Sony A7 mark II body (body a72 cũ) - sony a72
FOV meaningSlang
This is equation 18 in the Application Note linked above. In this parametric equation, rmax is the radius of this circle (any subsequent shape created by this setup is enclosed by this radius), T is the middle thickness of the fist prism, T' is the effective thickness of prism 2 after the deviated beam travels through it, Φi is the angle created from the beam's incidence on the first surface of the fist prism according to Snell's Law, Φp is the resulting angle the beam takes inside the prism relative to the first surface's normal according to Snell's Law, z is the distance from the second surface of the second prism to the scanning surface, S is the distance between the prisms, and Φo is the beam angle relative to the original optical axis after exiting the second surface of the first prism.
An Application Note was prepared to describe this process in further detail, and will be referenced periodically here. For a full download of the Application Note, click the button at the upper right of this tab. To the upper right is also a a download for an Excel spreadsheet which can be used to model a Risley Prism Scanner.
FOV meaningin gaming
This is equation 21 in the Application Note linked above; please reference that Application Note or the accompanying spreadsheet for the definitions of these variables. As an example, the long-exposure photograph to the right shows two wedge prisms being used to trace out a spiral. This was realized by first setting the beam to be undeviated, and then having the prisms rotate in the same direction, with one prism set to rotate 0.5 deg/s faster than the other. This, and many other shapes, can be created on the "Third Approx." sheet of the downloadable Excel sheet above. To create this spiral, try inputting 25 deg/s to ω1 (rotation speed of prism 1), 24.5 deg/s to ω2 (rotation speed of prism 2), and 80 seconds to t (run time), with a Δθ (home position offset) of 180 degrees.
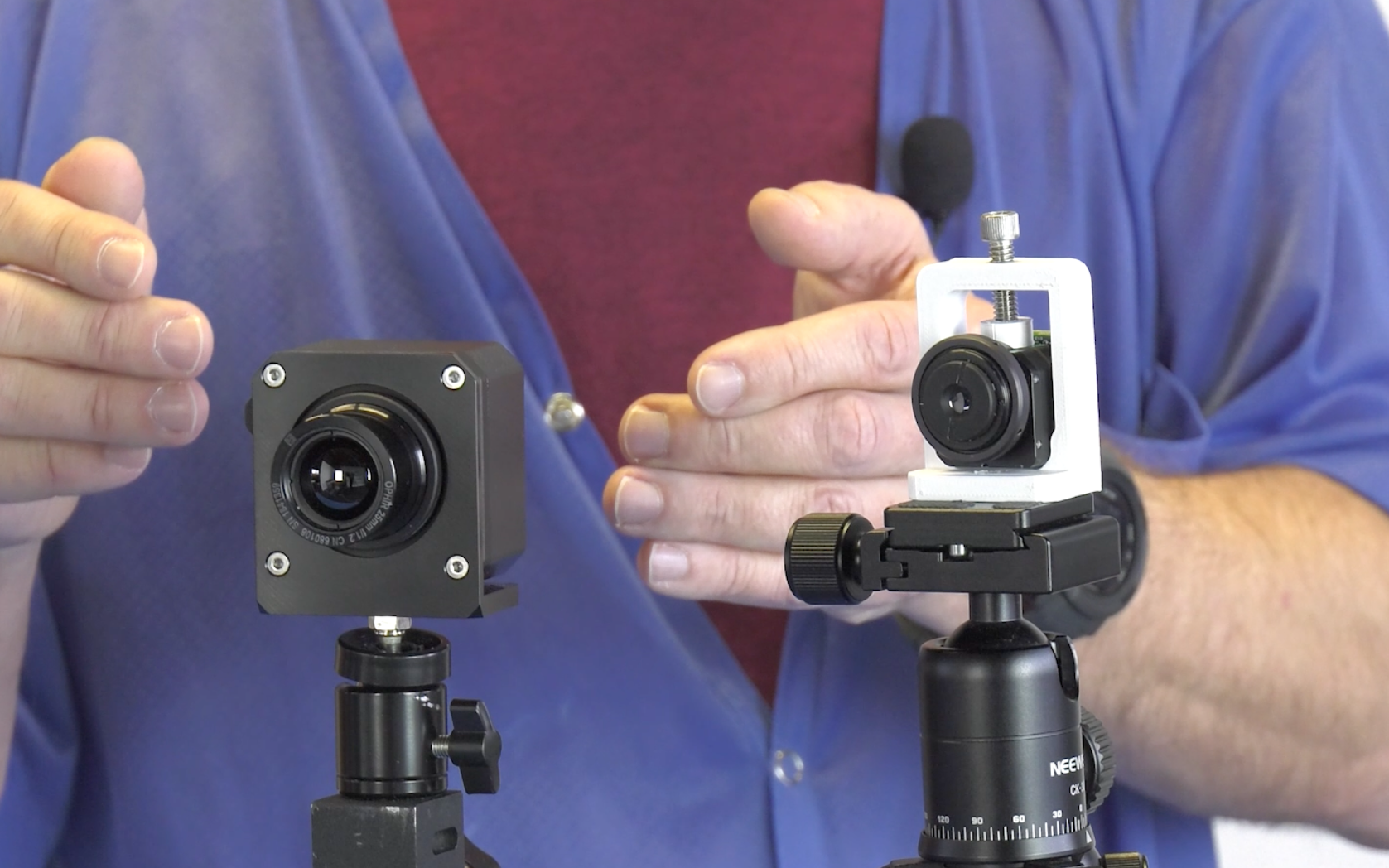
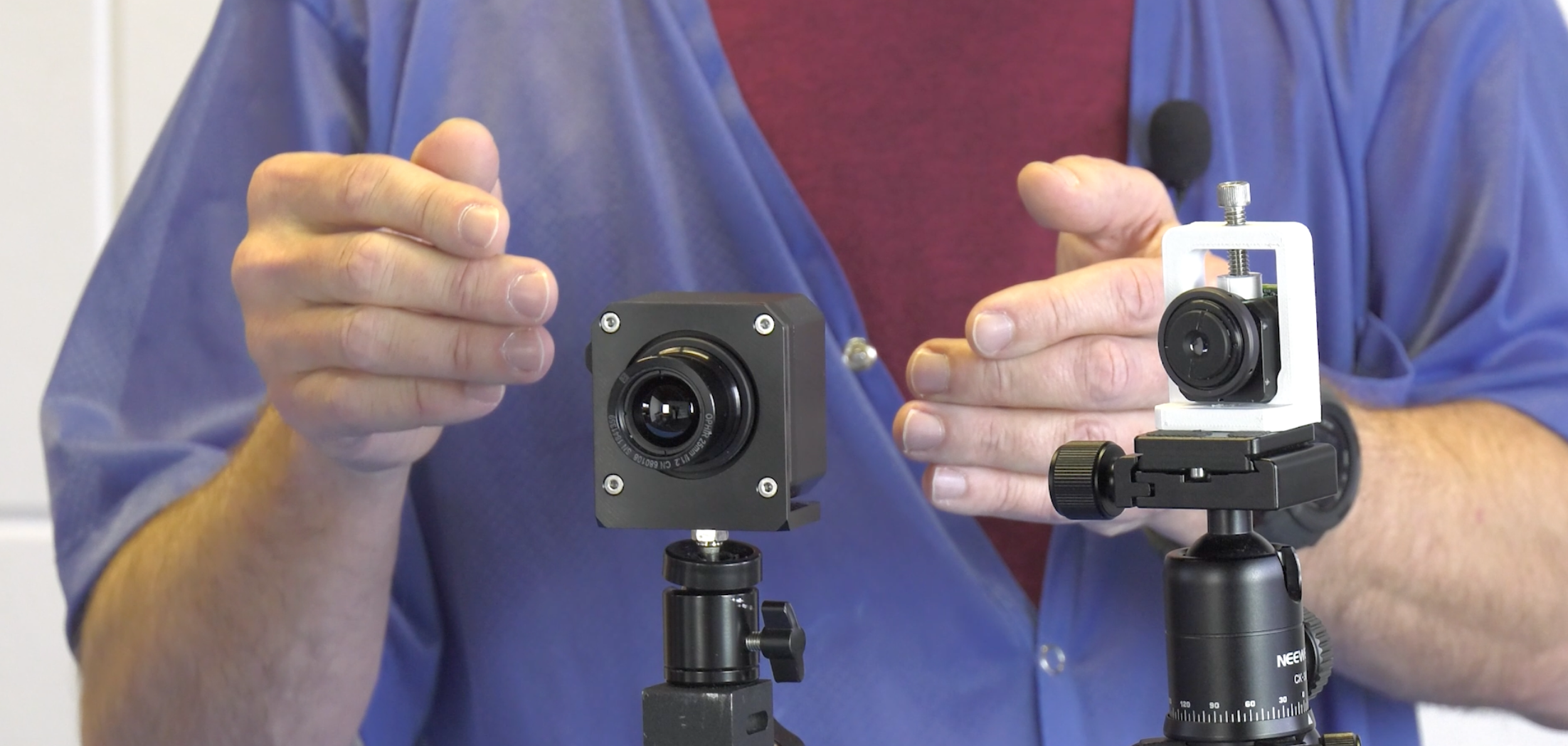
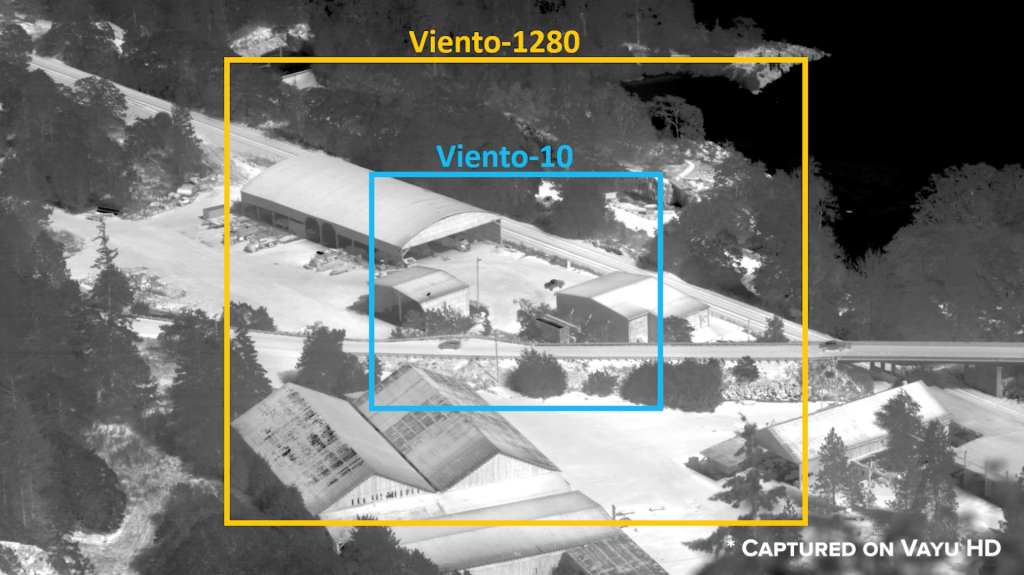
There are two knobs that we have that we can turn to adjust this. One is the size of the detector array in the system, and the other is the focal length of the lens that we put on the system. Let’s talk about detector array size first. Let’s assume that we have the same focal length lens on this on these two cameras to take that out of consideration. This is the Viento-10, which has a 640 pixel array of ten micron pixels. This is the Viento 1280 (figure 1), which has the same ten micron pixels, but it has twice as many pixels in width, 1280 pixels in width. So its detector array is twice as large as the Viento-10 with a detector array twice as large as the Viento- 10 (figure 1). The Viento 1280 has roughly twice the field of view as the Viento-10 (figure 2). Notice so far I’m just talking in terms of the detector array with 640. In the case of the Viento-10, 1280 pixels in the case of the Viento 1280 detector arrays usually have a different height than they do width. That means they also have a vertical field of view that can be calculated. But for simplicity of this discussion, I’m just going to talk about the horizontal field of view.
Field of viewmeaning
Tracing a Spiral with Two PrismsIt can be shown that a large variety of shapes can be traced while rotating the two prisms at constant speeds. These shapes are dictated by the equation:
Tracing a Circle with One PrismFor this application, only one prism was mounted in a rotation mount. The incoming beam was deviated off axis by the wedge prism. Once the rotation mount was activated, the wedge prism was spun about the optical axis, which caused the deviated beam to trace out a small circle, as shown in the long-exposure photograph to the right. The radius of this circle can be calculated as:
FOV meaningFortnite
Field of view depends on the application. If we decrease the focal length, we will increase the overall field of view, but we will also increase that number I talked about earlier, the instantaneous field of view, the IFOV. That has the effect of lowering the spatial resolution down at the level of the individual pixel. That may be okay for some applications, situational awareness applications that just rely mostly on a big picture view of a scene, for example. On the other hand, there can be applications where you want a large field of view, but you also want to maintain spatial resolution. In that case, the way you would increase field of view would be to increase the detector array size. That would provide a larger field of view while maintaining the same spatial resolution as before. These are the kinds of considerations that we can help you work out in deciding how to use an infrared imaging system in which system to choose.
FOVcamera
This is equation 9 in the Application Note linked above. In this equation r' is this circle's radius, S is the distance from the last surface of the prism to the scanning surface, T is the center thickness of the prism, Φo is the beam angle relative to the original optical axis after exiting the second surface of the prism, Φi is the angle created from the beam's incidence on the first surface of the prism according to Snell's Law, and Φp is the resulting angle the beam takes inside the prism relative to the first surface's normal according to Snell's Law.
Welcome back to Ask an Expert. I’m Stan Voynick, Chief Technology Officer at Sierra-Olympia Technologies. Today, we’ll be discussing field of view and instantaneous field of view, how they work together to form the thermal images in airborne systems, security and surveillance, optical gas imaging, and other thermal imaging applications. Three of the most important factors we consider when we’re designing a thermal imaging system are field of view, aperture and spectral response. I’ll be going over some questions about Field of View and closely related cousin instantaneous field of view.
Field of view definition microscope
If we were to look at the Vayu HD with a 50 millimeters lens and a 25 millimeter lens, the 25mm lens has one half the focal length of the 50mm, and therefore again, it will roughly double the field of view if I install the 25mm lens instead of the 50 millimeters lens.
Field of view human eye
Tracing a Circle with Two PrismsFor this application, the rotation mounts are set so that the wedges of both prisms are aligned to the home position, where both prisms' thickest sections are vertical. Since each prism will deviate the beam by the deviation angle, the total beam deviation for two prisms with the wedges aligned will be approximately twice the size. If both prisms are rotated at the same rate and in the same direction, the beam will trace out a circle which is approximately twice the size of the circle traced out by a single prism. The long-exposure photograph to the right was taken with the prism assembly at the same distance from the screen as the one-prism circle above. Notice that the circle in the two-prism case is about twice the diameter of the one formed with one prism. The radius of this circle can be calculated as:

By pressing submit, your feedback will be used internally to improve Sierra-Olympia products and services. Privacy Policy
Field of view describes the entire extent of the whole image that is being detected by an infrared thermal imaging system. It can be stated in terms of the angle, the extent of the angle, starting from your imager out into the scene. Or it can be described as the linear extent of the scene at some distance from the imager. Instantaneous field of view, or IFOV, as we call it, is the angle subtended by just a single pixel in your detector array out into the scene. This can be calculated as the pixel size divided by the focal length.

Introduction and SetupWedge prisms are designed to be used, either individually or in a pair, for beam steering applications. This is done by individually controlling the rotation of each prism using our PRM1Z8 motorized rotation stages. The tables below correspond to either the imperial or metric product list for the configuration pictured to the right. Clicking on the item number will bring up a pop-up window with more information about that component.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500