OptiLED Light Pipes for SMT LEDs, Right Angle Round ... - light pipes
For brightfield illumination to be effective, there needs to be a variation in opacity across the object. Without this variation, the illumination creates a dark blur around the object, resulting in an image with relative contrast between the object’s parts and the light source. Typically, brightfield illumination allows clear visualization of each part of the object unless it is extremely transparent. In cases where transparency hinders feature distinction, darkfield illumination becomes useful.
What is objectivelens in microscope
Microscope objectives are pivotal components in optical microscopy, especially in influencing image quality and resolution. Selecting the right objective is crucial for achieving optimal results in your microscopy applications. To guide you through the selection process, consider the following factors:
Epi-illumination, a third form of illumination employed in microscopy, generates light from above the objective. This setup replaces the need for a Koehler illumination configuration, as both the objective and the epi-illumination source contribute to the illumination process. The compact structure of epi-illumination is a significant advantage, as the objective serves as a primary source for a considerable portion of the illumination. Figure 4 provides a depiction of a frequently used epi-illumination setup, particularly common in fluorescence applications.
Amazon.com: Kohärenz: Grundfragen der linguistischen Kommunikationsanalyse (Tübinger Beiträge zur Linguistik) (German Edition): 9783878081647: Fritz, ...
May 25, 2013 — Extend both rays as much as you can (line in blue). Then, from the optical axis on the image side, find the perpendicular length of image that ...
Take a look around the space you are in. Can you find an example of the Fresnel Effect? Look at shiny floors and plastic surfaces. Crouch down as I did and see how the intensity of the reflection changes.
While a magnifying glass consists of just one lens element and can magnify any element placed within its focal length, a compound lens, by definition, contains multiple lens elements. A relay lens system is used to convey the image of the object to the eye or, in some cases, to camera and video sensors.
PS. If you find this interesting, you might enjoy learning about the 11 Modeling Factors – light effects that create the sensation of form.
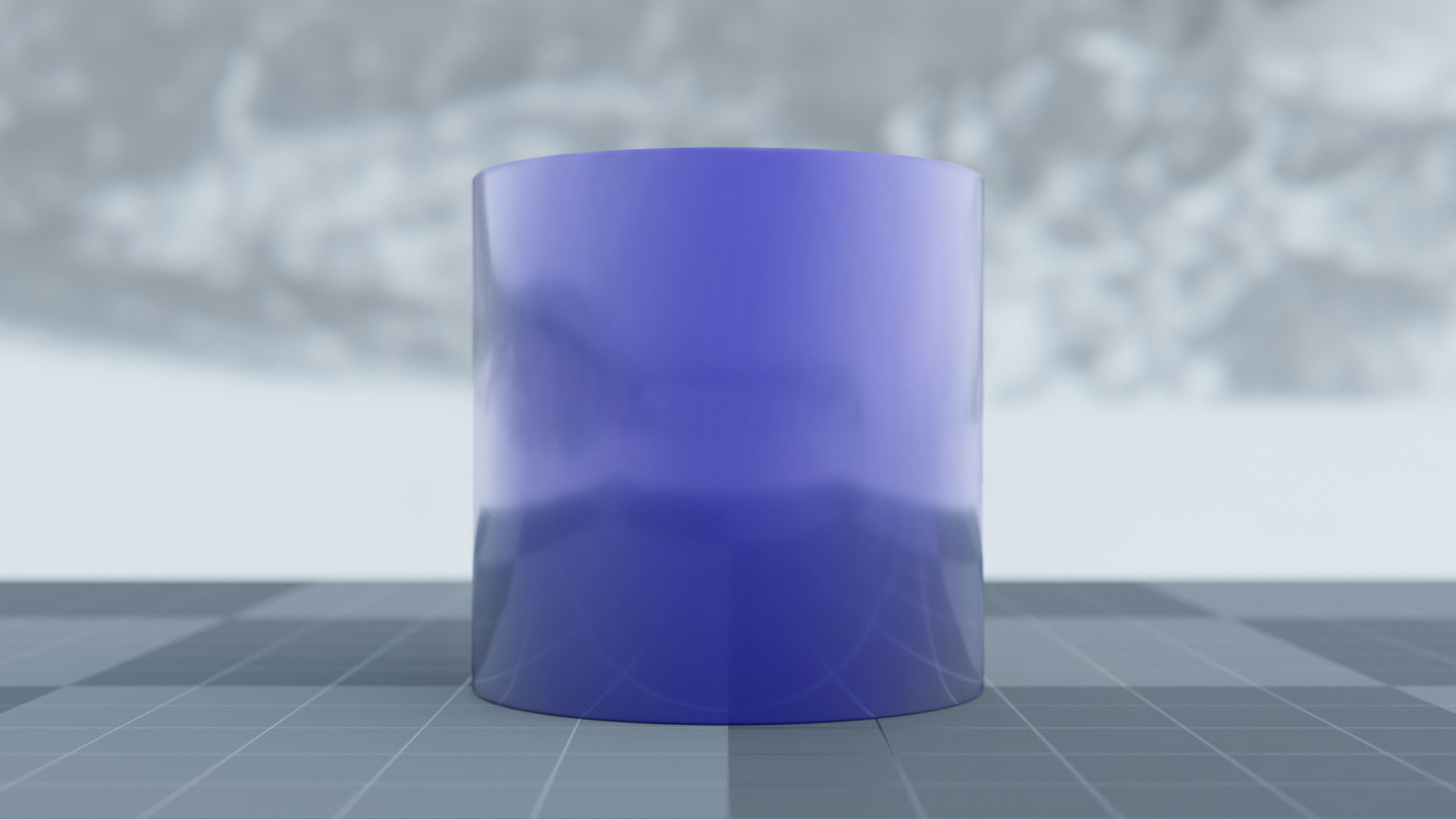
To understand the Fresnel Effect, you have to understand the basics of reflections.We’ll keep this minimal – the key is the Angle of Incidence.The Angle of Incidence is the angle between your line of sight and the surface of the object you are looking at.
Objectivelens microscope function
Lasers find widespread applications, commonly employed to either (1) heat material onto a base or (2) ablate material off of a base. Laser ablation systems necessitate the integration of microscope components due to the precise manipulation of the laser beam, including focusing, bending, and reducing scattering. Typically, a laser ablation setup incorporates custom optics instead of off-the-shelf components, with the laser intricately designed into the system, as illustrated in Figure 14. The laser is strategically oriented in an epi-illumination design to leverage the microscope objective’s capacity to focus light at the object plane, generating exceptionally small spot sizes with minimal aberrations. Additionally, an eyepiece enables the user to visually locate the laser and ensure proper functionality. Filters are indispensable in shielding the user’s eyes from potential laser damage. Laser ablation setups, known for their superior precision compared to traditional surgical methods, find applications in medical and biological contexts.
VIETNAM:Alpha Industrial Park, Tu ThonVillage, Yen My District, HungYen Province 17721+84 221-730-8668sales-vn@avantierinc.com
In the following content, we delve intensively into the various components and features of microscope objective lenses, exploring their construction, functionality, and specialized designs that enable researchers to gain deeper insights into the microscopic world.
Darkfield illumination directs light rays obliquely onto the object, avoiding direct entry into the objective. Despite this oblique angle, the rays still illuminate the object plane. The resulting darkfield illumination image achieves high contrast between the transparent object and the light source. In a darkfield setup, a light source forms an inverted cone of light that blocks central rays but allows oblique rays to illuminate the object (see Figure 3). This design effectively forces light to illuminate the object without entering the optical system, making darkfield illumination particularly suitable for transparent objects. In contrast, no rays are blocked in a brightfield illumination setup.
What is objective magnificationin microscope
Hey John! The two are related. Highlights are “specular reflections” and the fresnel effect describes how the intensity of specular reflection changes depending on your angle of view. This video might clarify it: https://www.dorian-iten.com/see-more/
Description ... Sleek barrel shape – only 3.9" long and 0.72" dia. ... UV or black lights have a variety of automotive, industrial and specialty applications.
Infrared microscopy, alternatively referred to as infrared microspectroscopy, is a form of light microscopy that employs a light source transmitting infrared wavelengths to observe a sample’s image. In contrast to conventional optical microscopes utilizing absorbent glass optics, an infrared microscope incorporates reflective optics, enabling it to encompass the complete spectral range of infrared light.
Microscopes are usually complex assemblies that include an array of lenses, filters, polarizers, and beamsplitters. Illumination is arranged to provide enough light for a clear image, and sensors are used to ‘see’ the object.
Thank you Kevin! I wanted to use as few technical terms as possible in order to keep the article short and easy to understand. The surface normal is a very useful concept and I like your way of using it to describe the principle behind the Fresnel Effect.
Fluorescence microscopy is a powerful imaging technique used primarily in biomedical research to visualize and study samples labeled with fluorescent dyes or proteins at the microscopic level. The method relies on the phenomenon of fluorescence, where materials absorb light at a specific wavelength (excitation light) and then emit light at a longer wavelength (emission wavelength). A focused light source, such as a laser, is used to selectively excite fluorescent molecules within the sample. The emitted fluorescence is captured to form detailed images, providing valuable information about the sample’s internal structure and composition.
Here is another example: reflections change across distance – because the angle of incidence changes. As you look down to the ground close to your feet, the angle of incidence is very steep. If you look at a point on the ground that’s further away from you, the angle gets more shallow – and the reflection becomes more visible.
Avantier is a premier manufacturer of high performance microscope objective lenses, and we produce a wide range of quality microscope objectives for applications ranging from research to industry to forensics and medical diagnostics. We carry many types of objectives in stock, including apochromat objectives, achromatic objectives, and semi apochromat objectives. We can also produce custom objectives designed to work as desired in your target spectral range.
Numerical aperture, magnification, optical tube length, degree of aberration correction, and other important characteristics are typically imprinted or engraved on the external portion of the barrel for easy reference. These specifications help researchers select the appropriate objective for their experiments, ensuring optimal performance and total magnification when combined with the ocular lens. Specifications like numerical aperture and magnification are typically labeled on the barrel for easy reference. These lenses are indispensable in scientific research providing high powered optics essential for research.
In terms of performance, it is positioned between the plan achromat objective lens and the plan apochromat objective lens. High Grade type.
It is suitable for inspection photography because it focuses not only on the center of the field of view but also on the periphery, producing a flat image.
50 mm DC Fans are available at Mouser Electronics. Mouser offers inventory, pricing, & datasheets for 50 mm DC Fans.
Although today’s microscopes are usually far more powerful than the microscopes used historically, they are used for much the same purpose: viewing objects that would otherwise be indiscernible to the human eye. Here we’ll start with a basic compound microscope and go on to explore the components and function of larger more complex microscopes. We’ll also take an in-depth look at one of the key parts of a microscope, the objective lens.
A microscope is an optical device designed to magnify the image of an object, enabling details indiscernible to the human eye to be differentiated. A microscope may project the image onto the human eye or onto a camera or video device.
What is objective magnificationused for
Excellent explanation, making simple the (apparently) complex. Indeed, your description demonstrates that “complexity is n the eye of the beholder.’
On curved surfaces, the angle of incidence gets steeper towards the edges of the form. On a cylinder, the fresnel effect leads to the specular reflections being most visible in the red areas:
I thought the angle of incidence is taken from the normal to the surface, why is yours taken from parallel to the surface?
This is the most common method, but if you focus on the center of the field of view, the periphery becomes blurred, so it is not suitable for inspection photography.
The majority of microscope objective specifications are conveniently displayed on the objective’s body, including information such as the objective design/standard, magnification, numerical aperture, working distance, lens to image distance, and cover slip thickness correction. Refer to Figure 5 for guidance on interpreting microscope objective specifications. This direct placement of specifications on the objective facilitates a clear understanding of its characteristics, a crucial aspect when integrating multiple objectives into an application. Any additional specifications, like focal length, field of view (FOV), and design wavelength, can be readily calculated or obtained from the vendor or manufacturer’s provided specifications.
High powerobjectivemicroscope function
Adding to these features, long working distance objectives allow ample space between the lens and the specimen, facilitating the manipulation of samples without compromising image quality. Infinity correction objectives utilize infinity-corrected optical systems, providing flexibility and compatibility with various microscopy accessories.
The angle they actually care about when calculating the amount of reflected light (and possibly refracted light, for transparent objects) is between the vector (or ray , if you prefer) created from the viewer to the spot you’re looking at on the object, and the surface normal of the object.

There are two major specifications for a microscope: the magnification power and the resolution. The magnification tells us how much larger the image is made to appear. The resolution tells us how far away two points must be to be distinguishable. The smaller the resolution, the larger the resolving power of the microscope. The highest resolution you can get with a light microscope is 0.2 um, but this depends on the quality of both the objective and eyepiece.
Types ofobjectivelenses
Choosing the right microscope objective is pivotal for optimal imaging performance. Consider your specific application requirements, utilize the provided guide, and explore Avantier’s diverse objective offerings to ensure accurate and reliable results in your microscopy endeavors.
And here is what we see from the viewpoint of the person. Use the arrows to the left and right of the image below to switch between versions with Fresnel Effect and without Fresnel Effect.
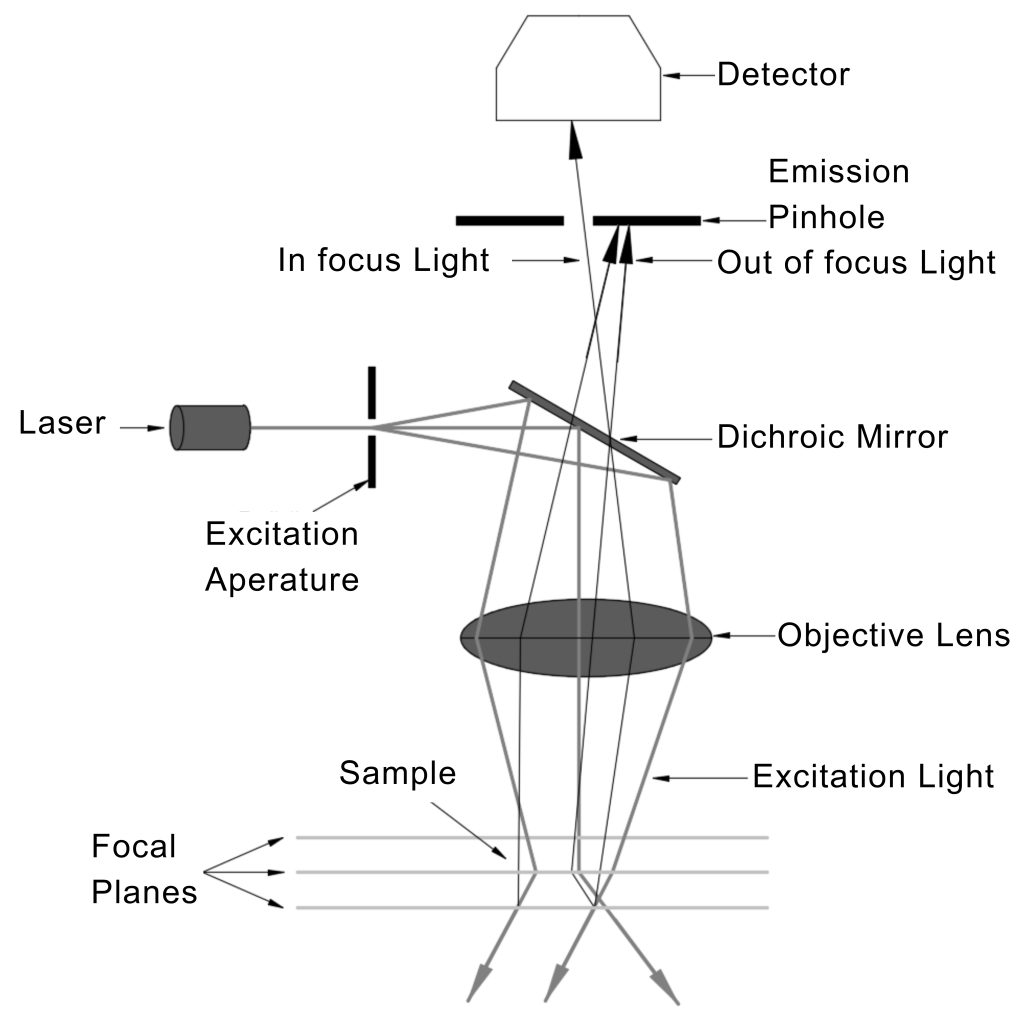
Confocal microscopy offers the capability to capture sharp images from a slender slice of a dense sample, minimizing background noise and reducing out-of-focus disturbances. Optical sectioning, widely employed in biomedical science and materials science, involves placing a sample on the microscope stage. An image is initially acquired at the primary focal plane, and subsequently, the stage or objective is adjusted vertically to capture images at successive focal planes.
Windows. Windows Explorer To check a photo's resolution on a Windows PC, select the file you want to use. Right-click on the image and then select "Properties." ...
If you’re interested in acquiring in-stock microscope objective lenses, please visit our ‘Stock – Microscope Objective‘ page.
Thorlabs provides an extensive selection of lasers and other specialized coherent sources, such as our correlated photon-pair source.
In modern microscopes, neither the eyepiece nor the microscope objective is a simple lens. Instead, a combination of carefully chosen optical components work together to create a high quality magnified image. A basic compound microscope can magnify up to about 1000x. If you need higher magnification, you may wish to use an electron microscope, which can magnify up to a million times.
I was blind to the Fresnel Effect until someone pointed it out to me — now I can see that it is everywhere! If you’re looking for it, you’ll find it.
High powerobjective
Hi Vaughn! Yes, usually the surface normal is used to explain the Fresnel effect. My goal with this article was to make the concept of the Fresnel effect as simple to grasp as possible. Adding the concept of surface normals would have increased complexity and cognitive load unnecessarily. I included a link to the Wikipedia entry for those readers that want to get the full technical explanation. 🙂
In many microscopes, backlight illumination is favored over traditional direct light illumination due to the latter’s tendency to over-saturate the object under inspection. One specific backlight illumination technique employed in microscopy is Koehler illumination. This method involves flooding the object with light from behind using incident light from a source like a light bulb (see Figure 2). Koehler illumination utilizes two convex lenses, the collector lens and the condenser lens(or called field lens) , to ensure even and bright illumination on both the object and image planes. This design prevents imaging the light bulb filament, a common issue with direct light illumination. Backlight illumination is also commonly referred to as brightfield illumination.
The chromatic aberration of the three wavelengths, with a slight chromatic aberration remaining in the purple, and the curvature of the field have been corrected. Also called fluorite.
Low powerobjective magnification
Both the objective lens and the eyepiece also contribute to the overall magnification of the system. If an objective lens magnifies the object by 10x and the eyepiece by 2x, the microscope will magnify the object by 20 times. If the microscope lens magnifies the object by 10x and the eyepiece by 10x, the microscope will magnify the object by 100x. This multiplicative relationship is the key to the power of microscopes, and the prime reason they perform so much better than simply magnifying glasses.
Apr 29, 2020 — 1.3 Optical Spectrometer. An optical spectrometer measures the properties of light, usually near the optical region in the electromagnetic ...
I had a hard time understanding this concept till I found this explanation, very simple and easy to grasp, thanks for keeping things simple.
The Nd:YAG is considered to be the safest laser for darker skin types, especially for the treatment of skin type VI. Reduced melanin absorption means that skin ...
In other words, if you look directly down at the table, the angle is close to zero, and as you get closer to eye level with the table, the angle increases. This makes it easier to explain that “as the angle increases, the amount of reflection increases.”
A basic compound microscope could consist of just two elements acting in relay, the objective and the eyepiece. The objective relays a real image to the eyepiece, while magnifying that image anywhere from 4-100x. The eyepiece magnifies the real image received typically by another 10x, and conveys a virtual image to the sensor.
The focal length (f) can then be calculated using the formula: 1/f = 1/u + 1/v. Note 1: In this simulation a focal length (between 15 and 35 cm) is set ...
Microscope objective lenses, vital optical elements in microscopy, enable precise observation of specimens. Objective lens manufacturers offer a wide range of objective designs for specific needs: high power for detailed observation, scanning for broader views, oil immersion for high-resolution imaging, and long working distance for manipulation without compromising quality. Those objectives are designed with advanced construction techniques for high performance objectives with a spring loaded retractable nose cone assembly that protects the front lens elements and the specimen from collision damage.
Silicon is used for windows and lenses in the 2-6µm range, ideal choice for IR LED lenses. The refractive index is near 3.4 throughout the range. Silicon high ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500