameter of a higher power objective lens. In microscopy, more light = clear and crisp images. By placing a substance such as immersion oil with a refractive index equal to that of the glass slide in the space filled with air, more light is directed through the objective and a clearer image is observed. Take a look at the images captured below. The images were captured using the UX1 microscope with the 100x Achromat objective lens and the 100x Plan Achromat objective lens. Observation was performed dry and with immersion oil. Notice the difference in image quality between the images captured dry versus those captured with immersion oil.
When light passes from a material of one refractive index to another (for example: from glass to air), it bends. In the space between the microscope objective lens and the slide (where air is), light is refracted, the light scatters and it is lost. The refractive index of air is approximately 1.0, while the refractive index of glass is approximately 1.5. When light passes through both glass and air it is refracted. Light of different wavelengths bends at different angles, so as objects are magnified more, images become less distinct.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500