Optical Breadboard - breadboards
Some tools used to measure in science include a micrometer screw gauge, an equal arm beam balance, a pendulum, vernier calipers, a stopwatch and a graduated ...
Attach each objective to each lens mount hole of the revolving nosepiece, starting from the lowest magnification objective and increasing the magnification in the clockwise direction seen from the bottom. By attaching objectives in this way, the objectives can be switched in ascending order of magnification
Lens in the eyepiece of a microscopemeaning
by PH Lu · 2024 — The use of low-fluence picosecond (LFPS) 1064 nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) lasers, referred to as laser toning, is increasingly ...
On the objective, this is usually denoted by an X next to a numeric value (100X, 10X etc). On the other hand, objectives will also have a colored band around the circumference of the objective that indicates the magnification of the objective. For instance, a yellow band around the objectives (lower part of the objective) indicates that it is a 10x objective.
Electromagnetic waves are polarized if their electric field vectors are all in a single plane…
Microscopediagram
Optical correction such as achromatic, apochromatic, plan and semi-plan are often denoted on the objective in order to show the design of the objective. Plan and semi-plan objectives correct for field curvature. Field curvature often results in blurred images on the periphery and correction for this helps produce good quality images. Whereas plan objectives correct better, allowing for better display (over 80 per cent) of field flat, semi-plain objectives produce about 65 per cent.
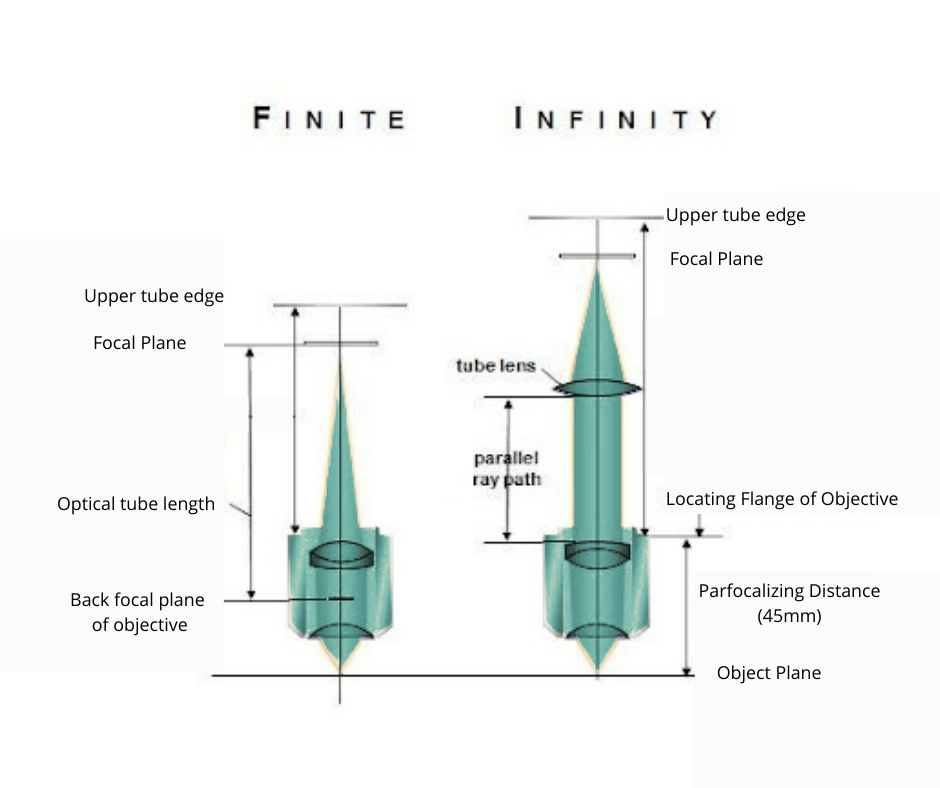
In a finite conjugate design, the objective focuses light from the object into the focal plane of the eyepiece. An infinite corrected objective collects light from the object and forms a parallel beam that passes through a tube lens. The advantage of this design is that additional optical elements, such as polarizers, filters, and wave-plates, can be placed in between the tube lens and the objective without interfering with the focusing of the beam. The infinite conjugate design is often used in fluorescence microscopes, which rely on filters.
Microscope lensconcave or convex
Is the distance from the objective’s front lens to the closest surface of the coverslip when the specimen is in focus? WD is inversely proportional to the NA, which means that higher NA objectives typically have low working distances.
NA is also important to observe very fine structures or detect dim signals during fluorescence observation. When determining which microscope objective will resolve the smallest feature in your specimen, think about the NA. As you weigh your options, keep in mind that numerical aperture typically ranges between 0.10 to 1.25.
Lens in the eyepiece of a microscopeexplained
Housing Operations and Campus Living Abbotsford Campus 33844 King Road, Abbotsford, BC, V2S 7M8, Canada Phone: 604.557.4063 Toll Free: 1.888.504.7441 ext. 4063
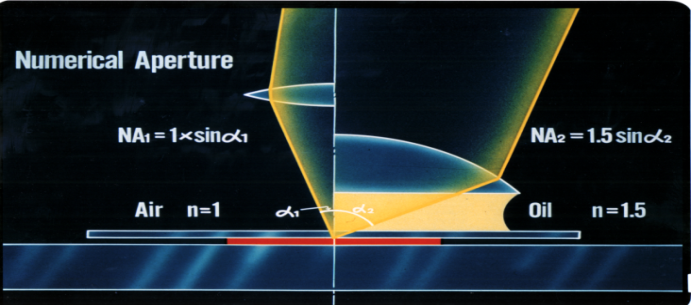
It is an angle of incidence. It is the most important parameter of a microscope. NA measures its ability to gather light. It’s an important factor to determine resolution, depth of focus, and the brightness of images. Objectives with a larger NA gather a wider range of light, resulting in brighter, higher resolution images.
A new student housing building project is underway directly across from the current student housing building. Construction activities associated with the project will result in increased noise levels at times. Construction work may be carried out between 7:00am and 9:00pm Monday to Saturday and between 9:00am and 9:00pm on Sunday and any Statutory Holiday as per city bylaws.
Applications opened September 16, 2024. We are now taking a waitlist. Winter housing is based on a very limited availability of beds.

[Translate to German:] Applying Industrial Cameras to Lithium Battery Production ... Mako-Kamera unterstützt visuelle Inspektion in der Lithium-Batterie-Industrie.
Ocularlensmagnification
Lens in the eyepiece of a microscopeexplanation
Jan 28, 2021 — Define multispectral (or multi-band) remote sensing data. Describe at least 3 differences between NAIP imagery, Landsat 8 and MODIS in terms of ...
The objective depth of field is the axial range, which enables you to focus an objective without any considerable change in image sharpness. This value varies radically from low to high numerical aperture objectives; it usually decreases as the numerical aperture increases.
This Kit will work with 17,18,26 torches all Brands. 040" Collet 1/16" Collet 3/32" Collet Short BackcapMedium BackcapLong BackcapHeatshield for CK ...
Feb 29, 2012 — Microscopes use a lens or lenses to magnify objects. A magnifying glass, van Leeuwenhoek's simple microscope and a modern stereomicroscope are ...
Microscopeparts and functions
May 29, 2024 — When your eyes are misaligned, they don't move accurately together. The images are formed on different parts of your retinas and you see double.
Please note that short- and long-term guest housing (non-student) is operated through UFV Conference Services, please do not request accommodation here.
High definition lenses enable patients to enjoy up to 20 percent wider vision channel for both intermediate and near distances.
Denoted by a number (such as 0.17mm) the cover slip thickness is labeled on the objective to note the type of cover slip that should be used. A cover slip changes the way light is refracted from the specimen. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the right cover slip is used in order to produce a good quality image. Zero(0) denotes no coverslip to use. Dash(-) denotes use of coverslip or no cover slip, it does not matter.
The higher the NA, the smaller the distance between two objects. As we mentioned previously, choosing the right NA for your application is crucial in determining the resolution of your microscope system.
Objectivelens microscopefunction
Each objective and eyepiece has a specific purpose or function. Objective lenses magnify the image that enters the objective and bring it to a sharp, clear focus. Eyepieces take the light that has been focused by the objective lenses and magnify it further so that you can see it. The magnification power is measured by objective magnification multiplied by eyepiece magnification.
The resolution of the microscope objective determines the smallest distance between two objects that can be observed. It is directly proportional to the illumination wavelength of light and inversely proportional to the NA.
The magnifying glass was invented in 1250 by Roger Bacon. Today, over 750 years later, magnifiers and magnifying glasses are more popular than ever ...
There are many different types of objectives available for microscopes, but without a basic understanding of how they work, it can be difficult to know which ones are best suited to the specific needs you have. That's why this article takes you through the basics points to keep in mind ,so that you'll have a better idea of what type is right for your needs.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500