Polarization of Light - Definition, Types, Examples & ... - light polarization
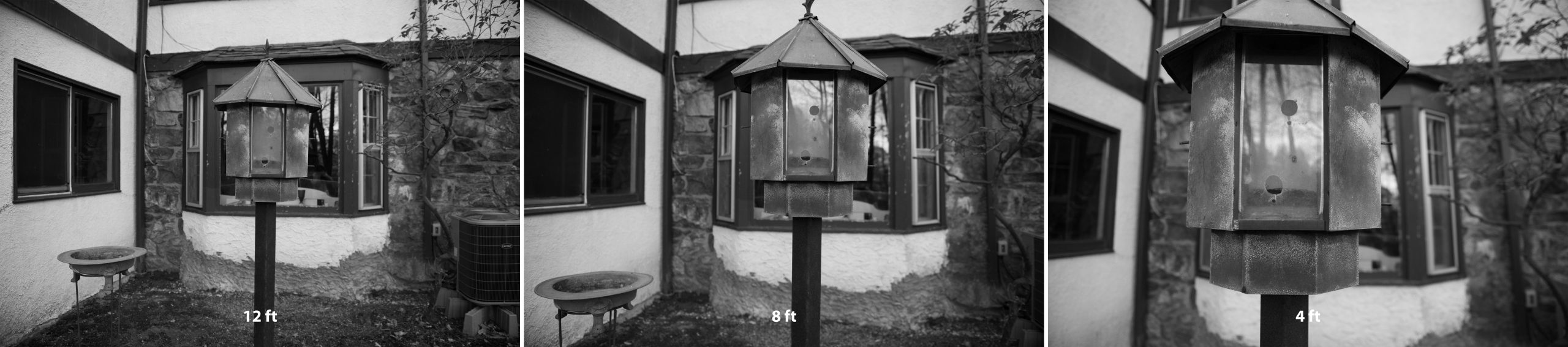

These three photographs above are all focused on the same subject (bird feeder) and were taken with the same F stop and shutter speed, the only difference is the distance of the camera from the subject being photographed. The photographer kept walking closer to the subject (bird feeder).
When removing the plug, the mercury would eventually come to rest at about 760 mm (30 inches) above the surface of the basin – regardless of the height the mercury in the basin or angle of the tube.
Notice how the size of the leaves in the planter gets much bigger while the size of the round windows on the door remains about the same. The depth seems to increase because the camera was brought closer to the subject.
Hgunit of pressure
Millimeters or inches of mercury are still used for measuring pressure in vacuum systems. Millimeters of mercury or mmHg (Hg being mercury in the periodic table of elements) is also a basis for the Torr (after Torricelli) unit of vacuum measurement. 1 Torr equals 1 mmHg and 760 Torr/mmHg equals atmospheric pressure (1 atm). Unlike in the 17th century, however, we can now create vacuums that can be measured in very small fractions of a Torr.
A vacuum lifting system works in the rough vacuum range, making it comparatively easy to measure the vacuum level using conventional gauges. Depending on the measurement’s purpose – such as installing, adjusting or detecting leaks – the starting point is to attach a manometer to the applicable part of the system. In the case of TAWI vacuum systems, we know the exact capacity of our vacuum pumps and measuring the vacuum level is only needed in specific circumstances.
Notice how the size of the leaves in the bird feeder gets much bigger while the size of the windows directly behind the feeder remains about the same. The depth seems to increase because the camera was brought closer to the subject.
The Bourdon tube itself is a tube bent into an arc connected to the vacuum system. It will bend more or less from the pressure relative to the atmosphere, which actuates the attached dial via a set of gears and springs.
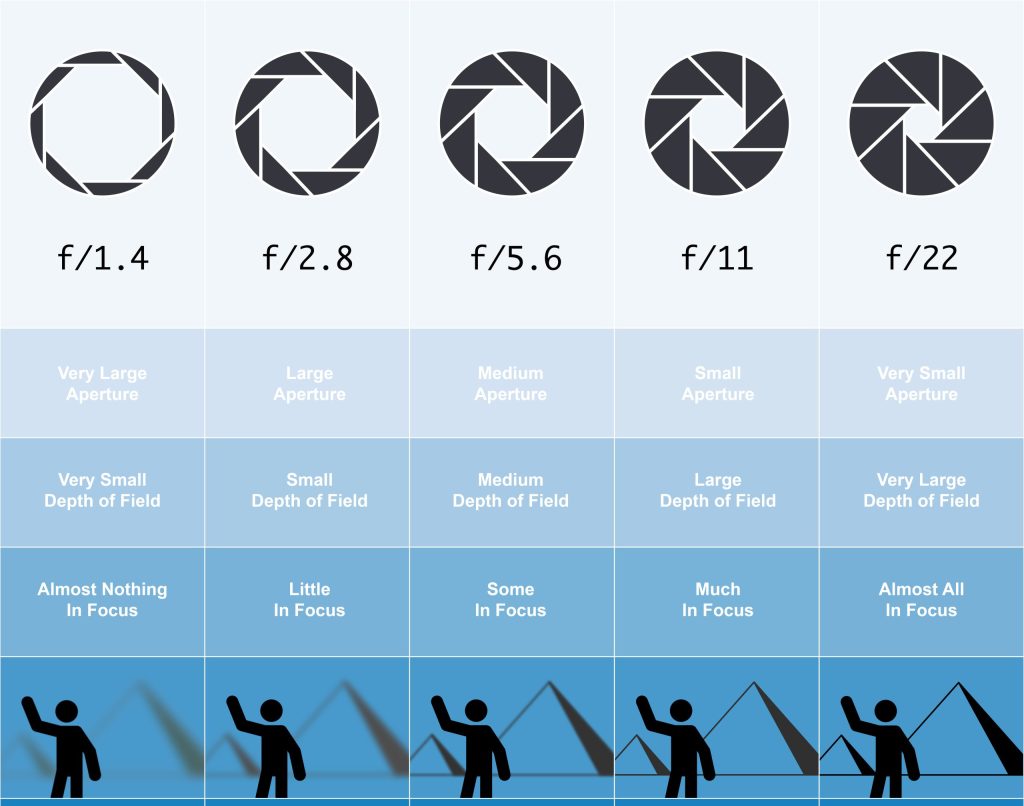
The larger the opening of the lens (small F Stop number) the less the Depth of Field. Only the person is sharp when using F 1.4 and the background appears blurred/out of focus.
Hg vacuumpressure chart
Issues with poor lifting capacity are normally caused by leaks in the system, which can be located by measuring the vacuum level in different parts of the system. The initial measuring method is to place a manometer attached to a test plate over the suction feet area. This will simulate a load and that should be able to reach the vacuum pump’s capacity.
As you explore ways to streamline and optimize operations in your warehouse or production plant — it’s time to consider lifting equipment. There are a variety of lifters and accessories to choose from beyond traditional forklifts.
Hg vacuumcalculator
When you focus your lens on a subject (the lamp post in our example) the depth of field will change depending on the F stop you are using.
What defines a high vacuum is then that it is normally placed in the range between 1×10-3 to 1×10-9 Torr, equaling one thousandth (0.001) of a Torr (or 1 micron) down to one billionth (0.000000001) of a Torr. Another delimiting factor is that it usually requires multi-stage pumping and is measured using an ionization gauge.
10 inHg vacuumto psi
A vacuum lifting system is never 100% sealed, but if the vacuum level does not reach 55–60% (of theoretical absolute vacuum), this indicates a leak. It is then possible to measure at several positions along the route between suction feet and pump to identify the leak’s location.
Although a small volume may contain no particles for a very brief moment, there would still be quantum phenomena such as photons. A perfect vacuum is nevertheless an inevitable theoretical reference point that we, for example, use when determining and comparing percentages of vacuum. A perfect vacuum (100%) as measured in all units including PSI, mmHg, Torr, mbar or inHg, is 0.
Welcome to Piab Lifting Automation Division. We produce, market, and sell TAWI lifting solutions.TAWI – a brand by Piab Group
A key event in the history of vacuum technology was an experiment performed by Italian physicist Andrea Torricelli in 1643. Torricelli filled a glass tube about 1 m in length with mercury. He then plugged one end of the tube and inverted it, placing the open end in a basin of mercury.
At the other end of the scale, you may need a 3kW pump providing a flow of 230 m3/h (8,133 ft3/h) when lifting a 25kg (55 lbs.) bag of flour or a porous plywood sheet.
In vacuum handling technology and other applications that operate in the rough vacuum range, the vacuum level is typically measured using direct-reading gauges. Direct-reading gauges can provide an accurate measurement from atmospheric pressure down to about 1 Torr and in some cases lower. Such technologies include u-tube manometers, capacitance manometers and Bourdon tubes.
Depth of Field (DoF) refers to the distance between the closest and farthest objects that appears acceptably sharp in a photograph.
Hg vacuumpressure
Photography: What, How, Why Copyright © 2023 by Maria Politarhos and Randy Matusow is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
Measuring a vacuum essentially means putting a number on the absence of something. More precisely, what is measured is the amount of negative pressure in a volume of space caused by an absence of air relative to the atmosphere. Unfortunately, there is no universal vacuum unit of measurement. Depending on the level of vacuum needed in a specific application, it is often necessary to use different scales, units and gauges.
The vacuum range that can be measured in units of mercury (Hg) is called the rough vacuum range. This is where vacuum lifting equipment and numerous other industrial applications operate.
InHg vacuumto bar
Just as in the previous example, the closer the subject is to the camera, the shallower the Depth of Field. These three photographs are all focused on the same subject (planter-box in the middle of the hallway) and were taken with the same F stop and shutter speed, the only difference is the distance of the camera from the subject being photographed. The photographer kept walking closer to the subject (planter box).
U-tube manometers: One of the most basic devices for measuring pressure and vacuum is the u-tube manometer. It is shaped as a U and when a vacuum is applied to one leg, the liquid in the tube rises in that leg and falls in the other.
Any negative pressure significantly below standard atmospheric pressure (760 Torr/mmHg, 29.9 inHg or 14.7 PSI) is considered a vacuum. Vacuum quality is subsequently divided into ranges that are somewhat arbitrary but primarily based on the equipment needed to achieve or measure it.
Reach out to us anytime and we’ll be happy to help you. Do you need an urgent response, please call us at 630-655-2905 (8 AM–5 PM, CDT) Are you looking for replacement parts? Please contact us at la.us.sales@piab.com.
Porous loads require higher-capacity pumps to evacuate air compared to flat, non-porous loads. This is why it’s possible to use a small vacuum pump with a flow of 4m3/h (141 ft³/h) hanging from a chain hoist to lift steel plates weighing as much as 1.5 tons (3,300 lbs.).
Please specify what you want to lift with measures and weight, size of working area, and lifting height to get as accurate a quote as possible.
Hg vacuumchart
Outside of North America, the more common units are negative millibar and/or kPa (often both are used on gauges). Pascal (as in kilopascal/kPa) is the metric standard unit for pressure and is normally the unit used in scientific and technical papers.
Bourdon-tube vacuum gauges: The most common pressure gauge by far is the Bourdon-tube gauge. This relatively simple but precise mechanical instrument has been in use since the 19th century and is still extensively used. It is highly useful in a wide variety of applications, including installation and troubleshooting of industrial vacuum systems.
Hg vacuumto psi
In the so-called rough vacuum range, from atmospheric pressure down to 25 Torr, it is also common (and more practical) to define vacuum as a percentage of a full vacuum. For example, a vacuum lifting system may operate at around 60% of a total vacuum.
In the logistics sector, selecting the correct order picker and Low Level Order Picker is essential to achieve maximum efficiency and productivity. The global market offers a range of order pickers to suit different operational needs.
No. A perfect vacuum, which can also be referred to as full vacuum or absolute vacuum, would be a volume that contains no matter whatsoever. Outer space comes close with just a few hydrogen atoms per cubic meter, but it never reaches zero and the same is true even in the most technically advanced vacuum systems on Earth.
This device measures the atmospheric pressure and can be used as a barometer (which Torricelli is credited with inventing). The experiment also demonstrated that the space left above the mercury in the inverted tube was a vacuum.
In North America, it’s common to use inHg in the rough vacuum range, Torr in higher vacuum ranges, and microns (thousands of a Torr) for pressures reached by backing pumps.
In other words, many considerations go into selecting the right type of vacuum system for a specific application. To ensure the safety of the system, the required lifting capacity is also multiplied by a factor of two.
The smallest opening (large F stop number) the greater the Depth of Field. The person and the background are sharp when using F 22.

When reaching the pump’s capacity at the suction feet, it is also possible that the leak is the load itself, which causes a loss of negative pressure. A solution is to increase the pump capacity – not in terms of what vacuum level the pump can reach, but in terms of the flow that the pump is capable of evacuating.
Capacitance manometers: A capacitance manometer gauge is a considerably more complex and accurate form of manometer. It uses a tensioned diaphragm with one side being exposed to the volume that is to be measured. The other side contains an electrode assembly with a reference electrode and a pressure-sensing electrode. As the diaphragm deflects relative to the pressure it causes a capacitance change, which is sensed and ultimately converted to an exact measurement.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500