Optical Design Software for SOLIDWORKS and Rhino ceros - optical design software
CCD stands for charge-coupled device. It is an image sensor technology that turns light into electrical signals for digital image capture. CCDs are made up of an array of light-sensitive capacitors known as pixels, which store and transfer charge during the image capture process
CMOS is an abbreviation for complementary metal-oxide semiconductor. It is a type of image sensor technology that is commonly used in digital cameras, cellphones, and other imaging devices. For digital image capture, CMOS sensors transform light into electrical signals. CMOS sensors, as opposed to CCD sensors, integrate amplifiers and converters at the pixel level, which results in a different operational mechanism.
This diagram shows the hazard distances of a 5 mW green laser pointer. It is an eye hazard up to 52 feet from the laser, causes temporary flashblindness to 260 feet, causes glare and visual disruption to 1,200 feet, and is a distraction to 11,700 feet (2.2 miles). Click to enlarge.
DrawbacksCCD sensors have some drawbacks. They require more power than CMOS sensors, which results in increased heat generation. CCDs' readout speeds are also slower, limiting their utility in high-speed applications. In addition, CCD sensors are more expensive to manufacture than CMOS sensors.
Cmos vs ccd image sensorprice
Charge Storage:In a CCD sensor, each pixel has a potential well (a capacitor) that can hold and store the generated charge. During the exposure duration, the photoelectrons are collected and accumulated in the potential well.
CMOS vs CCDcomparison table
Tutorials Point is a leading Ed Tech company striving to provide the best learning material on technical and non-technical subjects.
CCD sensor
Charge TransferFor further processing, the accumulated charge in each pixel must be transmitted from one pixel to the next. A series of shift registers moves the charge along rows or columns within the sensor to accomplish this transfer.
This shows five typical battery-powered lasers, along with their eye and skin hazard distances, and the distances at which they can cause visual interference to persons such as aircraft pilots. Click to enlarge.
This movement may also be due to the illuminated person moving their head and eyes to avoid directly staring into the beam.In both cases, the laser light does not have as much time to stay on one spot on the retina. This reduces the chance of causing a lesion or burn.Of course, if a laser is powerful enough and a person is close enough — say, within the NOHD and certainly within the ED50 distance — a brief 1/4 second exposure can cause a retinal lesion.But for laser illuminations of pilots at aircraft distances of many hundreds or thousands of feet, even powerful lasers are considered by experts to be unlikely to cause serious or permanent harm.
Analog-to-Digital Conversion:An analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) turns the analogue voltage signal into a digital value when the charge is transferred to voltage. Each pixel's intensity or brightness is represented by a digital value.
Public domain photo from the U.S. FAA, showing how a laser beam spreads over long distances and can fill the windscreen. The FAA’s highest-resolution version is here.
CCD (charge-coupled device) and CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensors are two types of image sensors that are often used in digital cameras, camcorders, and other imaging devices. While both CCD and CMOS are used to capture and transform light into electrical signals, they differ in terms of underlying technology and performance
Charge-to-Voltage AmplificationEach pixel in a CMOS sensor has its own charge-to-voltage amplifier. The charge generated in the photodiode is amplified within the pixel, producing a voltage signal proportional to the amount of charge.
Cmos vs ccd image sensorcost
Structure:A CCD sensor consists of an array of pixels that are arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is a photosensitive element capable of detecting light and converting it into an electrical charge.
Light DetectionSimilar to CCDs, when light strikes a pixel's photodiode, it generates photoelectrons through the photoelectric effect. The number of photoelectrons produced is proportional to the incident light intensity.

A helicopter being deliberately targeted by a laser pointer. The light is a distraction and, if bright enough, can cause temporary flashblindness. It is NOT likely to cause any permanent injury. A video of this incident is here.

CCD vs CMOSpros and cons
AdvantagesCCD sensors have typically provided a number of benefits, including great image quality with low noise levels, a broad dynamic range, and excellent color accuracy. They are well-suited for high-quality image applications such as professional photography and scientific imaging
Signal Processing:CMOS sensor data, like CCD sensor data, can undergo additional signal processing, such as noise reduction, color interpolation, and image enhancement. Typically, this processing is performed by the camera's image processing pipeline.
“Dumb Ways to Blind” is a 2014 public service video that warns the Internet generation about the many ways lasers can be misused. As of February 2024, this has had almost 10 million views on YouTube.
In most incidents, the beam only directly hits the aircraft windscreen a few times. That’s because it is almost impossible to hand-hold a laser onto a target hundreds or thousands of feet away. For example, these frames show 8 seconds of a laser illumination. Only in one of the frames — 1/2 second out of 8 — does a direct hit obscure the pilot’s vision. Of course, the waving beam is a distraction.
Tutorials Point is a leading Ed Tech company striving to provide the best learning material on technical and non-technical subjects.
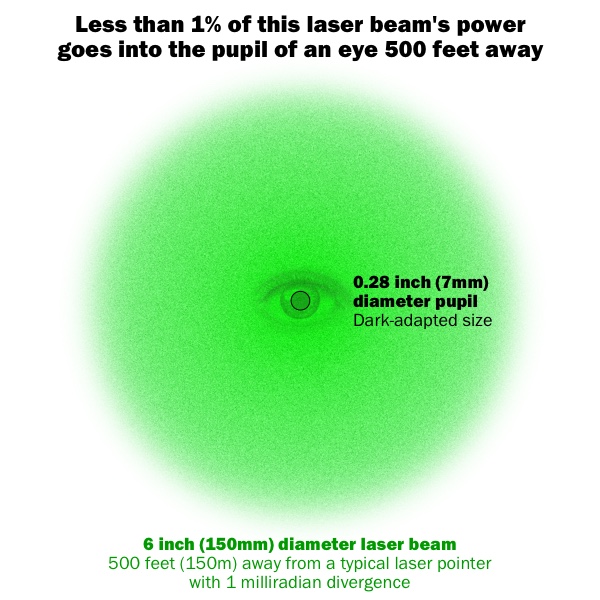
That’s why a laser beam that can pop balloons or light cigarettes up close, could be eye-safe hundreds of feet away.Now, an eye-safe beam may still be very bright. It could cause temporary flashblindness, or vision-blocking glare, or be a distraction. This would be a hazard to persons such as pilots during critical phases of flight. The second part of the calculator above lists the distances for those visual interference hazards.
DrawbacksWhile CMOS sensors have made tremendous advances, they have always had lower image quality than CCD sensors. However, as technology has advanced, the image quality gap has decreased dramatically. In low-light circumstances, CMOS sensors may nevertheless have greater noise levels and a lower dynamic range than CCDs.
This diagram shows various ways to help reduce laser pointer incidents. These include: pilot training and glasses, arrests and prosecutions, laser labeling, user education, and new laws & restrictions. Click to enlarge.
In conclusion, CCD and CMOS image sensors are two types of image sensors used in digital imaging devices. CCD sensors store and transport charge using capacitors, whereas CMOS sensors use individual pixels with in-built amplifiers and converters.
Cmos vs ccd image sensorreddit
It is important to note that technological developments have minimized the performance gap between CCD and CMOS sensors. The decision between the two is influenced by unique application needs as well as desired trade-offs in image quality, power consumption, and cost.
Light Detection:When light strikes a pixel, the photoelectric effect produces photoelectrons. The number of photoelectrons produced is proportional to the incident light intensity.
Analog-to-Digital ConversionAn analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) within each pixel turns the analogue voltage into a digital value after the charge has been amplified into a voltage signal. Each pixel's digital value represents its intensity, or brightness.
CMOS vs CCDastrophotography
CCD vs CMOS sensor imagequality
Pixel ReadoutCMOS sensors use a parallel readout architecture in which the digital value of each pixel is read out from the sensor at the same time. This parallel reading enables faster frame rates than CCDs, making CMOS sensors suitable for high-speed image capture applications.
Structure:A CMOS sensor, like a CCD sensor, consists of an array of pixels arranged in rows and columns. A light-sensitive photodiode, a charge-to-voltage amplifier, and an analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) are all built into each pixel.
In April 2019 the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration posted this animated powerpoint. The narration says "…pointing a laser at an aircraft can distract or temporarily blind the pilot, potentially putting the lives of many innocent passengers at risk. That's why it's a federal crime with serious consequences like fines up to $250,000 or up to five years in jail…"
The ED50 distance is about 1/3 of the NOHD. At the ED50 distance, there is a 50/50 chance of the laser causing the smallest medically noticeable retinal lesion under laboratory conditions where both the laser and the eye are stationary. Often such a lesion will heal, in the same way that a minor skin burn can heal. Beyond the ED50 distance, the chance of having a retinal lesion is further reduced.For a 5 mW 1 mrad laser, the ED50 distance is 16 feet. For a 499 mW 1 mrad laser, the ED50 distance is about 164 feet.This helps explain why a laser that is nominally hazardous at a certain distance (the NOHD) is extremely unlikely to cause even a small injury at that distance.There is more information about the NOHD and the ED50 distance on this page.
Signal ProcessingThe CCD sensor's digital image data can be further processed, such as through noise reduction, color interpolation, and image enhancement. These operations are usually handled by the camera's image processing pipeline.
Serial Readout:The charge is serially read out once it has been transported to the desired spot within the sensor. Each pixel contains a charge-to-voltage amplifier that converts the charge into a voltage signal.
CCD (charge-coupled device) and CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensors are two types of image sensors that are often used in digital cameras, camcorders, and other imaging devices. While both CCD and CMOS are used to capture and transform light into electrical signals, they differ in terms of underlying technology and performance Read this article to find out more about CCD and CMOS and how they are different from each other What is CCD? CCD stands for charge-coupled device. It is an image sensor technology that turns light into electrical signals for digital image capture. CCDs are made up of an array of light-sensitive capacitors known as pixels, which store and transfer charge during the image capture process Features of CCD Technology Here are some of the important features of CCD technology: Structure:A CCD sensor consists of an array of pixels that are arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is a photosensitive element capable of detecting light and converting it into an electrical charge. Light Detection:When light strikes a pixel, the photoelectric effect produces photoelectrons. The number of photoelectrons produced is proportional to the incident light intensity. Charge Storage:In a CCD sensor, each pixel has a potential well (a capacitor) that can hold and store the generated charge. During the exposure duration, the photoelectrons are collected and accumulated in the potential well. Charge TransferFor further processing, the accumulated charge in each pixel must be transmitted from one pixel to the next. A series of shift registers moves the charge along rows or columns within the sensor to accomplish this transfer. Serial Readout:The charge is serially read out once it has been transported to the desired spot within the sensor. Each pixel contains a charge-to-voltage amplifier that converts the charge into a voltage signal. Analog-to-Digital Conversion:An analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) turns the analogue voltage signal into a digital value when the charge is transferred to voltage. Each pixel's intensity or brightness is represented by a digital value. Signal ProcessingThe CCD sensor's digital image data can be further processed, such as through noise reduction, color interpolation, and image enhancement. These operations are usually handled by the camera's image processing pipeline. AdvantagesCCD sensors have typically provided a number of benefits, including great image quality with low noise levels, a broad dynamic range, and excellent color accuracy. They are well-suited for high-quality image applications such as professional photography and scientific imaging DrawbacksCCD sensors have some drawbacks. They require more power than CMOS sensors, which results in increased heat generation. CCDs' readout speeds are also slower, limiting their utility in high-speed applications. In addition, CCD sensors are more expensive to manufacture than CMOS sensors. What is CMOS? CMOS is an abbreviation for complementary metal-oxide semiconductor. It is a type of image sensor technology that is commonly used in digital cameras, cellphones, and other imaging devices. For digital image capture, CMOS sensors transform light into electrical signals. CMOS sensors, as opposed to CCD sensors, integrate amplifiers and converters at the pixel level, which results in a different operational mechanism. Features of CMOS Technology Following are some of the important features of CMOS technology: Structure:A CMOS sensor, like a CCD sensor, consists of an array of pixels arranged in rows and columns. A light-sensitive photodiode, a charge-to-voltage amplifier, and an analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) are all built into each pixel. Light DetectionSimilar to CCDs, when light strikes a pixel's photodiode, it generates photoelectrons through the photoelectric effect. The number of photoelectrons produced is proportional to the incident light intensity. Charge-to-Voltage AmplificationEach pixel in a CMOS sensor has its own charge-to-voltage amplifier. The charge generated in the photodiode is amplified within the pixel, producing a voltage signal proportional to the amount of charge. Analog-to-Digital ConversionAn analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) within each pixel turns the analogue voltage into a digital value after the charge has been amplified into a voltage signal. Each pixel's digital value represents its intensity, or brightness. Pixel ReadoutCMOS sensors use a parallel readout architecture in which the digital value of each pixel is read out from the sensor at the same time. This parallel reading enables faster frame rates than CCDs, making CMOS sensors suitable for high-speed image capture applications. Signal Processing:CMOS sensor data, like CCD sensor data, can undergo additional signal processing, such as noise reduction, color interpolation, and image enhancement. Typically, this processing is performed by the camera's image processing pipeline. DrawbacksWhile CMOS sensors have made tremendous advances, they have always had lower image quality than CCD sensors. However, as technology has advanced, the image quality gap has decreased dramatically. In low-light circumstances, CMOS sensors may nevertheless have greater noise levels and a lower dynamic range than CCDs. Difference between CCD and CMOS The following table highlights the major differences between CCD and CMOS: Characteristics CCD CMOS Integration Limited integration capabilities It can be easily integrated with other electronic components on a chip. Cost Higher manufacturing costs. Lower manufacturing costs. Speed Slower readout speeds Faster readout speeds, suitable for high-speed applications Power Consumption higher power consumption Lower power consumption Technology Utilizes capacitors to store and transfer charge. Uses individual pixels with integrated amplifiers and converters. Image Quality Excellent image quality, especially in low-light conditions Improved image quality but traditionally lower than CCDs. Shutter Mechanism Global shutter mechanism Rolling shutter mechanism Noise Levels Low noise levels High noise levels Dynamic Range higher dynamic range Improved dynamic range Conclusion In conclusion, CCD and CMOS image sensors are two types of image sensors used in digital imaging devices. CCD sensors store and transport charge using capacitors, whereas CMOS sensors use individual pixels with in-built amplifiers and converters. It is important to note that technological developments have minimized the performance gap between CCD and CMOS sensors. The decision between the two is influenced by unique application needs as well as desired trade-offs in image quality, power consumption, and cost.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500