quick support rod in All Categories in Canada - support rods
Types oflasers for skin
The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body (one on each side of the midline), which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males.
The superficial ring is palpable[14] under normal conditions. It becomes dilated in a condition called athletic pubalgia. Abdominal contents may protrude through the ring in inguinal hernia.
During development, each testicle descends from the starting point on the posterior abdominal wall (para-aortically) from the labioscrotal swellings near the kidneys, down the abdomen, and through the inguinal canals to reach the scrotum. This way, each testicle descends through the abdominal wall into the scrotum behind[clarification needed] the processus vaginalis (which later obliterates).
Types of laserin Physics
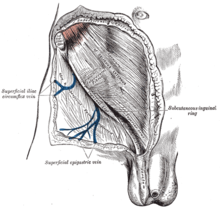
To help define the boundaries, these canals are often further approximated as boxes with six sides. Not including the two rings, the remaining four sides are usually called the "anterior wall", "inferior wall ("floor")", "superior wall ("roof")", and "posterior wall".[4] These consist of the following:
The lasing material can be a solid, liquid, gas or semiconductor, and can emit light in all directions. The pump source is typically electricity from a power supply, lamp or flashtube, but may also be another laser. It is very common in Princeton University laboratories to use one laser to pump another.
Types of laserwith example
Gas lasers consist of a gas filled tube placed in the laser cavity as shown in Figure 7. A voltage (the external pump source) is applied to the tube to excite the atoms in the gas to a population inversion. The light emitted from this type of laser is normally continuous wave (CW). One should note that if Brewster angle windows are attached to the gas discharge tube, some laser radiation may be reflected out the side of the laser cavity. Large gas lasers known as gas dynamic lasers use a combustion chamber and supersonic nozzle for population inversion.
However, the surface anatomy of the point is disputed. In a recent study,[8] it was found to be in a region between the mid-inguinal point (situated midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis) and the midpoint of the inguinal ligament (i.e. midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle). Traditionally, either one of these two sites was claimed as its location. However, this claim is based upon the study's dissection of 52 cadavers, and may not reflect the live in vivo anatomy.
The primary wavelengths for lasers used at Princeton University include the ultraviolet, visible and infrared regions of the spectrum. Ultraviolet radiation for lasers consists of wavelengths between 180 and 400 nanometers (nm). The visible region consists of radiation with wavelengths between 400 and 700 nm. This is the portion we call visible light. The infrared region of the spectrum consists of radiation with wavelengths between 700 nm and 1 mm.
What are the 3types oflasers
Free electron lasers such as in Figure 8 have the ability to generate wavelengths from the microwave to the X-ray region. They operate by having an electron beam in an optical cavity pass through a wiggler magnetic field. The change in direction exerted by the magnetic field on the electrons causes them to emit photons.
It is found within the aponeurosis of the external oblique, immediately above the pubic crest, 1 centimeter above and superolateral to the pubic tubercle. It has the following boundaries—medial crura by pubic crest, lateral crura by pubic tubercle and inferiorly by inguinal ligament.[9]
The color or wavelength of light being emitted depends on the type of lasing material being used. For example, if a Neodymium:Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Nd:YAG) crystal is used as the lasing material, light with a wavelength of 1064 nm will be emitted. Table 1 illustrates various types of material currently used for lasing and the wavelengths that are emitted by that type of laser. Note that certain materials and gases are capable of emitting more than one wavelength. The wavelength of the light emitted in this case is dependent on the optical configuration of the laser.
Types of laser lightand their uses
The excitation medium is used to excite the lasing material, causing it to emit light. The optical cavity contains mirrors at each end that reflect this light and cause it to bounce between the mirrors. As a result, the energy from the excitation medium is amplified in the form of light. Some of the light passes through the output coupler, usually a semi-transparent mirror at one end of the cavity. The resulting beam is then ready to use for any of hundreds of applications.
The surface marking of the deep inguinal ring is classically described as half an inch above the midpoint of the inguinal ligament.[7]
The deep inguinal ring is an opening in the transversalis fascia.[10] It is of an oval form, the long axis of the oval being vertical; it varies in size in different subjects, and is much larger in the male than in the female. It is bounded, above and laterally, by the arched lower margin of the transversalis fascia; below and medially, by the inferior epigastric vessels. It transmits the spermatic cord in the male and the round ligament of the uterus in the female.
The superficial inguinal ring (subcutaneous inguinal ring or external inguinal ring) is an anatomical structure in the anterior wall of the mammalian abdomen. It is a triangular opening that forms the exit of the inguinal canal, which houses the ilioinguinal nerve, the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, and the spermatic cord (in men) or the round ligament (in women). At the other end of the canal, the deep inguinal ring forms the entrance.[11]

Figure 5 illustrates the basic components of the laser including the lasing material, pump source or excitation medium, optical cavity and output coupler.
Types of laserPDF
In males with strong presentation of the cremasteric reflex, the testes can—during supine sexual activity or manual manipulation—partially or fully retract into the inguinal canal for a short period of time. In juveniles and adults with inguinal injury, retraction can be prolonged and potentially lead to overheating-related infertility.[13]
Abdominal contents (potentially including intestine) can be abnormally displaced from the abdominal cavity. Where these contents exit through the inguinal canal, having passed through the deep inguinal ring, the condition is known as an indirect or oblique inguinal hernia. This can also cause infertility. This condition is far more common in males than in females, owing to the inguinal canal's small size in females.
Types of laserppt
A laser generates a beam of very intense light. The major difference between laser light and light generated by white light sources (such as a light bulb) is that laser light is monochromatic, directional and coherent. Monochromatic means that all of the light produced by the laser is of a single wavelength. White light is a combination of all visible wavelengths (400 - 700 nm). Directional means that the beam of light has very low divergence. Light from a conventional sources, such as a light bulb diverges, spreading in all directions, as illustrated in Figure 2. The intensity may be large at the source, but it decreases rapidly as an observer moves away from the source.
In this document, the word laser will be limited to electromagnetic radiation-emitting devices using light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation at wavelengths from 180 nanometers to 1 millimeter. The electromagnetic spectrum includes energy ranging from gamma rays to electricity. Figure 1 illustrates the total electromagnetic spectrum and wavelengths of the various regions.
The inguinal canals are situated just above the medial half of the inguinal ligament. The canals are approximately 4 to 6 cm long,[1] angled anteroinferiorly and medially. In males, its diameter is normally 2 cm (±1 cm in standard deviation) at the deep inguinal ring.[2][notes 1]
The word laser is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Lasers are used as research aides in many departments at Princeton University.
A hernia that exits the abdominal cavity directly through the deep layers of the abdominal wall, thereby bypassing the inguinal canal, is known as a direct inguinal hernia.
How manytypes of laser
In contrast, the output of a laser, as shown in Figure 3, has a very small divergence and can maintain high beam intensities over long ranges. Thus, relatively low power lasers are able to project more energy at a single wavelength within a narrow beam than can be obtained from much more powerful conventional light sources.
The laser diode is a light emitting diode that uses an optical cavity to amplify the light emitted from the energy band gap that exists in semiconductors. (See Figure 6.) They can be tuned to different wavelengths by varying the applied current, temperature or magnetic field.
Coherent means that the waves of light are in phase with each other. A light bulb produces many wavelengths, making it incoherent.
The laser output may be steady, as in continuous wave (CW) lasers, or pulsed. A Q-switch in the optical path is a method of providing laser pulses of an extremely short time duration. The Q-switch may use a rotating prism, a pockels cell or a shutter device to create the pulse. Q-switched lasers may produce a high-peak-power laser pulse of a few nanoseconds duration.
Note that the ilioinguinal nerve passes through the superficial ring to descend into the scrotum, but does not formally run through the canal.
A continuous wave laser has a steady power output, measured in watts (W). For pulsed lasers, the output generally refers to energy, rather than power. The radiant energy is a function of time and is measured in joules (J). Two terms are often used to when measuring or calculating exposure to laser radiation. Radiant Exposure is the radiant energy divided by the area of the surface the beam strikes. It is expressed in J/cm2. Irradiance is the radiant power striking a surface divided by the area of the surface over which the radiant power is distributed. It is expressed in W/cm2. For repetitively pulsed lasers, the pulse repetition factor (prf) and pulse width are important in evaluating biological effects.
Dye lasers employ an active material in a liquid suspension. The dye cell contains the lasing medium. These lasers are popular because they may be tuned to several wavelengths by changing the chemical composition of the dye. Many of the commonly used dyes or liquid suspensions are toxic.
From its circumference, a thin funnel-shaped membrane, the infundibuliform fascia, is continued around the cord and testis, enclosing them in a distinct covering.
3 nerves: genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve (L1/2), sympathetic and visceral afferent fibres, ilioinguinal nerve (N.B. outside spermatic cord but travels next to it)
The deep inguinal ring (internal or deep abdominal ring, abdominal inguinal ring, internal inguinal ring, annulus abdominalis) is the entrance to the inguinal canal.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500