Round Brackets - Punctuation - small brackets
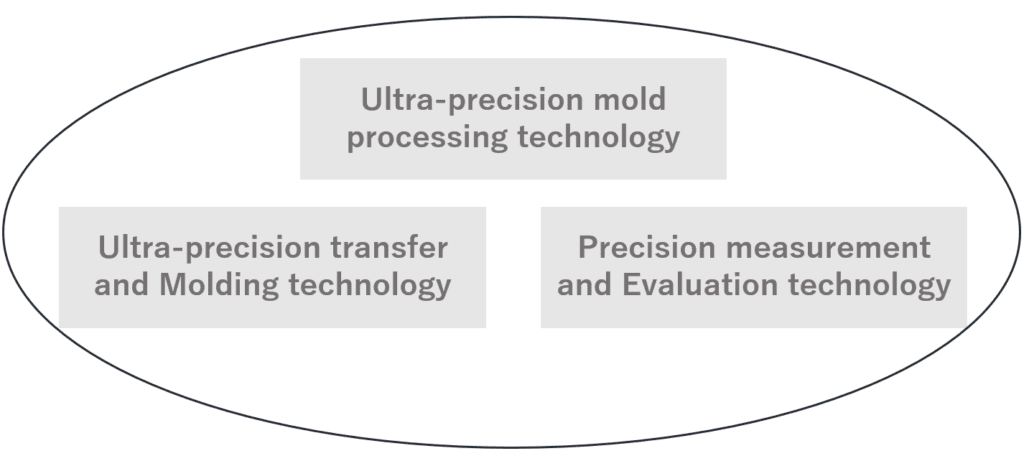
The method of manufacturing aspherical lenses by transferring and molding the aspherical shape of the mold onto the lens requires three technologies: ultra-precision mold processing technology, ultra-precision transfer and molding technology, and precision measurement and evaluation technology for these surface shapes.
If you are thinking about something like, “If only there was a product like this…”, or, “Is it possible to do these kind of things with lenses?”, Optical Design Technology Navigator, a website operated by a group of optical design professionals, is the place to go. If you have any questions about optical design, please feel free to contact us at Optical Design Technology Navigator.
Aspherical lens photography
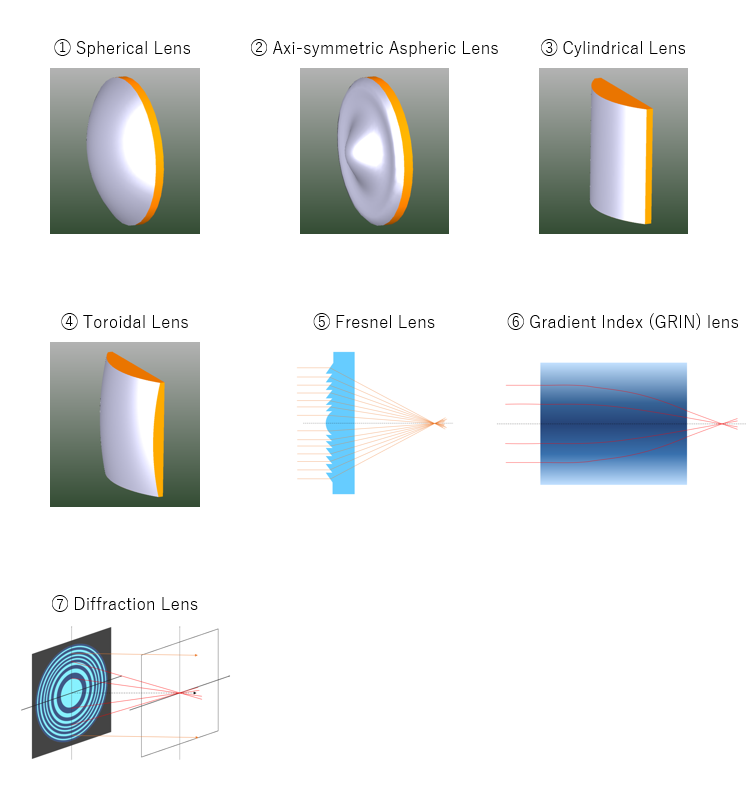
On the other hand, in the case of ⑥, the refractive index inside the lens is not homogeneous but distributed, and in the case of ⑦, light is focused and diverged by using the diffraction effect on the surface instead of refraction.
Aspherical surfaces are classified into two categories: axi-symmetric aspherical surfaces, which have axial symmetry (rotational symmetry) with respect to the lens optical axis, and aspherical surfaces, which do not have axial symmetry. Each type of aspheric surface has its own characteristics.
In this section, we will introduce the advantages and disadvantages of axi-symmetric (rotationally symmetric) aspheres in imaging optics. There are three major advantages.
At Optical Design Technology Navigator, we use state-of -the-art ultra-precision processing machines to process aspheric surfaces on a sub-micron order, transfer these aspheric surfaces using molding technology that incorporates a high level of know-how, and then transfer these aspheric surfaces into an ultra-precision 3D mold.
In imaging optics, multiple spherical lenses are used in combination to reduce aberrations such as image blur and distortion. By using aspherical lenses, it is possible to reduce the number of lenses while maintaining the same performance. For example, you can achieve the same performance of an 5-spherical-lens optical system with a total of 4 lenses using 2 spherical lenses and 2 aspherical lenses.
In this section, we will explain the features, advantages / disadvantages, and manufacturing methods of aspheric lenses.
What are aspheric lensesused for
Complete the inquiry form to request more information and discuss your application with one of our representatives. As always, be sure to ask about volume discounts. SST reserves the right to modify pricing at any time.
SST products and services include: vacuum feedthroughs, hermetic connectors, ceramic-to-metal sealing, metalizing and brazing of ceramics, glass-ceramic sealing, and custom feedthrough design.
What are aspheric lensesfor glasses
Spherical surfaces are characterized by the fact that the radius of curvature is the same at all positions on the sphere, and this leads to the fact that they are easy to polish and high precision can be obtained. On the other hand, aspheric lenses require the radius of curvature to be made different depending on the position, which requires precision mold processing and technology to precisely transfer and mold the aspheric shape.
Aspheres that are not axi-symmetrical (rotationally symmetrical) can be used to change the magnification of vertical and horizontal images in imaging optics. Also, in illumination and focusing optics, light emitted from a point light source can be projected in the form of a line. In this way, aspheres that are not axisymmetric (rotationally symmetric) can achieve new functions that cannot be achieved with spherical lenses alone.
Asphericlens benefits
TOYOTEC, operator of the Optical Design Technology Navigator, is an all-around optical manufacturer with proficiency in optical, mechanical, and electronical technology. We can design and develop products from scratch based on our customers’ needs, and provides integrated support from design to productization. In addition to manufacturing aspheric lenses, we offer one-stop manufacturing services from ultra-precision machining of lens cores to the design and assembly of lens units, including systems and peripheral components.
Solid Sealing Technology® designs and manufactures essential electrical components for today’s high-tech world. Our innovative material-joining technologies bond ceramics and glass to metal to create hermetic feedthroughs and connectors tailored for use in vacuum environments. Experts in design, SST offers a vast catalog of standard high-performance sealing solutions that improve reliability in demanding engineering settings. And for customers with unique challenges, SST’s skilled engineering group creates fully customized parts from the ground up.
Asphericmeaning
With fewer lenses, it is possible to reduce lens materials, processing costs, and assembly man-hours, leading to overall cost reductions.
There are many different types of lenses. They can be broadly classified as the following according to the principle of light focusing and divergence and the type of surface.
All SST parts are customizable! We regularly make modifications to our catalog parts and offer totally custom feedthroughs and hermetic connectors. If your project requires changes from what you see listed in these product specifications, please reach out to us using the contact form on this page.
Disadvantages ofaspheric lenses
Aspheric Lensesprice
In this way, aspherical lenses make it possible to reduce the size and weight of products, and even to cut costs. However, the production of aspherical lenses requires a very high level of manufacturing technology.
A spherical glass lens is processed by grinding one surface at a time, but grinding and polishing an aspherical lens one surface at a time would be very expensive. For this reason, aspheric shapes are generally processed into molds, which are then transferred and molded onto glass or plastic.
Lenses ① to ⑤ are lenses that have a focusing and diverging effect solely due to refraction on the lens surface. Of these, lenses ① to ④ have a continuous smooth surface, while lens ⑤ has a lens surface that is divided into discontinuous zones.
Lenses ② to ④ are lenses with continuous, smooth, non-spherical lens surfaces and are called aspherical lenses in a broad sense. ② is a lens with an aspheric surface that is axi-symmetric (rotationally symmetric) with respect to the optical axis of the lens, and is often used in imaging optical systems. Lenses ③ to ④ are aspheric lenses that do not have axisymmetry (rotational symmetry) with respect to the optical axis of the lens, and are mainly used in lighting and focusing optical systems.
Aspheric lensesadvantages disadvantages
An aspherical lens is a lens whose lens surface is not spherical. By using lenses with aspherical surfaces, which offer a high degree of freedom in design, it becomes possible to reduce aberrations that could not be fully corrected with spherical lenses alone.
Although the time required for transfer and molding is shorter than for the spherical polishing process, manufacturing of precision aspheric molds (which incurs cost) in advance are necessary. For this reason, consideration of whether or not to use aspheric lens prior to production, based on the estimated total cost of the production volume is necessary.
We are a comprehensive manufacturer of Opto-mechatronic systems that conceptualize customer needs from design to development.
In addition, when axi-symmetric aspheres are used in illumination and focusing optics, it is possible to achieve uniform illumination distribution and increase the degree of freedom in ray control.
Axi-symmetric aspheres include rotational parabolas, rotational hyperbolic surfaces, rotational elliptic surfaces, and rotational quadric surfaces. In imaging optics, the use of such axisymmetric aspheres increases the degree of freedom in shape and makes it possible to suppress aberrations that would be difficult with spherical lenses alone.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500