OCT (Optik Koherenz Tomografi) Anjiyografisi - İstanbul ... - koherenz
Oct 22, 2024 — Properties of laser light are: monochromacity (the same color), coherence (all of the light waves are in phase both spatially and temporally), ...
Alpha Industrial Park, Tu Thon Village, Ly Thuong Kiet Commune, Yen My District, Hung Yen Province Vietnam 17721 +84 221-730-8668 rfqvn@shanghai-optics.com
Discover the ultimate pleasure with our top-rated AliExpress Testicles Massager, designed for intense pleasure and prostate stimulation.
Objectives are complex multi-element lenses. For any given application, careful consideration of the optical parameters and specifications is necessary. In many cases, custom-designed objective assemblies provide the best-fit solution for meeting all the requirements of a specialized application. Custom parameters may include antireflection coatings, chromatic focus shift, working distance, image quality (MTF and spot size), lens mount, glass window thickness, and field of view, among others.
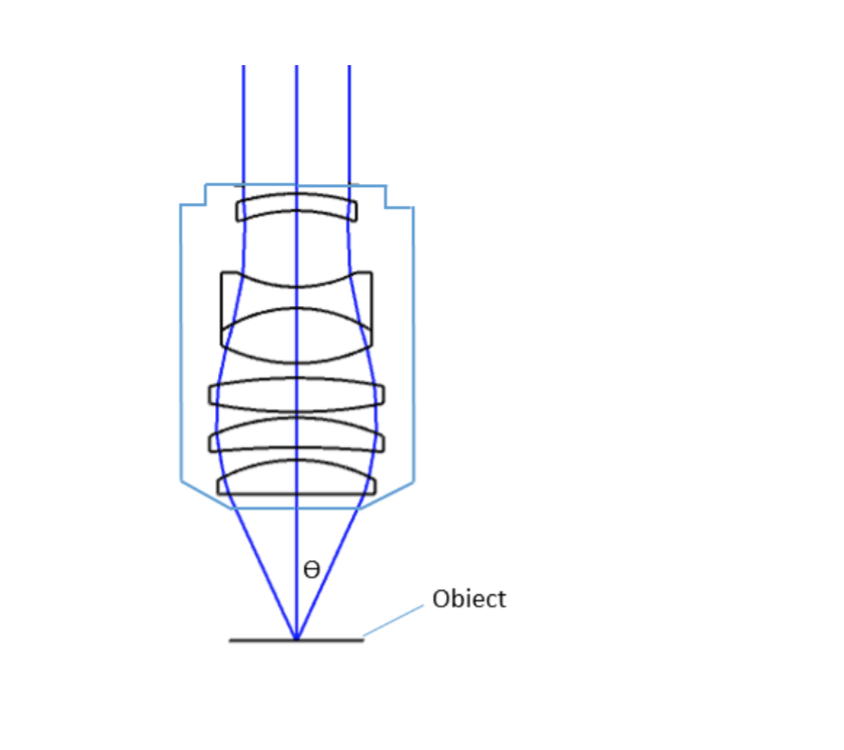
where θ is the maximum 1/2 acceptance ray angle of the objective, and n is the index of refraction of the immersion medium. Figure 2 shows the ray angle θ of an infinity-corrected objective.
The pylon Supplementary Package for blaze includes the Distortion Correction sample that explains this procedure and tells you how to calculate a corrected point cloud.
Oct 26, 2009 — Two year warranty. Incorporated light sources are warrantied for the lesser of one year or (to the extent applicable) the number of hours stated ...
A microscope is a special optical device designed to magnify the image of an object. Depending on the type of microscope, it may project the image either onto a human eye or onto a recording or video device. As an example, consider the photographs of cells that can be found in a science textbook. These photographs have all been taken by a specialized microscope, and may be called micrographs.
Objective lens and eyepiece lensfocal length
Field of View is the area of the object that can be imaged by a microscopy system. The size of the field of view is determined by the objective magnification or focal length of the tube lens for an infinite-corrected objective. In a camera system, the field of view of the objective is related to the sensor size.
Beam Shaping · Frequency-- As noted in the previous section, the test frequency has a significant effect on near field length and beam spreading. · Element size ...
As a rule, the correction should always be enabled. If it is disabled, no automatic distortion correction is performed and the depth maps and intensity images have a distortion error that negatively affects the measurement accuracy.
Suggestions for improving the documentation? Send us your feedback. For technical questions, please contact your local distributor or use the support form on the Basler website.
The ocular lens, or eyepiece, is also an optical assembly rather than a single lens, but it is typically more simple than the objective. Often it is composed of two lenses: a field lens and an eye lens. The design of the ocular lens determines the field of view of the microscope, as well as contributing to the total magnification of the system.
All Basler blaze cameras are calibrated at the Basler factory. The calibration includes the DistortionCorrection parameter. When enabled, this feature automatically removes any distortion effects. The feature uses the distortion coefficients of the Brown-Conrady model that allow correction of both radial and tangential distortion.
The blaze-101 and blaze-102 use the distortion coefficients of the Brown-Conrady model. The radial distortions are corrected using the following two coefficients:
eyepiece and objective lens= total magnification
The distortion coefficients are specific to each camera and can be read out via the Scan3dDistortionCoefficientSelector and Scan3dDistortionCoefficientValue parameters if distortion correction is disabled.
Objective and eyepiece lensof telescope
Since the objective is closest to the specimen being examined, it will relay a real image to the ocular lens. While doing so, it contributes a base magnification of anywhere from 4x (for a scanning objective lens, typically used to provide an overview of a sample) to 100x (for oil immersion objectives).
Microscope Objectives or Objective lenses are in many ways the heart of the microscope, and are typically mounted on a rotating nosepiece or turret to enable easy selection. Many microscopes will be equipped with a scanning objective (4x), a low power objective (10x), a high power objective (40x), and perhaps even an oil immersion objective lens.
We use cookies to provide site search, store your settings, and to analyze the usage of the documentation. With your consent, you're helping us to make our documentation better.
Two major lens components—the objective lens and the ocular lens, or eyepiece—work together to project the image of the specimen onto a sensor. This may be the human eye or a digital sensor, depending on the microscope setup.
What iseyepiece in microscope
For the blaze-112, the general camera model for wide-angle and fisheye lenses is used. Four coefficients are used here. These are sufficient to map the projection curves with acceptable accuracy.
At Shanghai Optics, we design and manufacture custom objectives and imaging systems to support our customers’ needs in many industries, including medical, biomedical, machine version, scientific research, and metrology, etc. Taking the client’s budget and precision requirements into consideration, our experienced engineering team ensure that each design can be manufactured at a reasonable cost and the optical performance is being met based on fabrication, assembly, and alignment tolerance analysis.
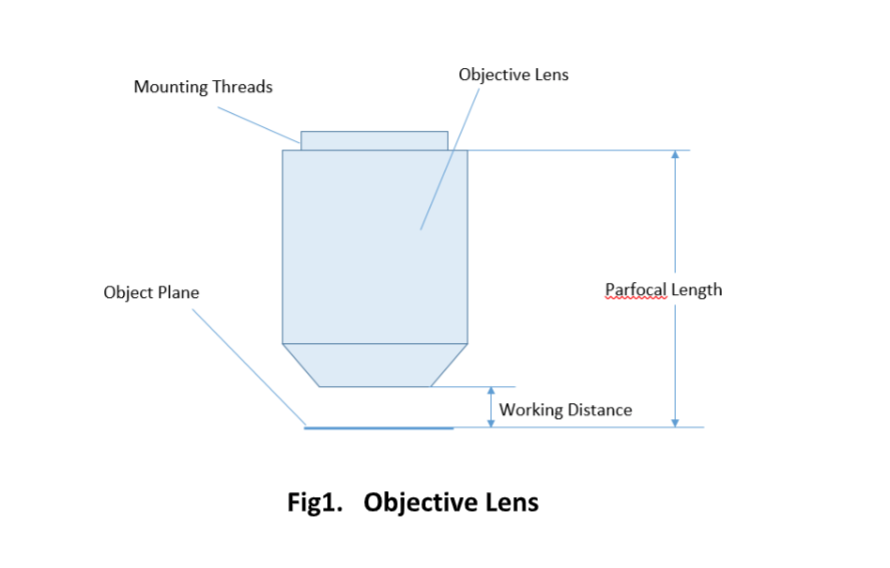
For keeping the objective at the proper position, there are mounting threads on almost all objectives. Commonly used mounting threads include RMS, M25 x 0.75, M26X 0.706, M32 x 0.75.
Important specifications are marked on the barrel of the objective, so students or researchers can easily identify the properties of an objective and determine the optical performance and working conditions for proper use. Figure 1 shows a diagram of an objective lens. A detailed discussion of the objection specifications is provided below.
This website is being translated through machine translation by a third-party service. Basler does not warrant the accuracy, reliability or timeliness of any information translated by this system and will not accept liability for loss or damage incurred as a result. Content that has not yet been translated appears in English. Switch to English version
Optical glass is a special type of glass widely used for lens and prism manufacturing. Mehrabi et al. [78] investigated the machining performance of B270 glass ...
Magnification is one important parameter. Magnification is usually denoted by an X next to a numeric value. Objectives are available in a range of magnifications from 2X to 200X.
The parfocal length is the distance between the objective mounting plane and the specimen / object. This is another specification that can often vary by manufacturer.
Objective lens and eyepiece lensmagnification
A simple magnifier (magnifying glass), works when the object to be examined is situated within focal length of the magnifier lens, enabling larger virtual image is produced. This type of magnifier is very limited in both resolution and magnification. A compound microscope, on the other hand, uses a relay lens system instead of the single lens, and since each lens component can contribute magnifying power, the result is greatly increased capability.
The optical aberration correction determines the optical performance of an objective lens and plays a central role in the image quality and measurement accuracy of imaging or microscopy systems. According to the degrees of the aberration corrections, objective lenses are generally classified into five basic types: Achromat, Plan Achromat, Plan Fluorite (Plan Semi-Apochromat), Plan Apochromat, and Super Apochromat.
The field of self-cleaning coatings on glass is divided into two categories: hydrophobic and hydrophilic. These two types of coating both clean themselves ...
The laser resonator determines the spatial characteristics of the laser beam. Most Helium Neon (HeNe) lasers have spherical-mirror Fabry-Perot res- onators that ...
To access the Basler Product Documentation, use one of the following browsers: Google Chrome Microsoft Edge Mozilla Firefox
Unlike for concave mirrors, the image will always virtual, upright, and reduced in size no matter where the object is placed in front of the mirror. Unlike ...
Since indirect backlight illumination is generally more effective than direct illumination, most microscopes do not include an internal light source. Instead, they rely on daylight or on background illumination such as a lightbulb. In brightfield illumination, also known as Koehler illumination, two convex lenses saturate the specimen with external light admitted from behind. These two lenses, the collector lens and condenser lens, work together to provide a bright, even, and constant light throughout the system: on the image plane as well as on the object plane. This system of illumination is used in many compound microscopes, including student microscopes and those found in many research labs.
What is the purpose of theobjective lens ina lightmicroscope
Room 609, 6/F, Global Gateway Tower, No.63 Wing Hong Street, Cheung Sha Wan, Kowloon, Hong Kong +852-54993705 info@shanghai-optics.com
Some mechanical hysteresis while focusing the lens may be the reason for the moving FOV. Lenses are build from several individual lenses.
Each microscope objective is itself a complex assembly of lenses, and besides contributing to the magnification, it is the objective lens which determines the resolution power of the microscope. An objective lens can also provide optical aberration corrections. A reflective objective, for instance, includes two mirrors within the assembly. These mirrors can focus laser light as well as provide chromatic corrections.
A microscope objective is an important component of a microscopy or imaging system for a range of science research, biological, industrial, and general lab applications.. An objective lens determines the basic performance of an optical microscope or imaging systems and is designed for various performance needs and applications. It is located closest to the object and is an important component in imaging an object onto the human eye or an image sensor.
Objective lens microscopefunction
Distortion is a form of optical aberration that causes a geometrical imaging error where straight lines don't appear straight in an image.
What isobjective lens in microscope
While the simplest of microscopes is simply a magnifying glass with a single lens, compound microscopes used today are highly complex devices with a carefully designed series of lenses, filters, polarizers, beamsplitters, sensors, and perhaps even illumination sources. The exact combination of optical components used will depend on the application of the microscope; the wavelength of light with which it is intended to be used, and the resolution and magnification required in the final image.
The ocular lens, located at the top of a standard microscope and close to the sensor (receiving eye) receives the real image from the ocular lens, magnifies the image received and relays a virtual image to the sensor. While most eyepieces magnify 10x, there are some which provide no magnification and others which magnify as much as 30x. The magnification power of the microscope can be calculated by multiplying the magnification power of the eyepiece, or ocular lens, by the magnification power of the objective lens. For example, an objective lens with a magnification of 10x used in combination with a standard eyepiece (magnification 10x) would project an image of the specimen magnified 100x.
Most objectives are designed to image specimens with air as the medium between the objective and the cover glass. However, for achieving higher working numerical apertures, some objectives are designed to image the specimen through another medium such as special oil with a refractive index of 1.51.
Objective lenses can be classified based on the objective construction, field of use, microscopy method, performance (optical aberration corrections), and magnification. Many microscope objective manufacturers offer a wide range of objective designs, which provide various degrees of optical aberration corrections for supporting different needs. Mirrors or reflective elements are used in objective lenses for the applications that requires chromatic aberration over board spectral ranges. Most traditional microscopy systems use refractive objectives such as achromatic objectives (the cheaper objectives) for laboratory microscope applications and plan apochromats (expensive objectives) for biological and science research microscope applications.
Many objectives are designed to be used with a cover glass. Using an incorrect coverslip thickness can greatly reduce the optical performance of a microscopy system.
The Elite Plus, powered by a 12V lithium polymer battery, is a lightweight, compact resin UV LED Curing Light. Cures up to 50 repairs on afull charge.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500