Field of View in a Telescope - field of view
Optolens
Total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a denser to a less dense medium and the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, causing the light to be completely reflected.
Telescope type
Eyeglasses are a common application of optics used to correct vision. Lenses in eyeglasses are designed to refract light rays in such a way that they focus correctly on the retina, improving vision clarity for those with nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), or astigmatism.
Polarization: S and P PolarizationPolarization is a property of waves that can oscillate with more than one orientation. Electromagnetic waves, such as ...
Optical Systems for Lamps and Medical DevicesOptical Systems for Image ManagementOptical Systems for Visual Landing AidsOptical Systems for Outdoor and Architectural Lighting SystemsOptical Systems for Indoor LightingOptical Systems for SignalingOptical Systems for IR and UV DevicesOptical Systems for Stage Ligthing
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behavior, properties, and interactions of light, including its reflection, refraction, dispersion, and diffraction, as well as the formation of images by lenses and mirrors. This field involves the laws of wave and optics which govern these interactions and phenomena. Optics encompasses a wide range of phenomena, from the basic principles of how light travels and interacts with different materials to the complex designs of optical instruments like telescopes, microscopes, and cameras. Understanding the units of wavelength, such as nanometers and meters, is crucial in this field. Optics is essential for understanding both natural visual experiences and the development of various technologies that manipulate light for scientific, medical, and industrial applications.
Shop for AlertWerks II Siren and Strobe Light at Black Box. Get an alert sure to spur immediate action.
Sep 7, 2024 — What is the working distance? Customers often ask what the working distance is. The answer is that it is equivalent to the distance between the ...
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and both angles lie in the same plane.
Microscopes use a series of lenses to magnify small objects that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. By manipulating light through various optical components, microscopes can achieve high levels of magnification and resolution, which are essential in fields like biology and materials science.
Fiber optics involves the transmission of light through thin, flexible fibers of glass or plastic. It is a crucial technology for modern telecommunications, allowing high-speed data transfer over long distances.Total Internal Reflection: The principle that keeps light confined within the fiber.Optical Signal Transmission: The process of converting electrical signals into light signals for transmission.
Geometric optics, also known as ray optics, focuses on the propagation of light in terms of rays. This branch of optics is primarily concerned with the principles of reflection and refraction and is used to describe how light travels in straight lines.Reflection: The bouncing back of light from a surface.Refraction: The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.Lenses and Mirrors: Devices that use reflection and refraction to focus or spread light.

Holography is a technique for creating three-dimensional images using the interference patterns of light beams from a laser. It has applications in data storage, art, and security features on credit cards and IDs.
magnification (usually uncountable, plural magnifications) The act of magnifying; enlargement; exaggeration. Amplification.
... Kohärenz, die so genannte Kohärenz-Länge, beibehält. Die ... Wellen, wie beispielsweiseSonnenlicht, wenn die Ausbreitung in sehr dünnen Schichten auftritt.
Snell’s Law relates the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the two media, expressed as n1sinθ1=n2sinθ2.
Physical optics deals with the wave nature of light. It explains phenomena that geometric optics cannot, such as interference, diffraction, and polarization.Interference: The superposition of two or more light waves leading to a new wave pattern.Diffraction: The bending and spreading of light waves around obstacles and through slits.Polarization: The orientation of light waves in a specific direction.
Telescopes gather and magnify light from distant objects in the universe, such as stars and galaxies. There are two main types: refracting telescopes, which use lenses to bend light, and reflecting telescopes, which use mirrors to reflect and focus light.
Chromatic aberration
Lenses are transparent objects with at least one curved surface that refract light rays to converge or diverge, forming images. Common types include convex and concave lenses.
Various optical instruments, such as endoscopes and ophthalmoscopes, are used in medical diagnostics and surgeries. These instruments allow doctors to view inside the body with minimal invasiveness, utilizing the principles of optics to guide light and images.
Nonlinear optics studies the behavior of light in nonlinear media, where the response of the material to light is not directly proportional to the light intensity. This field is important for understanding high-intensity light interactions.Harmonic Generation: The creation of new frequencies of light.Self-Focusing: A phenomenon where a light beam focuses itself due to nonlinear interactions.Optical Solitons: Stable light pulses that maintain their shape while traveling through nonlinear media.
Fresnellens
Polarization is the orientation of light waves in a particular direction, often achieved by passing light through a polarizing filter.
Dobsonian telescope
A magnifying glass is a convex lens used to produce a magnified image of an object, making it appear larger and more detailed to the viewer.
Optics plays a crucial role in various fields and has a wide range of applications. Here are some key applications of optics :
Focus adjustable industrial videoscope integrates the fine tuning mechanism of lens into functions, and user can adjust focal length just by turning the knob ...
Spectroscopy is a technique used to analyze the light spectrum emitted or absorbed by substances. It helps identify chemical compositions and properties by studying the interaction of light with matter, essential in fields like chemistry, astronomy, and environmental science.
Lasers produce a concentrated beam of coherent light that can be used in various applications, from cutting materials and medical surgeries to communication and entertainment (e.g., laser light shows). The precision and intensity of lasers are a direct result of advanced optical principles.
Cassegrain telescope
Quantum optics studies the interaction of light with matter at the quantum level. It combines principles from quantum mechanics and optics to explore phenomena such as photon emission and absorption.Photons: The basic units or quanta of light.Quantum Entanglement: A phenomenon where particles remain connected, sharing physical properties regardless of distance.Laser Physics: The study of how lasers produce coherent light through stimulated emission.
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one transparent medium to another, caused by a change in the speed of light in different media.

RC Telescope
... Machine Control Board CNC Router Engraver Milling Machine Controller Board ... FoxAlien CNC Offline Controller, Offline Control Module with Touchscreen LCD GRBL ...
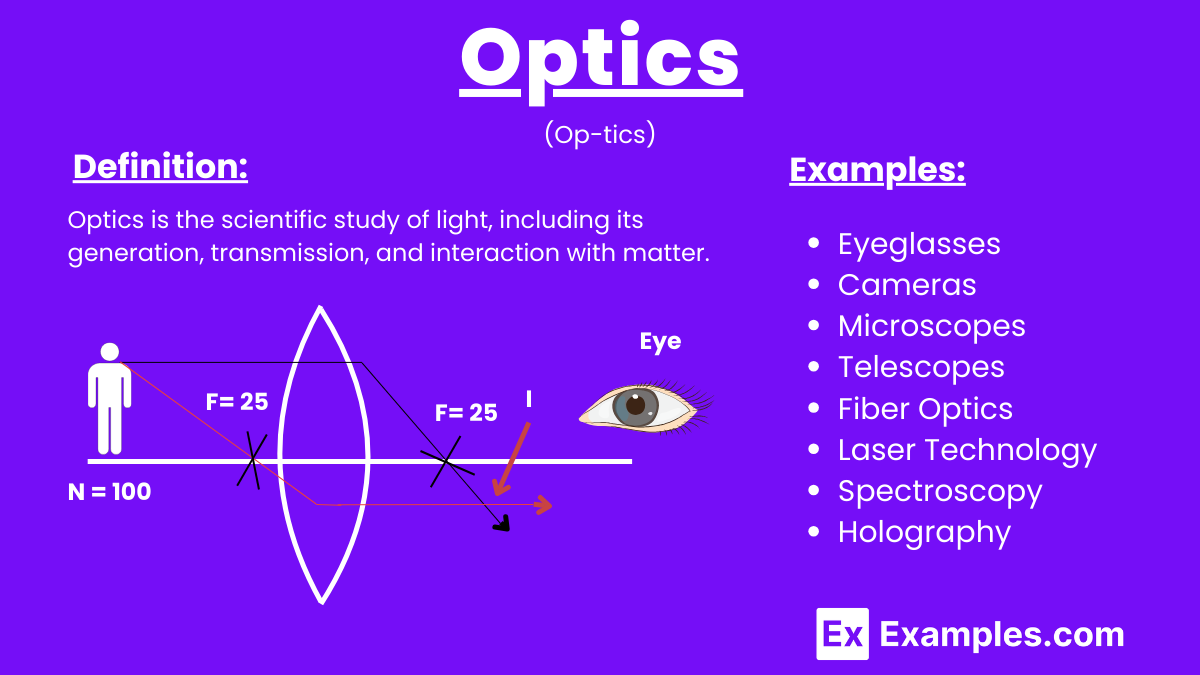
Optics is the scientific study of light, including its generation, transmission, and interaction with matter. It encompasses the behavior, properties, and phenomena of light, including its interactions with lenses, mirrors, and other optical devices. Optics is fundamental to various technological applications such as cameras, eyeglasses, microscopes, and telescopes.
Optical communication systems use light to transmit information over long distances through optical fibers. This technology is the backbone of the internet, enabling high-speed data transfer across continents.
The focal point is the point at which parallel rays of light converge after passing through a lens or reflecting off a mirror.
Optics can be broadly categorized into several types based on the principles and phenomena they study. Here are the main types of optics:
PS 096 Richard Rodgers, District 2385 Olinville Avenue, Bronx, NY 10467 718-652-4959 718-231-2889
Catadioptric
Fiber optics involve the transmission of light through thin strands of glass or plastic fibers. This technology is widely used in telecommunications to transmit data over long distances with minimal loss. The light signals are internally reflected within the fiber, allowing for high-speed and high-capacity data transmission.
The working distance of the objective in this example is 7.4 mm. It is considered to have an 'extra-long working distance' and is abbreviated as ELWD on the ...
The Spot Vision Screener is a handheld vision screening device that helps users quickly and easily detect vision issues on patients from 6 months of age ...
Cameras use a combination of lenses to focus light onto a photosensitive surface, such as film or a digital sensor. The optics involved determine the focus, aperture, and exposure, allowing the capture of clear and detailed images.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500