Optik: Neue Quelle für kohärentes Licht? - kohärentem licht
A Raman spectrum therefore consists of a number of bands, each associated with a vibrational mode. The spectrum is unique to the material and enables you to identify it. Some researchers aim to fully understand each Raman band and how it relates to vibrational modes. However, most analysts simply identify samples using a spectral library.
Ramanspectroscopy diagram
25/11/2024 25 novembre. Da oggi sotto il Palazzo del Consiglio una panchina rossa, uno dei simboli della lotta alla violenza contro le donne
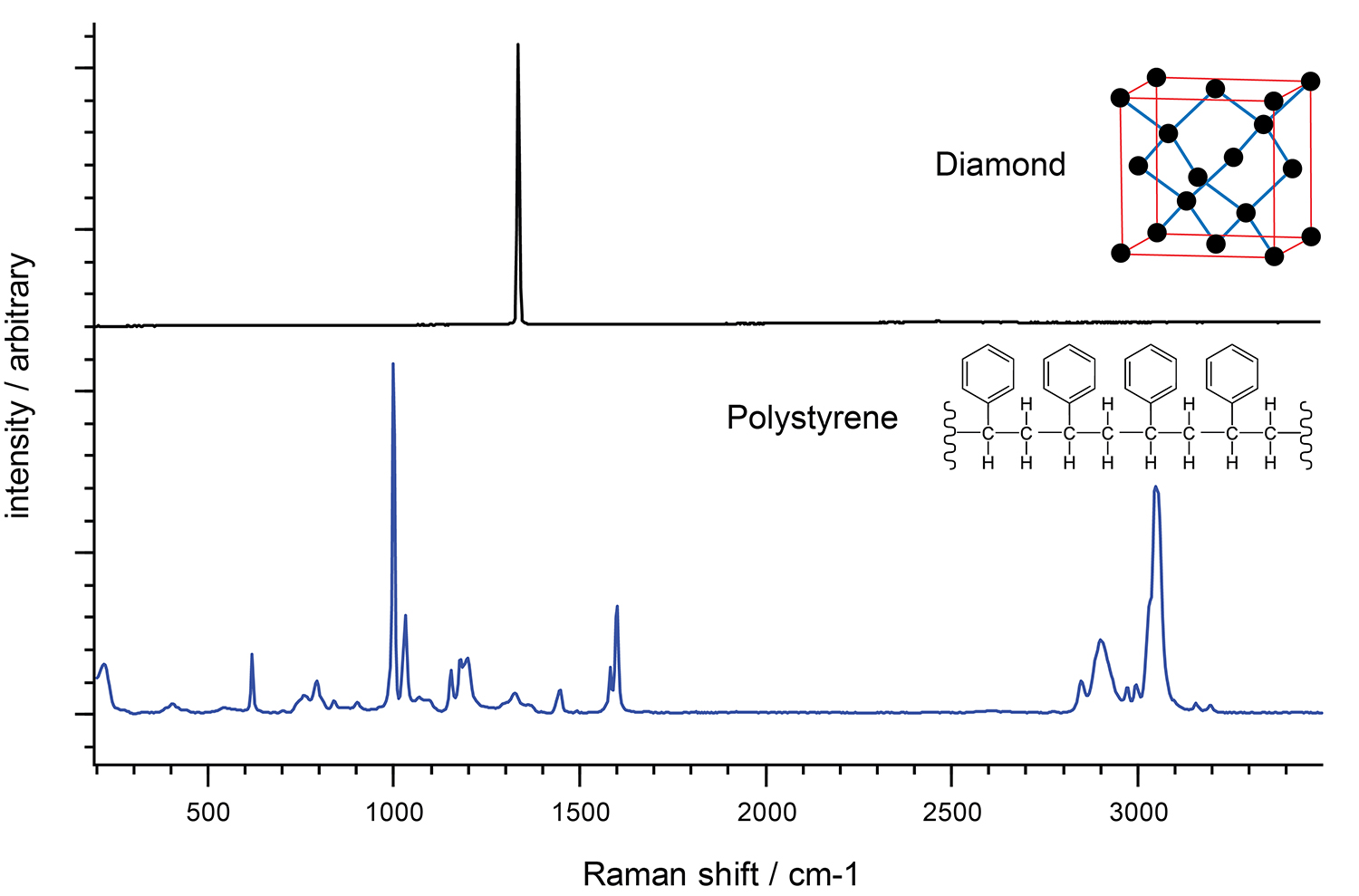
Similarly, we see the vibrations of two carbon atoms linked by strong double bonds (C=C) at around 1600 cm-1. This is at a higher frequency than two carbon atoms linked by a weaker single bond (C-C, 800 cm-1).
What is raman spectrain chemistry
Continue your exploration of Raman and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy. We answer your questions on Raman microscopy, fast Raman imaging, data analysis, fluorescence and complementary analytical techniques.
Ramaneffect
In contrast, the Raman spectrum of polystyrene is more complex. The molecule is less symmetric and has hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms. There are also different bond types connecting the atoms.
We graphically display the results of our Raman spectroscopy measurements as Raman spectra. The y-axis represents the intensity of the scattered light, while the x-axis represents the energy (frequency) of light. We are interested in the shift in frequency of the Raman-scattered light, so we plot the x-axis frequencies relative to that of the laser. We label the x-axis as the Raman shift (shown by the units cm-1).
Low-frequency Raman bandsYou can also study molecular vibrational and rotational modes with low-frequency Raman shifts, below 100 cm-1. These originate from very heavy atoms or very large-scale vibrations, such as the whole crystal lattice vibrating. Renishaw's Raman instruments enable you to study these modes. You can explore a wide range of materials and crystals, easily distinguishing between different crystalline forms (polymorphs) and layered structures.
Raman shifts are sensitive to neighbouring bondsYou can see more subtle effects if you inspect Raman spectra closely. For example, the C-H vibrations of polystyrene appear in two bands, at approximately 2900 cm-1 and 3050 cm-1. The carbons in the former band are part of aliphatic carbon chains, whereas the carbons in the latter band form part of aromatic carbon rings.
Ideally, you would use a Raman instrument with high spectral resolution across the whole Raman range. This gives you better chemical specificity. You can then identify, differentiate and investigate a wider range of materials.
What is raman spectraand how does it work
One way of understanding a Raman spectrum is to consider the molecular functional groups as distinct units. This makes it easy to interpret the Raman spectrum of crystals with a regular array of identical atoms, all in the same configuration. For example, diamond contains carbon atoms in a regular tetrahedral network. In these cases, you often see just one dominant Raman band because there is just one molecular environment of the crystal.
Ramanpeak identification Table
Ramanspectroscopy instrumentation
We can identify unknown materials from their unique Raman spectral fingerprints, typically using software searches of spectral libraries. We use the Raman bands in the fingerprint region (from 300 cm-1 to 1900 cm-1) to identify molecules.
You can study differences in material structure by comparing their Raman spectra. You could quantify the degree of crystallinity and distinguish similar crystal forms (polymorphism) of the same chemical. To do this, you would need a Raman spectrometer with high spectral resolution, such as an inVia™ confocal Raman microscope.
22/11/2024 Riaperti i termini per l’acquisizione delle candidature per l’elezione delle componenti la Commissione regionale per la realizzazione della parità tra uomini e donne di cui alla legge regionale 13 giugno 1989, n. 39
You can interpret Raman spectra to identify chemicals and get structural information. Raman scattering results from the interaction of light with molecular vibrations. These vibrations are very sensitive to changes in chemistry and structure, so you can spot subtle differences in molecular environment. Generally, all materials produce Raman spectra, except for pure metals.
Characteristic vibrational frequencies of chemical bondsThe frequencies of vibration depend on the masses of the atoms involved and the strength of the bonds between them. Heavy atoms and weak bonds have low Raman shifts. Light atoms and strong bonds have high Raman shifts.
Ramanspectroscopy PDF
Raman spectra of two polyethylene samples showing differences in intensities and band widths. These spectral differences are due to varying degrees of crystallinity.
22/11/2024 Militari della Brigata Sassari feriti in Libano. La solidarietà del Presidente Comandini: “Il Governo nazionale intervenga per garantire la sicurezza”
In the polystyrene spectrum, we see the high frequency carbon-hydrogen (C-H) vibrations at about 3000 cm-1. The low frequency carbon-carbon (C-C) vibrations are at around 800 cm-1. The C-H vibrations have a higher frequency than the C-C vibrations because hydrogen is lighter than carbon.
Raman spectra of diamond and polystyrene. The Raman spectrum of polystrene is more complex than that of diamond due to differing bond types.
What is raman spectraused for
You can view the vibrations of a complex molecule as partly consisting of many simple diatomic vibrations. However, you should also consider the vibrations of larger groups of atoms to get a full understanding of the Raman spectrum. For example, the Raman spectrum of polystyrene has a band at 1000 cm-1. This is due to the expanding and contracting ‘breathing mode' of the aromatic carbon ring in polystyrene.






 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500