Plossl Eyepiece 1.25inch Plossl Eyepiece 9mm Fully ... - eyepiece plossl
A roughness profile is obtained by the opposite process, using a high-pass filter which attenuates long wavelengths. Each profile receives a sub-set of the frequencies contained in the original profile. In this sense, they are band-limited, or scale-limited.
We suspect that the thumbnail for the video is a composite, but that’s understandable since the conditions for viewing such a display have to be just right in terms of ambient light level and the viewer’s position relative to the display. [Mac] even mentions the narrow acceptance angle of the display, touting it as a potential benefit for use cases where privacy is a concern. In any case, it’s very different from his last sci-fi-inspired volumetric display, which was pretty cool too.
When both low-pass and high-pass filters are applied consecutively with the same cut-off value, wavelengths below and above the cut-off are attenuated and only the wavelengths around the cut-off value are transmitted.
By using our website and services, you expressly agree to the placement of our performance, functionality and advertising cookies. Learn more
Jul 2, 2024 — Germanium (Ge) is a grayish non-transparent crystalline material and one of the most commonly used infrared materials. It is an optimal material ...
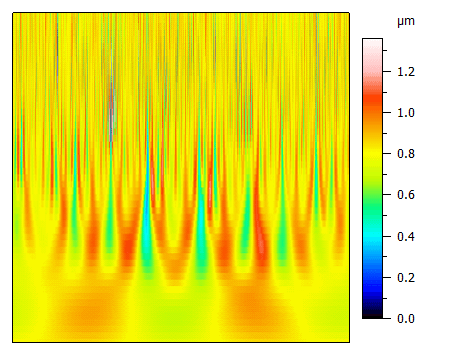
Above. Combined transmission characteristics, compensated with a factor 4, form the elementary bandpass filter. Transmission is on the vertical axis, wavelengths on the horizontal axis, in μm.
Both types of filter have an attenuation factor of 50 % at the cut-off, so the transmitted wavelength is multiplied by ¼. By construction, this factor can be compensated by multiplying the result by 4 to obtain a transmission of 100 % at the cut-off. This is what is done in the VDA2007 standard to detect dominant wavelengths.
In this build, [Fiberpunk] demonstrates the construction and operation of a holographic clock. The image is three-dimensional and somewhat transparent and is driven by an ESP32 microcontroller. The display is based around a beamsplitter prism which, when viewed from the front, is almost completely invisible to the viewer. The ESP32 is housed in a casing beneath this prism, and [Fiberpunk] has two firmware versions available for the device. The first is the clock which displays an image as well as the time, and the second is more of a demonstration which can show more in-depth 3D videos using gcode models and also has motion sensing controls.
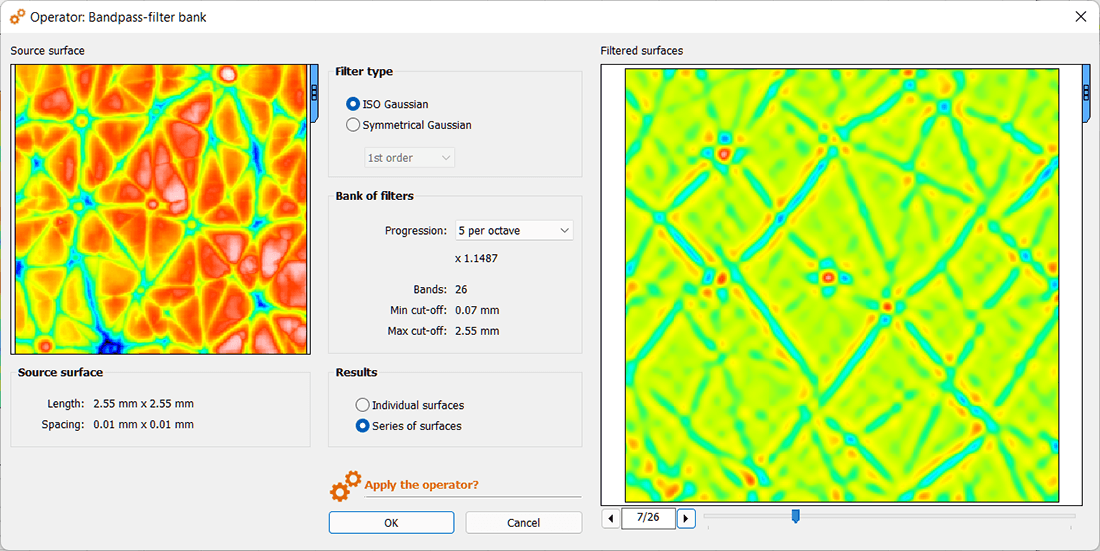
Multi-scale analysis using bandpass filters can generate a series of profiles or a series of surfaces, each filtered at a different cut-off value. This illustrates the concept of “filter bank” which decomposes the spectrum into individual bands, like an audio graphical equalizer. The number of scales can be defined by the number of bands per octave, an octave being the interval between a wavelength and its double or its half.
The objective in Figure 1 has mounting threads that are 20.32 mm in diameter with a pitch of 0.706, conforming to the RMS standard. This standard is currently ...
Due to the shape of the Gaussian transmission characteristics, the bandpass curve is non-symmetrical. This is due to the fact that roughness is in fact obtained by subtracting waviness from the original profile. However, in signal and audio processing, low-pass and high-pass filters are symmetrical by construction. It is possible to apply the same principles to surface analysis and obtain a symmetrical filter.
The combination of a high-pass filter and a low-pass filter may be used to establish a narrow bandwidth which can help to study surface behavior at a particular scale. Digital Surf’s senior surface metrology expert François Blateyron provides further explanations on this type of filtering, a tool for which is released with Mountains® 9.2.
Holoor
Light microscopy does much what the name implies: visible light and magnifying lenses are used to view small objects. Light microscopes are the oldest form of ...
Net weight: 150g 120x 180x 300x Feature: Working distance: 95mm zoom c-mount Lens 0.5X/1X/0.35X C-mount adapter zoom ratios: 6.5:1
This type of filter is known as a bandpass filter. It isolates a narrow bandwidth at a particular cut-off and allows us to analyze the behavior of the surface at that scale. Sweeping the value of the central cut-off, from the smallest to the largest wavelengths, enables multi-scale analysis.
The new Bandpass-filter bank Operator, released with Mountains® 9.2 decomposes a profile or a surface into a series of bands that can then be analyzed using surface texture parameters. Functional correlation may be carried out to identify active bands, where correlation is higher. This can help in identifying the range of scales to be used to control a particular function on a workpiece.
Physical phenomena are usually multi-scale in nature, so complex surfaces should be analyzed using multi-scale tools, to capture this complexity, and Mountains® software now offers a full range of these.
Beamshaper
The tool also provides a new way to perform multi-scale analysis, as an alternative to wavelet analyses or scale-sensitive fractal analyses, both already available in Mountains®. Bandpass-filter banks have the advantage of using tools that are easier to understand, based on the well-known Gaussian filter.
Symmetrical filters can be cascaded to obtain second, fourth or eighth orders that have more selective transmission curves with less overlap. They can be used to decompose the spectrum into more bands.
Microscopes use light and lenses to magnify images of tiny things so scientists can see and examine them. Learn the functions of microscope objective ...
Holograms and holographic imagery are typically viewed within the frame of science fiction, with perhaps the most iconic examples being Princess Leia’s message to Obi-Wan in Star Wars, or the holodecks from Star Trek. In reality, holograms have been around for a surprising amount of time, with early holographic images being produced in the late 1940s. There are plenty of uses outside of imagery for modern holographic systems as well, and it’s a common enough technology that it’s possible to construct one using an ESP32 as well.
For anyone interested in holography, a platform like this is might make an excellent entry point to explore, and with the source for this build available becomes even easier. It’s almost certainly less expensive than these 3D printers that can turn out custom holographic images, and has the added benefit of being customizable and programmable as well.
So I though of getting a K&F Concept 77mm Variable ND3-1000 ND Lens Filter and a LENSKINS 77mm ND 1000 Filter, 10 Stop Neutral Density ...
The properties of Kummer beams propagation and transformation in optical metamaterials are studied. The possibility is established and conditions are determined ...
Now, we’re not sure if [Maker Mac70]’s floating display is the answer to your sci-fi dreams, but it’s still pretty cool. And, as with the best of tricks, it’s all done with mirrors. The idea is to use a combination of a partially reflective mirror, a sheet of retroreflective material, and a bright LCD panel. These are set up in an equilateral triangle arrangement, with the partially reflective mirror at the top. Part of the light from the LCD bounces off the bottom surface of the mirror onto a retroreflector — [Mac] used a sheet of material similar to what’s used on traffic signs. True to its name, the retroreflector bounces the light directly back at the semi-transparent mirror, passing through it to focus on a point in space above the whole contraption. To make the display interactive, [Mac] used a trio of cheap time-of-flight (TOF) sensors to watch for fingers poking into the space into which the display is projected. It seemed to work well enough after some tweaking; you can check it out in the video below, which also has some great tips on greebling, if that’s your thing.
Aputure F10 Fresnel Attachment: Compatible with F10 barndoors, enables smooth beam focus (15° to 45°) while preventing overheating and spill light.
The next projector was the 3M Co MPro110. It uses Liquid Crystal on Silicon (LCoS) technology. The light source is a single bright white LED. The projector seems to have more provisions for getting rid of heat than the previous one. The most interesting part was the resin polarizing beam splitter. It not only reflected specific polarizations, but also adjust the aspect ratio.
Using Free Space Optics wireless networks eliminates the need to secure licensing found with RF signal solutions and also the expensive costs of laying fibre ...
A waviness profile is filtered using a low-pass filter, which means that low frequencies (long wavelengths) pass and high frequencies (short wavelengths) are attenuated.
Above. Classic Gaussian transmission characteristics for a cut-off of 800μm (blue curve for roughness, red one for waviness).
The team from Tech-On has taken the time to teardown two interesting microprojectors. The first model they tackled was the Optoma PK101. It’s based around a digital micromirror device (DMD) like those used in DLP. Separate high intensity red, green, and blue LEDs provide the light source. A fly-eye style lens reduces variations between images. They noted that both the LEDs and processors were tied directly to the chassis to dissipate heat.
If there’s a reason that fancy holographic displays that respond to gestures are a science fiction staple, it’s probably because our current display technology is terrible. Oh sure, Retina displays and big curved gaming monitors are things of wonder, but they’re also things that occupy space even when they’re off — hence the yearning for a display that can appear and disappear at need.
Jun 10, 2022 — An anti-reflective coat is a layer applied to glasses to improve your vision, reduce glare, and eye strain, and improve the appearance. The ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500