Eye Flashes & Floaters | New England Vision - strobe light vision
Novel optical imaging for more accurate glaucoma screening. Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness. Early diagnosis and treatment can slow or stop progression to blindness, but the current test for elevated intraocular pressure is inadequate for detecting glaucoma at an early stage. Changes in the collagen fibers of the sclera (white of the eye) play a significant role in the disease process, potentially offering a reliable marker of early stage glaucoma. NIBIB-funded biomedical engineers are developing a novel optical imaging technique that can detect changes in the structure of the collagen fibers of the eye sclera. The technique employs a computational model that correlates specific changes in sclera proteins with early onset glaucoma. The new test will enable early initiation of vision-sparing treatment and continuous non-invasive monitoring of the response to treatment.
Non-invasive imaging to monitor breast cancer chemotherapy. Bioengineers are developing non-invasive optical imaging techniques that can monitor tumor chemotherapy and rapidly identify the 20% of breast tumors that do not respond. Signals emitted from painless near-infrared light-based probes provide measurements of fat content, blood vessel formation, and oxygen levels, which indicate whether or not the chemotherapy has begun to shrink the tumor early in the course of treatment. Such information will allow physicians to stop chemotherapy and/or change treatment if the patient is not responding, enabling overall improved management of breast cancer treatment.
Optician meaning
FOV is simply a measurement of the diameter of the image that the viewer can see. It's typically expressed as the diameter in millimeters of the observer's field of vision, and is used to quantify the size of the object under inspection.
Opticalmeaning in bengali
At AmScope, we provide high-quality compound light microscopes and stereo microscopes, as well as a wide collection of eyepieces and lenses. We have the optical components to help you view your project at whatever field of view or magnification it needs. Check out our catalog today, and zoom in to the product that's right for you.
Defined as the minimum distance at which an observer can distinguish two adjacent points, resolution increases with magnification. That means especially detailed objects may require the superior resolution that comes with higher magnification, even if the FOV is reduced.
Endoscopy uses an endoscope, which is a flexible tube with a light source to illuminate an organ or tissue. An endoscope can be inserted through a patient’s mouth and into the digestive cavity to find the cause of symptoms such as pain, difficulty swallowing, or gastrointestinal bleeding.
If an eyepiece is added, the field size is equal to the field number divided by the total magnifying power of the entire assembly. Since magnifying power compounds geometrically, the total magnifying power is the product of the microscope eyepiece and microscope objective lens. In this case, the field size can be expressed as:
Define opticalin science
A measurement of the diameter of the visible image, field of view (FOV) clarifies how much of the object the viewer is actually observing. This allows the viewer to analyze the specimen more clearly, perform any needed operations with greater precision, and have a better understanding of what they see. In this article, we'll show you how to calculate field of view, what it is, and some FOV differences for compound and stereo microscopes. Here's a deeper look.
- Optical imaging can be combined with other imaging techniques, such as MRI or x-rays, to provide enhanced information for doctors monitoring complex diseases or researchers working on intricate experiments.
Assessing and treating neurological damage associated with cardiac arrest. Eighty to ninety percent of cardiac arrest (CA) survivors suffer significant neurological damage. Addressing these devastating effects has not been possible due to the need for imaging of rapid changes to blood flow and metabolism in the brain during CA and during emergency CPR. Engineers are developing an optical imaging system for critical real-time imaging that measures cerebral blood flow and metabolic functions such as oxygen consumption. Optical imaging will be paired with electroencephalography (EEG) to study neurological changes related to interrupted blood flow. The system will enable advanced study of brain injury during CA and CPR and offer real-time treatment options that can improve survival and outcome for CA patients.
Define opticalin medical terms
AmScope exclusive ALL-IN-ONE 3D DIGITAL INSPECTION MICROSCOPE. View different angles and perspectives of objects with ease.
The tradeoff between FOV and magnification means that observers have several factors to take into consideration when they choose how much power is right for their project. Two of these factors are resolution and depth of field.
FS = FN/(ME*MO), where FS = field size, FN = field number, ME = eyepiece magnification, and MO = objective magnification
Optical imaging uses light and special properties of photons to obtain detailed images of organs, tissues, cells and even molecules. The techniques offer minimally or non-invasive methods for looking inside the body.
From the life sciences and medicine to semiconductors and jewelry, microscopes have become essential tools for many industries. They bring details to light that the naked eye could never see, but the insights viewers gain can be skewed if they don't know how large the image is. That's what field of view expresses.
Opticalmeaning in Tamil
Photoacoustic Imaging delivers laser pulses to a patient’s tissues; the pulses generate heat, expanding the tissues and enabling their structure to be imaged. The technique can help monitor blood vessel growth in tumors, detect skin melanomas, and track blood oxygenation in tissues.
Super-resolution Microscopy encompasses a number of techniques to obtain very high-resolution images of individual cells. One example is photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM), which uses individual fluorescently marked molecules to create a super-resolution image comprised of a compilation of individual molecules in a cell or tissue.
The field number can be easily located on a microscope, as it's typically written on the side of each lens, next to its magnifying power. For example, if the numbers on a microscope's objective lenses are 10X/15, 40X/20, and 100X/25, the objective magnifications would be 10X, 40X, and 100X, while the field numbers would be 15, 20, and 25, respectively.
Opticalmeaning in computer
The mission of the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) is to transform, through technology development, our understanding of disease and its prevention, detection, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Optical imaging is particularly useful for measuring multiple properties of soft tissue. Because of the wide variety of ways different soft tissues absorb and scatter light, optical imaging can measure metabolic changes that are early markers of abnormal functioning of organs and tissues.
Once the field number and magnifying power of each lens in use are known, a simple equation exists to help observers find the total field size of the image in view. If the objective lens is the only magnifier in use, the field size is equal to the field number divided by the objective magnification of the lens, or:
The first step in determining the FOV is to find the field number on the objective lens. This number gives the diameter of the microscope field, assuming no other eyepieces or magnifiers are added.
- Optical imaging significantly reduces patient exposure to harmful radiation by using non-ionizing radiation, which includes visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because it is much safer than techniques that require ionizing radiation, like x-rays, optical imaging can be used for repeated procedures to monitor the progression of disease or the results of treatment.
The 3D images that stereo microscopes provide also require consideration of depth of field, or DOF. The calculations aren't as straightforward as those for FOV, but a higher magnification is directly proportional to a greater depth of field. As with resolution, if observers need to distinguish between multiple layers of their specimen, they may need higher magnification at the expense of FOV. However, stereo microscopes typically have a larger default FOV than conventional compound microscopes, so the tradeoff is less with this type of scope.
Opticalmeaning in Urdu
The field observation window also decreases quite rapidly when auxiliary lenses are added. A single eyepiece with a magnification power of 10X reduces the field of view by a factor of 10, so observers adding extra lenses should know just how much width they'll lose.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a technique for obtaining sub-surface images such as diseased tissue just below the skin. Ophthalmologists use OCT to obtain detailed images from within the retina. Cardiologists also use it to help diagnose coronary artery disease.
Calculating a microscope’s field of view differs somewhat for compound and stereo microscopes. Both involve a calculation based on the total magnification of the microscope and a parameter on the lens, but stereo microscopes have other factors to consider.
Opticalmeaning in Hindi
In the above equation, note that field of view is inversely proportional to magnification power; a lower total magnification allows for a larger field, and a higher magnification results in a smaller field. This is to be expected, because the closer an observer zooms into an object, the smaller the window they view.
Raman Spectroscopy relies on Raman scattering of visible, near-infrared, or near-ultraviolet light. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations in the material, with shifts in energy revealing the material’s chemical properties. Applications include identifying chemical compounds and the structure of materials and crystals. During surgery, Raman gas analyzers are used to monitor the mixture of gases used for anesthesia.
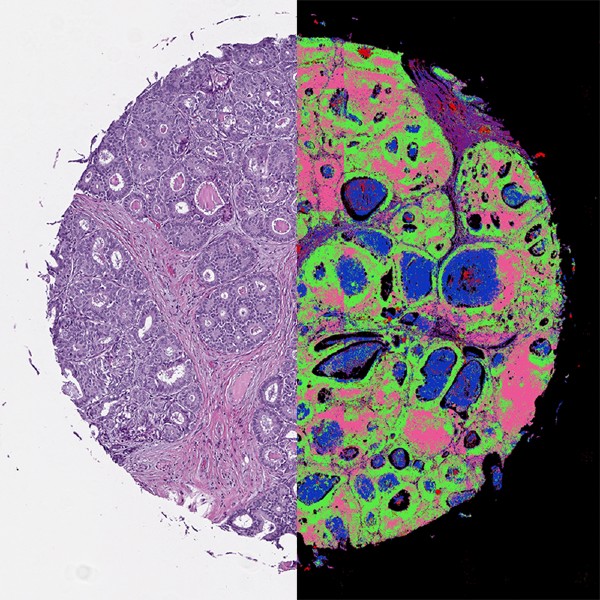
Diffuse Optical Tomography (DOT) and Imaging (DOI) are non-invasive techniques that use light in the near-infrared region to measure tissue properties such as total hemoglobin concentration and blood oxygen saturation. Because DOT and DOI work well in soft tissue, the techniques are widely used for breast cancer imaging, brain functional imaging, stroke detection, photodynamic therapy, and radiation therapy monitoring.
Whether you're examining a cell with an optical microscope or soldering components onto a printed circuit board (PCB), knowing the size of the object in view helps you complete your work more effectively. For example, knowing the size of a microscope field can help the observer determine how large an organelle within a microorganism is, and could also give other insights about important image features.
As an example, a microscope having an objective lens with 100X magnification power and a field number of 25 mm would have a field size of 25 mm/100, or 0.25 mm. Similarly, if the same microscope added an eyepiece having a magnification power of 20X, the field size would be 25 mm/(100*20), or 0.0125 mm. Because the field size can be quite small, instead of expressing field size in terms of millimeters, some observers may multiply their value by 1,000 to convert their units to micrometers




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500