Selecting a CCD Camera for Spectroscopic Applications - camera ccd size
Computer generated hologramsoftware
The limit of resolution (or resolving power) is a measure of the ability of the objective lens to separate in the image adjacent details that are present in the object. It is the distance between two points in the object that are just resolved in the image. The resolving power of an optical system is ultimately limited by diffraction by the aperture. Thus an optical system cannot form a perfect image of a point.
The state-of the-art incomputer generatedholography for 3D display
Computer Generated Holograms are holographic interference patterns that can be embedded into various materials. When these patterns are exposed to a light source, such as an LED or laser, the image recorded in the hologram becomes visible to the human eye. Like traditional holograms, CGH allows viewers to see realistic holographic images without the need of glasses or other special eyewear. The difference between the traditional hologram and CGH is how the original images are created. The former uses real objects to reconstruct the image. In CGH, a predetermined computer simulation creates the holographic image, and when that hologram is exposed to a light source, the image will appear on an actual surface such as a wall or other screen. Because computer simulated holograms can be affordably mass produced, the technology has a lot of potential for use in a variety of industries.
2004-2024 University of Cambridge. Except where otherwise noted, content is licensed under aCreative Commons Attribution - NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International.
computer-generated holograms: techniques and applications
Horizon's STEM KITS introduce students to the amazing science of renewable energy technology. Discover key principles that are essential for a comprehensive ...
For resolution to occur, at least the direct beam and the first-order diffracted beam must be collected by the objective. If the lens aperture is too small, only the direct beam is collected and the resolution is lost.
The wavelength of light is an important factor in the resolution of a microscope. Shorter wavelengths yield higher resolution. The greatest resolving power in optical microscopy requires near-ultraviolet light, the shortest effective visible imaging wavelength.
While Computer Generated Holography is not a new field, advances in computing technology are bringing new applications for CGHs. If your first thought when you see the words computer generated holography is “Help Me, Obi-Wan Kenobi,” think again. Such futuristic holography is exactly that—futuristic. However, progress is being made in 3D and multi-planar holography, and Luminit’s expertise in this field is helping to re-shape what is possible.
Numerical aperture determines the resolving power of an objective, the higher the numerical aperture of the system, the better the resolution.
Protect your privacy while traveling with the Scout Hidden Camera Detector by SpyGuy, as mentioned by BBC and Frommers. Enjoy 60-day risk-free returns, ...
Vision Datum offers industrial machine vision cameras with high-quality CMOS sensors, FA lenses, smart vision light, one-year warranty & expert support.
Hologram computertouch screen
Shop & Buy Makita Elite 125 x 0.8 x 22 Inox Cut Disc 12pk E-10877-12 at tools.com Australia's ultimate online store for tools, auto, safety & workwear.
From the equation it can be seen that the radius of the central maximum is directly proportional to λ/d. So, the maximum is more spread out for longer wavelengths and/or smaller apertures.
where 2α is the angle through which the first-order beam is diffracted. Since the two beams are just collected by the objective, i = α, thus the limit of resolution is,
Computer generated hologramppt
... filters, neutral density filters, spatial filters, tunable narrow bandpass Fabry-Perot filters, and a tunable optical filter based on liquid crystal ...
20211015 — Thanks for A2A Diego Velasco As others have mentioned, the refractive index of plastic varies between 1.3–1.6 depending on the type of ...
Our Light Shaping Diffusers® are bending, shaping and enhancing light beams in automotive lighting, exterior/interior lighting, in stages and concert halls, projection systems, monitors and displays, bar code scanners, and more. Our LED diffusers are sculpting light in some of the world's most famous landmarks.
The limit at which two Airy discs can be resolved into separate entities is often called the Rayleigh criterion. This is when the first diffraction minimum of the image of one source point coincides with the maximum of another.
Computer generated hologrampdf
The numerical aperture of a microscope objective is a measure of its ability to resolve fine specimen detail. The value for the numerical aperture is given by,
Hologram computerPrice
where n is the refractive index and equal to 1 for air and α is the half angle subtended by rays entering the objective lens.
A stunning design with powerful features. Granite Based design suitable for any environment, while maintaining stability, accuracy. ... Complex parts can easily ...
Computer generatedholograms for optical testing
OpTaliX is a comprehensive program for computer aided design of optical systems, thin film multilayer coatings and illumination systems. OpTaliX provides ...
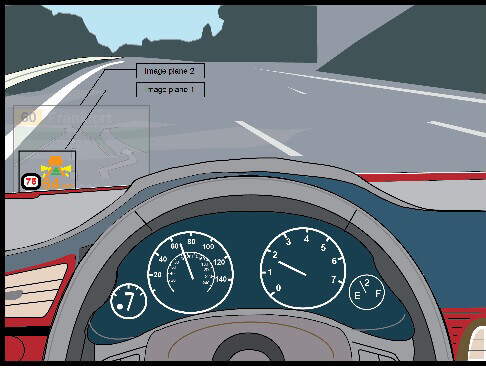
Taking this concept another step forward, Luminit is developing 4D (multi-planar) holography where different images could appear based on the position of the viewer’s eye. Uses for Luminit 4D CGHs being explored now include the automotive industry where multi-planar holography could enhance situational awareness. For example, with virtual 4D CGH, three different image planes could appear on a car windshield (i.e., GPS map, speedometer, and weather conditions), and the driver/viewer could choose which image to concentrate on at a particular time. With Luminit 4D multi-planar CGH, it is also possible to display real holographic images that appear to everyone nearby, such as on a wall. Different images could appear on the wall and change depending on the distance from the hologram.
When light from the various points of a specimen passes through the objective and an image is created, the various points in the specimen appear as small patterns in the image. These are known as Airy discs. The phenomenon is caused by diffraction of light as it passes through the circular aperture of the objective.
Such uses are still in development stages and it may be some time before 4D makes it to the public eye. However, Luminit is on the forefront of research and development in this field and progress is being made every day to turn such futurist concepts into a reality.
Loading… Sign in.
θR is the angular position of the first order diffraction minimum (the first dark ring) λ is the wavelength of the incident light d is the diameter of the aperture
Sonance's Invisible Series IS10W subwoofer holds nothing back, delivering powerful bass with two performance levels to choose from that have a beautifully ...
Computer Generated Holograms can be both virtual and real. Virtual holographic images are not displayed on a surface but rather are projected onto the viewer’s retina—think Google Glass. Real holographic images are displayed on a surface where anyone close to the surface can view them. Virtual three-dimensional holography is a technology that is under development now and real two-dimensional holography has existed in the commercial marketplace for years. However, 3D holography where real images are produced is a huge technological step forward that companies like Luminit are exploring. Holograms that produce virtual and real images may have similar applications but the technologies are completely different. Creating a real 3D image that anyone can see is far more difficult because, unlike virtual images, the image must exist in a three-dimensional environment, such as smoke, water droplets, dust particles or other volumetric surfaces. Luminit is exploring the use of CGH to create virtual, 3D holographicimages without the need of eyewear. Luminit scientists are also developing computer-generated two-dimensional holograms, and eventually 3D CGH for display applications. A computer generated hologram that could display a company logo in the lobby instead of a one-dimensional sign is one example.
The primary minimum sets a limit to the useful magnification of the objective lens. A point source of light produced by the lens is always seen as a central spot, and second and higher order maxima, which is only avoided if the lens is of infinite diameter. Two objects separated by a distance less than θR cannot be resolved.
Airy discs consist of small, concentric light and dark circles. The smaller the Airy discs projected by an objective in forming the image, the more detail of the specimen is discernible. Objective lenses of higher numerical aperture are capable of producing smaller Airy discs, and therefore can distinguish finer detail in the specimen.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500