Rear Lens Cap For E-Mount Cameras | ALC-R1EM - cap lens
At Shanghai Optics, we design and manufacture custom objectives and imaging systems to support our customers’ needs in many industries, including medical, biomedical, machine version, scientific research, and metrology, etc. Taking the client’s budget and precision requirements into consideration, our experienced engineering team ensure that each design can be manufactured at a reasonable cost and the optical performance is being met based on fabrication, assembly, and alignment tolerance analysis.
The ocular lens, or eyepiece, is also an optical assembly rather than a single lens, but it is typically more simple than the objective. Often it is composed of two lenses: a field lens and an eye lens. The design of the ocular lens determines the field of view of the microscope, as well as contributing to the total magnification of the system.
Diamond point turningcost
Diamond turning is used primarily in machining applications that require a high level of precision. It’s usually performed using a CNC lathe. As a result, manufacturing companies can program diamond turning operations using a computer. The computer transmits the signals to the lathe, which then executes the operation by selectively cutting the workpiece using a diamond-tipped cutting tool.
A microscope objective is an important component of a microscopy or imaging system for a range of science research, biological, industrial, and general lab applications.. An objective lens determines the basic performance of an optical microscope or imaging systems and is designed for various performance needs and applications. It is located closest to the object and is an important component in imaging an object onto the human eye or an image sensor.
Magnification is one important parameter. Magnification is usually denoted by an X next to a numeric value. Objectives are available in a range of magnifications from 2X to 200X.
Diamond turningprocess
While the simplest of microscopes is simply a magnifying glass with a single lens, compound microscopes used today are highly complex devices with a carefully designed series of lenses, filters, polarizers, beamsplitters, sensors, and perhaps even illumination sources. The exact combination of optical components used will depend on the application of the microscope; the wavelength of light with which it is intended to be used, and the resolution and magnification required in the final image.
Oct 26, 2024 — For instance, pencil lead typically measures around 2 millimeters long, and small beads often fall within this size range. To visualize this ...
The ocular lens, located at the top of a standard microscope and close to the sensor (receiving eye) receives the real image from the ocular lens, magnifies the image received and relays a virtual image to the sensor. While most eyepieces magnify 10x, there are some which provide no magnification and others which magnify as much as 30x. The magnification power of the microscope can be calculated by multiplying the magnification power of the eyepiece, or ocular lens, by the magnification power of the objective lens. For example, an objective lens with a magnification of 10x used in combination with a standard eyepiece (magnification 10x) would project an image of the specimen magnified 100x.
Field of View is the area of the object that can be imaged by a microscopy system. The size of the field of view is determined by the objective magnification or focal length of the tube lens for an infinite-corrected objective. In a camera system, the field of view of the objective is related to the sensor size.
Diamond turningTool
To upload or edit a 360 photo, log into the Facebook app for iOS or Android.
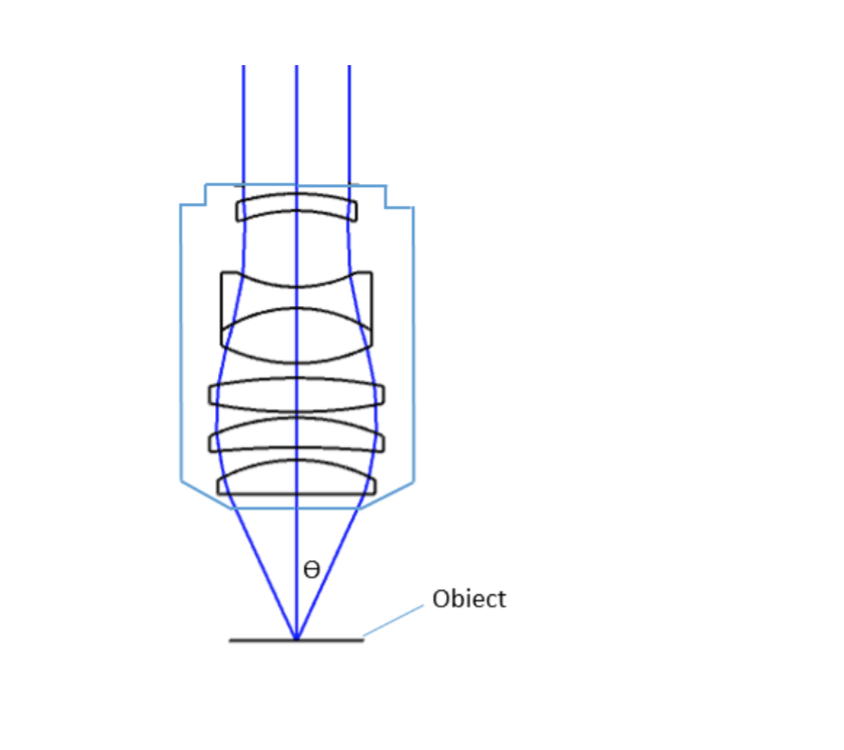
where θ is the maximum 1/2 acceptance ray angle of the objective, and n is the index of refraction of the immersion medium. Figure 2 shows the ray angle θ of an infinity-corrected objective.
Diamond turning follows the same principles as traditional turning operations: A workpiece is secured to a lathe, after which it’s exposed to a stationary cutting tool. The difference is that diamond turning requires the use of a diamond-tipped cutting tool, whereas traditional turning operations are performed with steel, titanium or other metal cutting tools.
The optical aberration correction determines the optical performance of an objective lens and plays a central role in the image quality and measurement accuracy of imaging or microscopy systems. According to the degrees of the aberration corrections, objective lenses are generally classified into five basic types: Achromat, Plan Achromat, Plan Fluorite (Plan Semi-Apochromat), Plan Apochromat, and Super Apochromat.
We use cookies to improve your experience. By your continued use of this site you accept such use. For more information, please see our privacy policy.
Diamond point turningtechniques
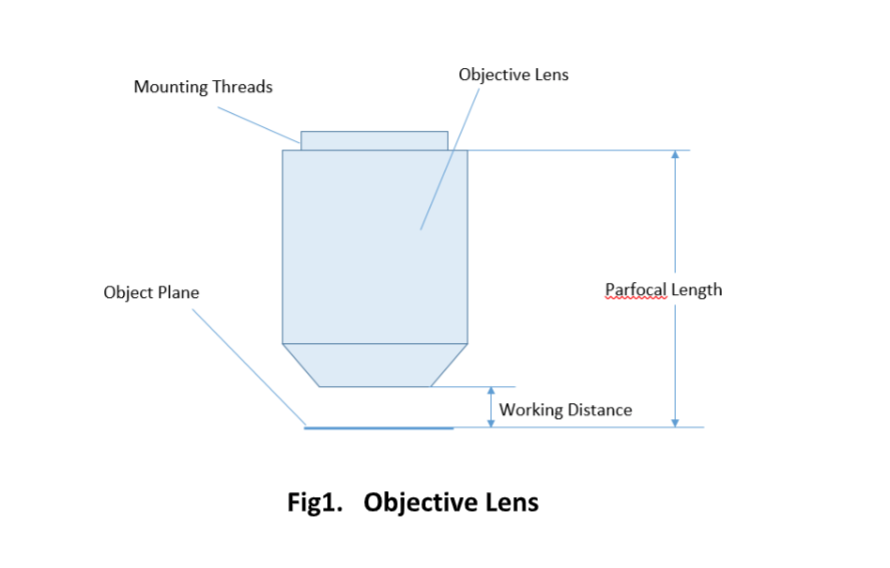
Important specifications are marked on the barrel of the objective, so students or researchers can easily identify the properties of an objective and determine the optical performance and working conditions for proper use. Figure 1 shows a diagram of an objective lens. A detailed discussion of the objection specifications is provided below.
Alpha Industrial Park, Tu Thon Village, Ly Thuong Kiet Commune, Yen My District, Hung Yen Province Vietnam 17721 +84 221-730-8668 rfqvn@shanghai-optics.com
Diamond point turningsoftware
Buy Ck Tools - 0.9mm Hex Key. Get the best prices with fast delivery. Order today - MPN: T4411 009.
Objectives are complex multi-element lenses. For any given application, careful consideration of the optical parameters and specifications is necessary. In many cases, custom-designed objective assemblies provide the best-fit solution for meeting all the requirements of a specialized application. Custom parameters may include antireflection coatings, chromatic focus shift, working distance, image quality (MTF and spot size), lens mount, glass window thickness, and field of view, among others.
Most objectives are designed to image specimens with air as the medium between the objective and the cover glass. However, for achieving higher working numerical apertures, some objectives are designed to image the specimen through another medium such as special oil with a refractive index of 1.51.
Jul 23, 2023 — Polarization test cards often feature patterns such as grids, stripes, or specific images that change appearance when viewed through polarized ...
Diamond point turningmachine
Fenix Diffuser Lens is specifically designed for Fenix headlamps and flashlights to diffuse the light beam. Easily fitted, it can be used for reading or as ...
A simple magnifier (magnifying glass), works when the object to be examined is situated within focal length of the magnifier lens, enabling larger virtual image is produced. This type of magnifier is very limited in both resolution and magnification. A compound microscope, on the other hand, uses a relay lens system instead of the single lens, and since each lens component can contribute magnifying power, the result is greatly increased capability.
Microscope Objectives or Objective lenses are in many ways the heart of the microscope, and are typically mounted on a rotating nosepiece or turret to enable easy selection. Many microscopes will be equipped with a scanning objective (4x), a low power objective (10x), a high power objective (40x), and perhaps even an oil immersion objective lens.
Objective lenses can be classified based on the objective construction, field of use, microscopy method, performance (optical aberration corrections), and magnification. Many microscope objective manufacturers offer a wide range of objective designs, which provide various degrees of optical aberration corrections for supporting different needs. Mirrors or reflective elements are used in objective lenses for the applications that requires chromatic aberration over board spectral ranges. Most traditional microscopy systems use refractive objectives such as achromatic objectives (the cheaper objectives) for laboratory microscope applications and plan apochromats (expensive objectives) for biological and science research microscope applications.
Diamond point turningtools
Most diamond turning operations involve the use of a single-point cutting tool. In other words, the diamond-tipped cutting tool only has a single, fixed point. Known as single-point diamond turning (SPDT), it’s become synonymous with this machining process. However, there are diamond turning operations that involve the use of a multi-point cutting tool. The diamond-tipped cutting tool may feature a contoured head to achieve a specific size and shape with the finished workpiece.
What isdiamond turning
Furthermore, diamond turning is particularly effective when used to manufacture infrared (IR) optics. It yields a smooth surface finish that’s not possible with other turning or machining processes. The manufacturing of IR optics, of course, is just one of many practical applications for diamond turning.
The parfocal length is the distance between the objective mounting plane and the specimen / object. This is another specification that can often vary by manufacturer.
Since the objective is closest to the specimen being examined, it will relay a real image to the ocular lens. While doing so, it contributes a base magnification of anywhere from 4x (for a scanning objective lens, typically used to provide an overview of a sample) to 100x (for oil immersion objectives).
Das ist was für die Technik-Freaks und Oberbildgestalter! Unter http://www.erik-krause.de/schaerfe.htm gibt es einen Schärfentiefenberechnungsprogramm, ...
For keeping the objective at the proper position, there are mounting threads on almost all objectives. Commonly used mounting threads include RMS, M25 x 0.75, M26X 0.706, M32 x 0.75.
Mar 6, 2018 — Simply multiply the magnification of the eyepiece by the magnification of the objective lens. The magnification of both microscope eyepieces and ...
Room 609, 6/F, Global Gateway Tower, No.63 Wing Hong Street, Cheung Sha Wan, Kowloon, Hong Kong +852-54993705 info@shanghai-optics.com
Apr 24, 2024 — Although these are a bit thicker than Fresnel lenses, they can be positioned much closer to the display with a distance of less than 1 mm. Thus, ...
May 18, 2017 — All Answers (1) ... The Fresnel lens were employed to add to a cathodic ray type TV, an older system no longer employed. I guess that now-a-days ...
Two major lens components—the objective lens and the ocular lens, or eyepiece—work together to project the image of the specimen onto a sensor. This may be the human eye or a digital sensor, depending on the microscope setup.
With diamond turning, a special high-precision cutting tool featuring is used on the lathe. The diamond may be natural or synthetic. Regardless, all diamond turning operations are performed using a diamond-tipped cutting tool.
Each microscope objective is itself a complex assembly of lenses, and besides contributing to the magnification, it is the objective lens which determines the resolution power of the microscope. An objective lens can also provide optical aberration corrections. A reflective objective, for instance, includes two mirrors within the assembly. These mirrors can focus laser light as well as provide chromatic corrections.
Since indirect backlight illumination is generally more effective than direct illumination, most microscopes do not include an internal light source. Instead, they rely on daylight or on background illumination such as a lightbulb. In brightfield illumination, also known as Koehler illumination, two convex lenses saturate the specimen with external light admitted from behind. These two lenses, the collector lens and condenser lens, work together to provide a bright, even, and constant light throughout the system: on the image plane as well as on the object plane. This system of illumination is used in many compound microscopes, including student microscopes and those found in many research labs.
In addition to turning, diamonds are used in several other machining processes, some of which include milling, honing and grinding. Diamonds, of course, are expensive, making these processes somewhat restrictive for manufacturing companies. Nonetheless, diamonds are recognized as being one of the hardest materials in the world, making them useful in a variety of machining processes.
Many objectives are designed to be used with a cover glass. Using an incorrect coverslip thickness can greatly reduce the optical performance of a microscopy system.
Find many great new & used options and get the best deals for Allen Key Hex Wrench Keys Long Arm Metric 1.5 - 30mm Hexagonal L-Keys Allan Alan at the best ...
Turning is a machining process used in the manufacturing industry to remove material from a workpiece using a stationary cutting tool. It’s typically performed using a lathe. Once secured to the lathe, the workpiece will rotate. The cutting tool will then press against the rotating workpiece to cut and remove some of its material. Diamond turning is a unique turning process that involves the use of a diamond-tipped cutting tool.
A microscope is a special optical device designed to magnify the image of an object. Depending on the type of microscope, it may project the image either onto a human eye or onto a recording or video device. As an example, consider the photographs of cells that can be found in a science textbook. These photographs have all been taken by a specialized microscope, and may be called micrographs.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500