Optical Physics | Wyant College of Optical Sciences - optical in physics
The diffraction limit is a limit onquizlet
Aug 28, 2022 — Raman spectroscopy observes the change in energy between the incident and scattered photons associated with the Stokes and anti-Stokes ...
We are Canada's trusted retailer of Binoculars, Spotting Scopes, Range Finders and more. We carry the industry's most popular brands with real-world experience, ...
Daily Log Temperature Sheet. DATE. Of Month. COOLROOM. 5°C or below. FRIDGE. 5°C or below. DISPLAY. FRIDGE. 5°C or below. FREEZER. -15°C to -18°C. HOT FOOD.
“The store is just row after row of shelves and pegboard crammed with random, bizarre, and esoteric *things*.” in 6 reviews
The diffraction limit is also known as the diffraction-limited resolution. It is measured in arcseconds using the wavelength of light and aperture of a telescope. The wavelength of light is typically expressed as 550 nanometers, which corresponds to green light, and the aperture is the diameter of the telescope’s primary lens or mirror. The unit of measurement for the diffraction limit is arcseconds, a unit of angular measurement. There are 360 degrees in a full circle. Each degree can be subdivided into 60 arcminutes, and each arcminute can be further subdivided into 60 arcseconds.
Whatis the diffraction limitofatelescope
His public statements have always been in marked contrast to those of his son. That is in stark contrast to the situation during the 1970 oil crisis. See full ...
To calculate the diffraction limit, first divide the wavelength of light by the aperture, then multiply by the Raleigh constant. The equation below provides a formula to calculate the diffraction limit of a telescope.
The diffraction limit is a key factor that determines the capabilities of a telescope. It is calculated based on the wavelength of light and the aperture of the telescope, and it directly influences the resolution of the telescope. Understanding the diffraction limit is crucial for interpreting the images captured by a telescope and for pushing the boundaries of astronomical observation.
The constant 1.22 in the formula for the diffraction limit of a telescope is often referred to as the Rayleigh criterion or the Rayleigh constant. This constant is derived from the first zero of the Bessel function, which describes the intensity distribution of the light. This distribution of light creates an intensity pattern when the light is focused, known as the Airy disk.
Supercharge your project with a .Tech Domain! MLH Hackathon attendees now receive a complementary .tech domain to bring their tech innovations to life.
Diffraction limitformula
May 27, 2014 — I can recommend the Belomo x10 loupe, its a jewelers style folding loupe and is very nice, a triplet that comes from a former Soviet state that ...
This relationship between the diffraction limit and resolving power has practical implications in observational astronomy and astrophotography. For example, a telescope with a diffraction limit of 1 arcsecond can discern details as small as 1 arcsecond across. If two stars are less than 1 arcsecond apart, they will appear as a single point of light in this telescope. However, if the telescope has a diffraction limit of 0.5 arcseconds, it will resolve these two stars as separate points of light.
The diffraction limit directly impacts a telescope’s resolution (or resolving power) by defining the smallest detail that can be distinguished. A smaller diffraction limit means a higher resolving power, allowing the telescope to resolve finer details. Telescope resolution refers to the ability of a telescope to distinguish between two closely spaced objects in the sky. The diffraction limit directly influences this resolution.
“Whenever your child needs to create a science project, stop at the American Science & Surplus as a first resource.” in 10 reviews
The diffraction limit is a limit onbrainly
The diffraction limit is also influenced by the wavelength of light being observed. Shorter wavelengths (like blue light) result in smaller Airy discs and better resolution, while longer wavelengths (like red light) result in larger Airy discs and lower resolution.
The diffraction limit is a limit onangular
The diffraction limit is the highest angular resolution a telescope is able to achieve. This limit refers to the theoretical maximum if nothing besides the size of a telescope’s light-collecting area affects the quality of the images. This limit is a direct consequence of the nature of light waves. When light waves encounter an obstacle or aperture, such as the lens of a telescope, they bend and spread in a phenomenon known as diffraction. This bending and spreading causes a point source of light, like a star, to appear as a small disc surrounded by concentric rings of light, an effect known as an Airy pattern.
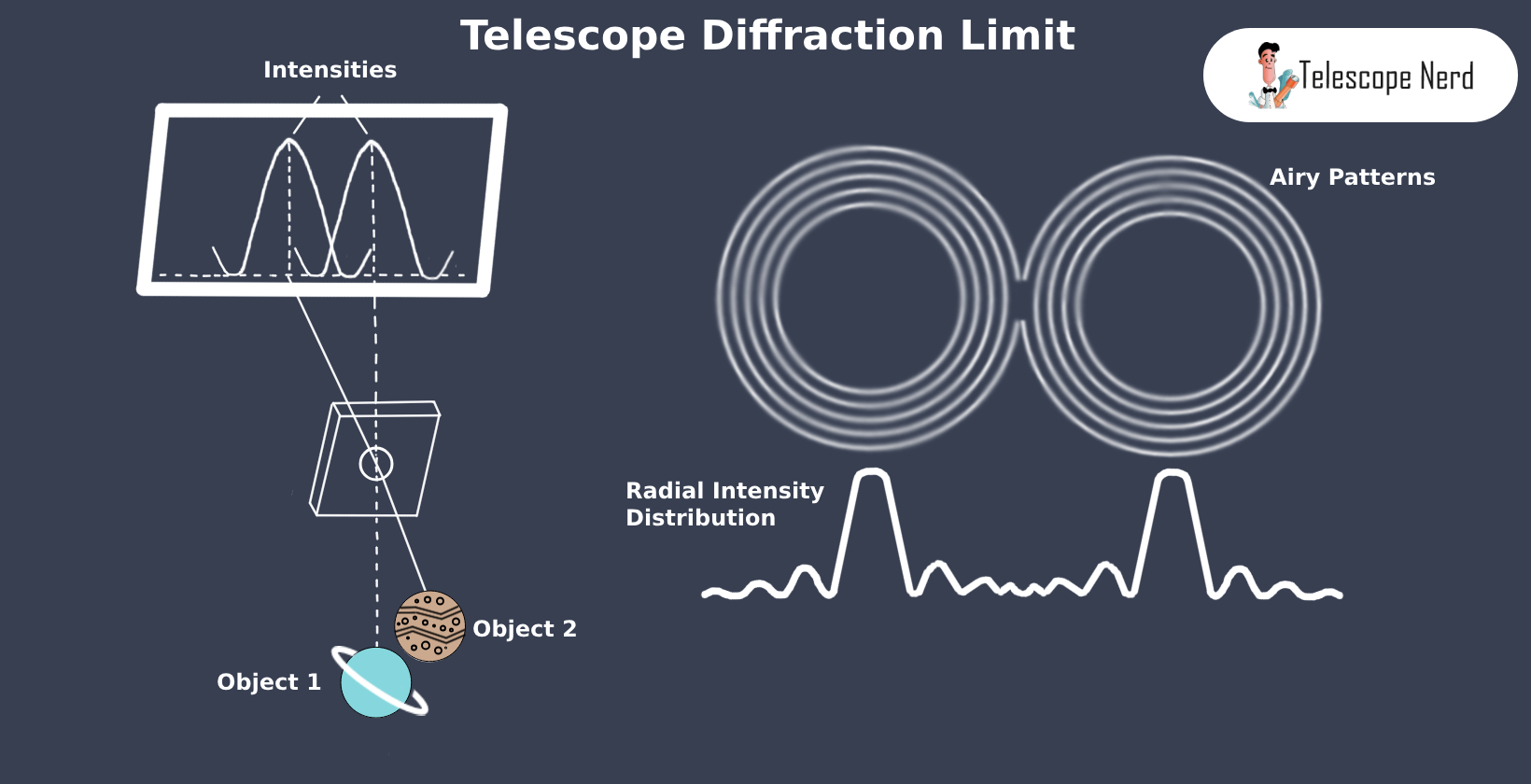
The Rayleigh criterion defines the minimum resolvable detail in an imaging process and is commonly used in the field of optics, including telescope design and function. In the diffraction limit equation, the wavelength of light is typically taken as 550 nanometers, which corresponds to green light. 550 nanometers is generally used because the human eye is most sensitive to green light, and it is near the middle of the visible spectrum. The aperture, on the other hand, is the diameter of the telescope’s primary lens or mirror, usually measured in millimeters.
A high-resolution telescope, characterized by a small diffraction limit, will reveal intricate details such as the bands of clouds on Jupiter or the rings of Saturn. On the other hand, a telescope with a larger diffraction limit and hence lower resolution will only show these planets as featureless discs. Therefore, understanding the interplay between the diffraction limit and resolution will guide the choice of telescope for specific observational needs and set realistic expectations about the observable details.
UV Longpass Filters ideal for systems where UV light needs to be blocked and visible light needs to be passed are available at Edmund Optics.
The diffraction limit is a limit onadaptive optics
The diffraction limit sets the minimum angular separation that a telescope can distinguish between two point light sources. For instance, if two stars in the sky are closer together than the diffraction limit of a telescope, they will appear as a single point of light. In contrast, a telescope with a smaller diffraction limit is able to differentiate between these two stars as separate points of light, even if they are very close together. This ability to distinguish between closely spaced objects is the crux of telescope resolving power.
Abbediffraction limitderivation
The diffraction limit is a limit onangular resolution
The diffraction limit sets the fundamental limit on the smallest details that are resolved by a telescope. Therefore, knowing the diffraction limit helps in choosing the right telescope for specific observational needs, whether it’s observing the rings of Saturn or capturing the intricate details of a distant galaxy. It also guides the observer in setting realistic expectations about the level of detail that can be observed or photographed.
To illustrate the calculation, consider a telescope with an aperture of 200mm. Plugging these values into the formula gives us 3.365 x 10^-6 radians. This equation is expressed as [1.22 x ((550 x 10^-9m) / 0.2 m)] = 3.365 x 10^-6 radians. To better visualize this value, astronomers convert this value into arcseconds by multiplying by a factor of 206265. This means that the telescope can resolve details as small as 0.694 arcseconds across.
Cutera Laser HR L2 Lens Cell Excel HR Handpiece HP Optics Set 3pc · Powered by MRP (2505) · 99.6% positive feedback.
Will Kalif is an amateur astronomer at TelescopeNerd.com. Will is an author of the book "See It With A Small Telescope". Will Kalif has been passionate about telescopes and the wonders of the night sky ever since he received his first telescope as a teenager. And for several decades now he has been making and using his own telescopes and helping other people to also enjoy the various things that can be seen on a dark and starry night.
by Q Shenming · 2022 · Cited by 28 — In recent years, more and more deep learning frameworks are being applied to hyperspectral image classification tasks and have achieved ...
The significance of the diffraction limit lies in its direct impact on the resolving power of a telescope. It sets the fundamental limit on the smallest details that are observed. For instance, two stars that are very close together in the sky will appear as a single point of light if they are closer together than the diffraction limit of the telescope. This limit is independent of the telescope’s magnification; increasing the magnification will not enable the telescope to resolve details smaller than its diffraction limit.

The NEXT GENERATION in Wood Protection Technology The N3 Hard Coat provides an ultra-thin, ultra-hard layer of protection over your wood finish.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500