Optical led diffuser with fixing screws - optical diffuser
Working with Empire Optics to upgrade our Fluorescence microscope was a great experience. They were extremely attentive, and we are incredibly happy with the outcome.
Bestaspheric optics
A spherical lens with a significant amount of aberration and an aspherical lens with almost no aberration can be seen(Figure 1). Aspherical Lenses address the issue by deviating from a perfectly spherical shape. An aspheric lens can be designed by modifying the curvature length and adjusting the conic constant and aspheric coefficients of the curved surface of the lens. By carefully shaping the lens, aspheric lenses ensure that all incoming light rays converge to a single focal point. minimizing spherical aberration and improving image quality.
Fabricating aspherical lenses poses greater challenges due to their complex surface profiles compared to conventional spherical lenses. Various methods are available for producing aspheric lenses, each with its distinct advantages and limitations.
One of the most important features of aspheric lenses is their ability to correct for spherical aberration. Spherical aberration is found in all spherical lenses, such as plano-convex or double-convex lens shapes. However, aspheric lenses excel in focusing light to a precise point, resulting in minimal blur and enhanced image quality. Spherical Aberration is the consequence of the uniform curvature of the lens surface and not the result of a manufacturing error. The outer rays converge at a different focal point than the inner rays resulting in blurred or distorted images.
Aspheric opticsprice
VisiLED Brightfield Ringlights provide incident (Top Down) Illumination. The 400.265 Brightfield Ringlight S80-65 has an 81 mm ID to fit significant diameter research grade stereo microscope objectives like those found on Zeiss Stereo Discovery and Leica M Series.
Asphericlens benefits

When the aspheric coefficients are equal to zero, the resulting aspheric surface is considered to be a conic. The following table shows how the actual conic surface generated depends on the magnitude and sign of the conic constant, k.
Asphericmeaning
The Schott VisiLED product line is a group of professional LED illumination components designed for the most demanding applications in Stereo Microscopy.
The choice of materials for aspherical lenses is influenced by factors such as wavelength requirements and manufacturing cost. The following summarizes materials compatible with each manufacturing process.
We spoke with Nick and the Digital Microscope he suggested is working great. It is super easy to operate and checks all our boxes.
The advantages custom aspheric lenses bring to high-performance optics are substantial. Particularly, these lenses are an optimal choice when designing systems with a limited footprint, as their inherent characteristics lend themselves well to compact assemblies.
Asphericlens vs spherical
Asphericlenses advantages disadvantages
Unlike conventional spherical optics, aspheric lenses use less elements to enhance aberration correction. An example would be zoom lenses. Zoom lenses typically use ten or more elements while two aspheric lenses can be replaced for a handful of spherical lenses in order to achieve similar or better optical results. The system size and overall cost of production are also potentially reduced.
Custom aspheric lenses play a crucial role in advancing high-performance imaging across various fields. From aerospace applications like night vision imaging optics to defense imaging systems, and from microscope imaging objectives to semiconductor wafer inspection tools, these lenses serve as indispensable components in precision imaging devices. A notable example is the Smite Cassegrain telescope, which utilizes custom aspheric lenses along with reflective elements to mitigate aberrations and achieve superior resolution.
In various industries, ranging from automotive sensors and LED lighting systems to cutting-edge cameras and medical diagnostic devices, the significance of aspheric lenses is steadily growing. These lenses are part of the subset defined by rotationally symmetric optics with a radially varying radius of curvature. Aspheric lenses play an increasingly crucial role in various aspects of the optics, imaging, and photonics industries. This is attributed to the unique advantages they provide compared to traditional spherical optics and spherical elements.
Asphericlens glasses
Unlike spherical lenses, which can be specified solely by the radius of curvature that fluctuates radially from the center of the lens, aspheric lenses exhibit a surface with varying local radii of curvature. The definition of rotationally symmetric aspheres often involves a surface sagitta (the measure of the surface shape in relation to a plane), or sag, expressed through an even aspheric polynomial.
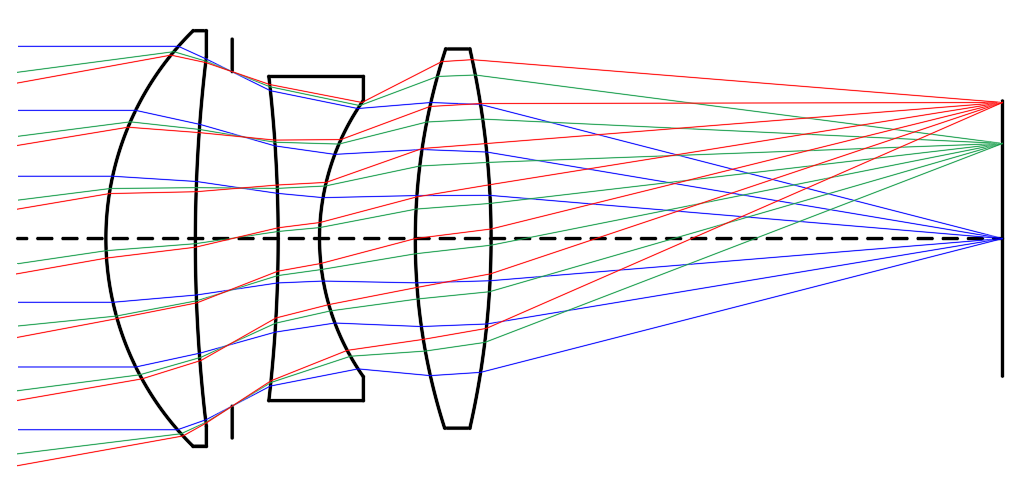
To achieve the necessary performance of an imaging lens, optical elements designers frequently resort to stopping down, or increasing the f/# of their design. Although the desired resolution goal is obtained, the approach results in a reduction in light throughput. Using aspheric lenses in the design, however, improves aberration correction and enables the creation of high-throughput systems with low f/#s, while also maintaining excellent image quality. The following table compares two designs: an 81.5mm focal length, f/2 triplet lens (depicted in Figure 2) with all spherical surfaces and the same triplet with an aspheric first surface. Both designs utilize identical effective focal length, f/#, field of view, glass types, and total system length. The table provides a comparison of the modulation transfer function (MTF) at 20% contrast for on-axis and off-axis collimated, polychromatic light rays at 486.1nm, 587.6nm, and 656.3nm. The triplet lens with the aspheric surface demonstrates significantly improved imaging performance at all field angles with high tangential and sagittal resolution values, surpassing those of the triplet with only spherical surfaces by factors as high as four.
Aspherical lens photography
In Figure 1, the difference in focusing performance of spherical lenses and aspheric lenses is further explained by the table below. It compares the performance of a spheric lens and an aspheric lens both with a diameter of 25mm and focal lengths of 25mm (f/1 lenses). The table presents a comparison of spot sizes, or blur sizes, for collimated 587.6nm light rays under different conditions: on-axis (0° object angle) and off-axis (at 0.5° and 1.0° object angles). The spot sizes of the asphere are significantly smaller, differing by several orders of magnitude compared to those of a spherical lens.
I really appreciate the level of personalized support Empire Optics offers. No matter what the issue is, we get help immediately.
For optical engineers, a crucial aspect is comprehending manufacturing techniques and selecting the most appropriate method based on lens application, performance requirements, development cost, sample cost, production part cost, and project timeline.
VIETNAM:Alpha Industrial Park, Tu ThonVillage, Yen My District, HungYen Province 17721+84 221-730-8668sales-vn@avantierinc.com




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500