Optics and Lasers Careers | American Institute of Physics - optics and lasers
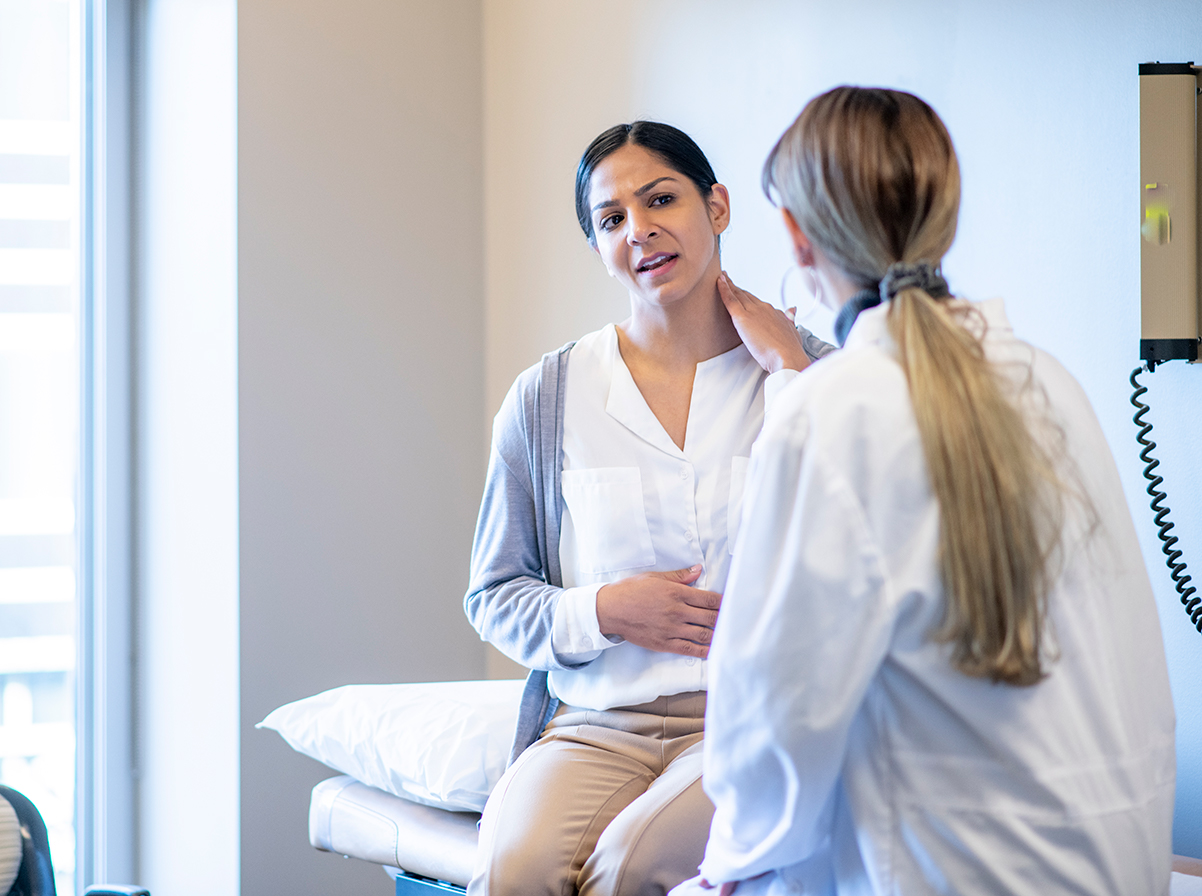
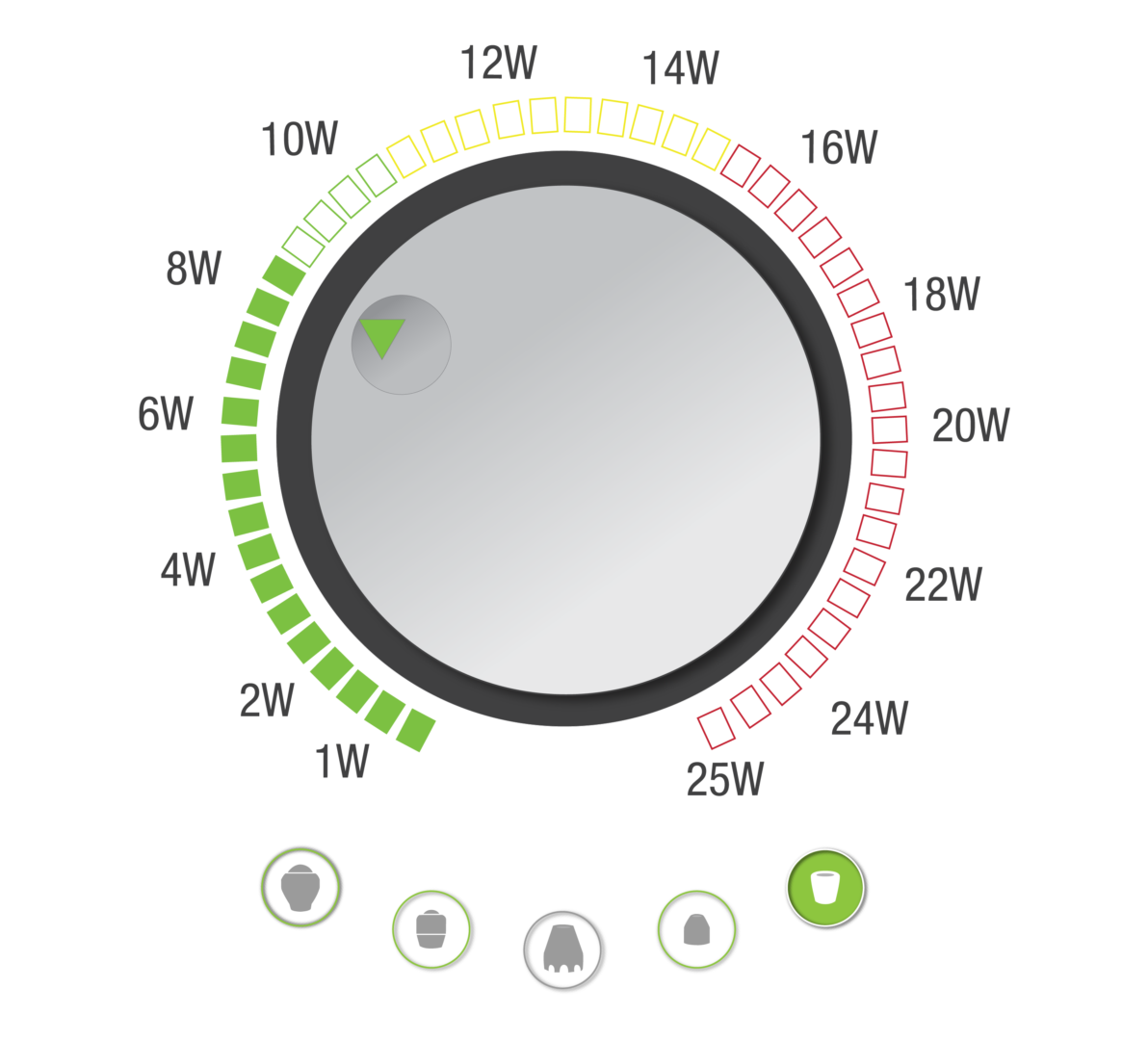
Smarter than your average laser. The new LightForce 25W XPi’s technology is smart enough to give real-time visual and haptic feedback on dosing speed to help provide the most effective patient treatments.
The Orthopaedic Section of the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) has an ongoing effort to create evidence-based practice guidelines for…
Partsof microscope

"Even in one treatment sometimes, we’ve had patients who’ve had problems for months with discomfort walk out and say I can already tell the difference."
The Orthopaedic Section of the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) has an ongoing effort to create evidence-based practice guidelines for…
Purpose of microscopein microbiology
"A professional footballer I worked with had a wound that hadn’t healed post-operation. At 11 weeks post-op, he still had a hole in his foot. Knowing what I’d learned, I started using the laser on a lower power and you could literally watch it begin to heal. Within a week of use, the hole had closed up and after two-and-a-half weeks, it has really knitted together well. For a professional footballer with a hole in his foot, laser therapy was literally game-changing."
Though modern microscopes can be high-tech, microscopes have existed for centuries â this brass optical microscope dates to 1870, and was made in Munich, Germany.
Introductionof microscope
"The medical staff has made this therapy device ‘one of our go to’ tools when treating sprains, strains, and other muscular skeletal conditions. The ease of application makes the whole treatment very efficient. I am confident in saying that the LiteCure laser helped us get our players back on the court faster. It also helped us keep injured players in action through some painful conditions."
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Designed for busiest practices who desire the fastest, most effective treatment solution, the 40W LightForce® XLi brings science and technology together to treat deeper structures more efficiently, making it easier to impact pain.
Purpose of microscopepdf
Adhesive capsulitis (also termed frozen shoulder) is a common condition characterised by spontaneous onset of pain, progressive restriction of movement…
What is objective lens inmicroscope
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Across the medical community, LightForce® Therapy Lasers are used to treat chronic and acute musculoskeletal conditions as well as post-activity recovery. As a non-drug, non-surgical solution, LightForce® Therapy Lasers have been proven to reduce pain without the side effects of medication.

Objective lensmicroscopefunction
While some older microscopes had only one lens, modern microscopes make use of multiple lenses to enlarge an image. There are two sets of lenses in both the compound microscope and the dissecting microscope (also called the stereo microscope). Both of these microscopes have an objective lens, which is closer to the object, and an eyepiece, which is the lens you look through. The eyepiece lens typically magnifies an object to appear ten times its actual size, while the magnification of the objective lens can vary. Compound microscopes can have up to four objective lenses of different magnifications, and the microscope can be adjusted to choose the magnification that best suits the viewerâs needs. The total magnification that a certain combination of lenses provides is determined by multiplying the magnifications of the eyepiece and the objective lens being used. For example, if both the eyepiece and the objective lens magnify an object ten times, the object would appear one hundred times larger.
This site collects information about you. To learn more about what we collect and how we use that information, see our Privacy Policy. If you do not wish DJO, LLC to share your information with our partners, please make adjustments in our Privacy Policy section.
LightForce's built-in protocols recommend which treatment heads are acceptable or not recommended for different power levels. The smart handpiece recognizes which head is in use and recommends the appropriate power level based on the selected head.
“The American College of Physicians (ACP) developed this guideline to present the evidence and provide clinical recommendations on noninvasive treatment…
Individual results may vary. Neither DJO, LLC nor any of the Enovis companies dispense medical advice. The contents of this website do not constitute medical, legal, or any other type of professional advice. Rather, please consult your healthcare professional for information on the courses of treatment, if any, which may be appropriate for you.
Typesof microscope
The 40W LightForce® XLi is equipped with the Empower IQ™ Delivery System that assesses the operator’s speed and gives real-time visual and sensory feedback, achieving more effective treatments and improving dosing accuracy.
A microscope is an instrument that is used to magnify small objects. Some microscopes can even be used to observe an object at the cellular level, allowing scientists to see the shape of a cell, its nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles. While the modern microscope has many parts, the most important pieces are its lenses. It is through the microscopeâs lenses that the image of an object can be magnified and observed in detail. A simple light microscope manipulates how light enters the eye using a convex lens, where both sides of the lens are curved outwards. When light reflects off of an object being viewed under the microscope and passes through the lens, it bends towards the eye. This makes the object look bigger than it actually is.
National Geographic Society is a 501 (c)(3) organization. © 1996 - 2024 National Geographic Society. All rights reserved.
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
Management of rotator cuff disease may include use of electrotherapy modalities (also known as electrophysical agents), which aim to reduce…
Importanceof microscope
LightForce® is leading the way in clinical research and evidence-based laser therapy treatment. Our innovations are founded on the science of reducing pain and inflammation.
The dissecting microscope provides a lower magnification than the compound microscope, but produces a three-dimensional image. This makes the dissecting microscope good for viewing objects that are larger than a few cells but too small to see in detail with the human eye. The compound microscope is typically used for observing objects at the cellular level.
"I think our outcomes have significantly improved since using Deep Tissue Laser Therapy™. I think we get a better result sooner meaning that patients feel better faster. I think they like it, so the come in more often, and they ask for it."
A microscope is an instrument that can be used to observe small objects, even cells. The image of an object is magnified through at least one lens in the microscope. This lens bends light toward the eye and makes an object appear larger than it actually is.
Over the course of the microscopeâs history, technological innovations have made the microscope easier to use and have improved the quality of the images produced. The compound microscope, which consists of at least two lenses, was invented in 1590 by Dutch spectacle-makers Zacharias and Hans Jansen. Some of the earliest microscopes were also made by a Dutchman named Antoine Van Leeuwenhoek. Leeuwenhoekâs microscopes consisted of a small glass ball set inside a metal frame. He became known for using his microscopes to observe freshwater, single-celled microorganisms that he called âanimalcules.â




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500