Numerical Aperture (NA) - Fibercore - Humanetics - numerical aperture
Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
A high power or compound microscope achieves higher levels of magnification than a stereo or low power microscope. It is used to view smaller specimens such as cell structures which cannot be seen at lower levels of magnification. Essentially, a compound microscope consists of structural and optical components. However, within these two basic systems, there are some essential components that every microscopist should know and understand. These key microscope parts are illustrated and explained below.
The emission filter passes only the wavelengths emitted by the fluorophore and blocks all undesired light outside this band – especially the excitation wavelengths.
A fluorescence microscope is a type of optical microscope that uses a high-intensity light source to illuminate the specimen and excite fluorochromes in the sample. The illumination of the specimen is usually done with a light source that emits ultraviolet light. They are widely used in biological, medical and industrial fields.
by P Martyniuk · 2023 · Cited by 22 — The APD operates at Geiger mode when the reverse voltage exceeds the APD's breakdown bias. Photoexcitation of the single carrier can cause the ...
Condenser is used to collect and focus the light from the illuminator on to the specimen. It is located under the stage often in conjunction with an iris diaphragm.
We carry The BEST selling reading magnifiers in America! Specialize in low vision products for example: Magnifying Glass and reading magnifiers designed for ...
Whatisthefunction of arm inmicroscope
Confocal Fluorescence Microscope: This type of fluorescence microscope combines laser scanning with fluorescent illumination to produce an image. It can be used in wide range of applications, such as studying cells and tissues, detecting proteins and other substances within cells, and measuring the thickness of materials.
It is the most common type of fluorescence microscope. The excitation of the fluorophore and detection of the fluorescence are done through the same light path (i.e. through the objective). The majority of fluorescence microscopes, especially those used in the life sciences, are of the epifluorescence design.
Coarse and Fine Focus knobs are used to focus the microscope. Increasingly, they are coaxial knobs - that is to say they are built on the same axis with the fine focus knob on the outside. Coaxial focus knobs are more convenient since the viewer does not have to grope for a different knob.
Objective Lenses are the primary optical lenses on a microscope. They range from 4x-100x and typically, include, three, four or five on lens on most microscopes. Objectives can be forward or rear-facing.
Basemicroscopefunction
The most common light sources are mercury, xenon, and LEDs. Mercury provides the best quality of light for fluorescence microscope. LEDs are becoming more popular because they are less expensive than other sources and they consume less power.
* The inches fraction result is rounded to the nearest 1/64 fraction. Millimeter. Millimeter (mm) is a unit of length. One millimeter is equal to 1/1000 of a ...
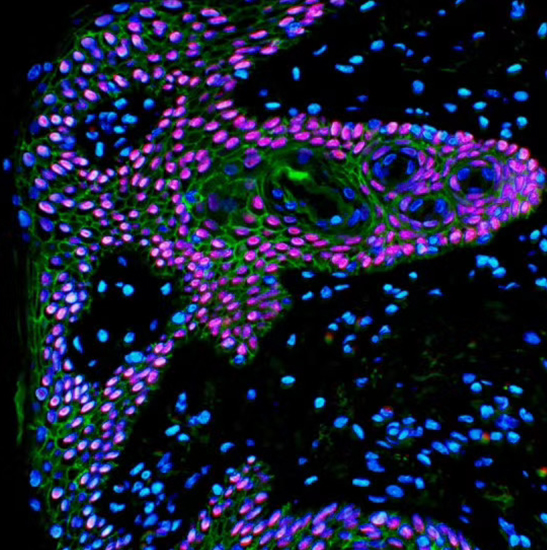
3. In the field of mineralogy, the fluorescence microscope is often used to study substances with spontaneous fluorescence properties, such as asphalt, petroleum, coal, graphene oxide and other minerals.
Stagemicroscopefunction
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Eyepiece or Ocular is what you look through at the top of the microscope. Typically, standard eyepieces have a magnifying power of 10x. Optional eyepieces of varying powers are available, typically from 5x-30x.
Objective lensmicroscopefunction
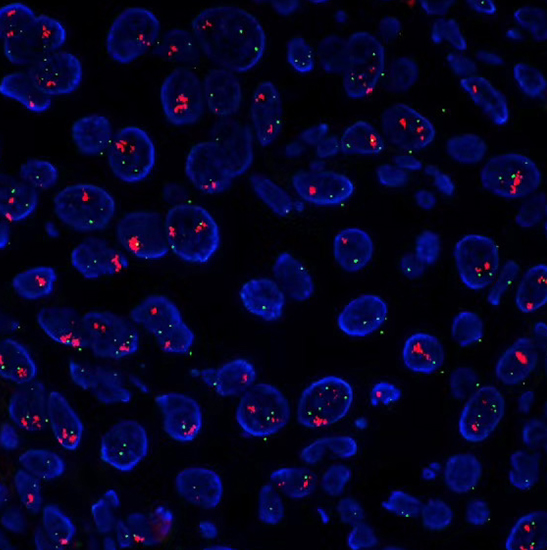
1. In the field of biology, the fluorescence microscope enables accurate and detailed identification of cellular and submicroscopic cellular components and activities with the help of fluorescent dye labeling.
Jun 3, 2023 — UV filters are no longer needed - a good quality (e.g. Hoya and upwards) protection filter is better. To reassure yourself, buy from somewhere ...
2. In the medical field, the fluorescence microscope can use fluorescent reagents to detect the presence and distribution of bacteria and viruses, or to assist in labeling surgical targets to facilitate surgery.
Microscopeparts and functions
Stage is where the specimen to be viewed is placed. A mechanical stage is used when working at higher magnifications where delicate movements of the specimen slide are required.
The resources are collected and organized on the Internet, and are only used for learning and communication. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete.
-The cells are susceptible to the phototoxic effect after staining with fluorescent dyes, as the fluorophore molecules absorb the high energy photons from the short-wavelength light.
Fluorescent dyes are organic compounds that possess a property of fluorescence, by which they can form a fluorescent image by emitting highly contrast visible green light after getting excited by the highly illuminating ultraviolet light. Commonly used fluorescent dyes are; DAPI (49,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole), acridine orange, auramine-rhodamine, Alexa Fluors, or DyLight 488.
Function of nosepiece inmicroscope
4. In materials science, the fluorescence microscope can be used in the textile industry or the paper industry to analyze fiber-based materials.
The excitation filter is essential for the operation of a fluorescence microscope. It passes the light of a shorter wavelength, which the fluorescent dye could absorb. Also, it blocks the other sources of exciting light.
Stage Clips are used when there is no mechanical stage. The viewer is required to move the slide manually to view different sections of the specimen.
Shop Target for Teacher Supplies you will love at great low prices. Choose from Same Day Delivery, Drive Up or Order Pickup. Free standard shipping with $35 ...
When to use a 50mm lens. No matter what type of photography you like, there's a good chance you can use a 50mm lens. It's one of the most popular lenses on the ...
Illuminator is the light source for a microscope, typically located in the base of the microscope. Most light microscopes use low voltage, halogen bulbs with continuous variable lighting control located within the base.
This kind of microscope’s light source and condenser are located on the top, facing downwards. The angle of illumination must be at 90 degrees with respect to the surface of the specimen being examined.
If the coating is applied to the top surface, it is called a first (or front) surface mirror. The other surface may be clear (during fabrication of the ...
by TW Cronin · 2011 · Cited by 148 — ... polarized, but polarization of light ... polarization will convert depolarized light to linearly polarized light. ... This is obvious in the example illustrated in ...
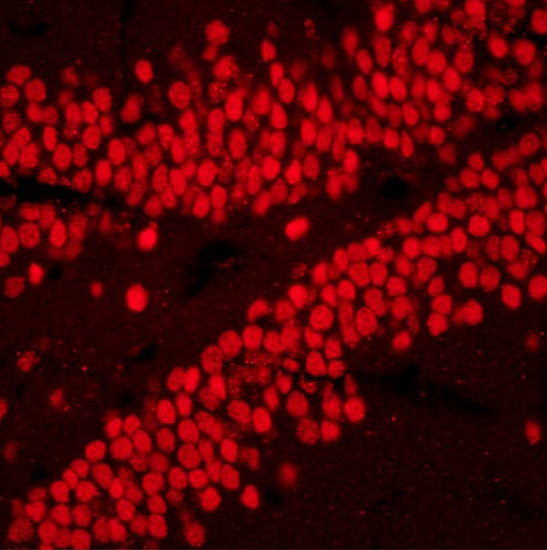
Fluorescence microscopes are widely used in various fields of research and application including biochemistry, cell biology, microbiology, immunology, and medicine.
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept", you consent to our use of cookies.
Whatiseyepieceinmicroscope
... beam's divergence angle (half-angle) and the radius of the beam at its narrowest point (the beam waist). The BPP quantifies the quality of a laser beam ...
-The photobleaching due to the electron excitation during the process of fluorescence may affect reactive molecules of the fluorescent dyes. As a result, the reactive dyes might lose their chemical property of fluorescence emission intensity.
by HM Carder · 2024 · Cited by 2 — The sugar cube: Network control and emergence in stereoediting reactions · Amplification of molecular selectivities · Synergy between stereo- ...
Function of body tube inmicroscope
Nosepiece houses the objectives. The objectives are exposed and are mounted on a rotating turret so that different objectives can be conveniently selected. Standard objectives include 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x although different power objectives are available.
The dichroic mirror is a type of optical filter that reflects light at certain wavelengths while transmitting others. It is used in fluorescence microscopes to separate the excitation and emission wavelengths.
A fluorescence microscope uses a mercury or xenon lamp to produce ultraviolet light. The light comes into the microscope and hits a dichroic mirror — a mirror that reflects one range of wavelengths and allows another range to pass through. The dichroic mirror reflects the ultraviolet light up to the specimen. Some specimens fluoresce naturally under ultraviolet light because they contain fluorescent substances such as chlorophyll. If the specimen to be viewed does not naturally fluoresce, it can be stained with fluorescent dyes called fluorochromes.
Eyepiece Tube holds the eyepieces in place above the objective lens. Binocular microscope heads typically incorporate a diopter adjustment ring that allows for the possible inconsistencies of our eyesight in one or both eyes. The monocular (single eye usage) microscope does not need a diopter. Binocular microscopes also swivel (Interpupillary Adjustment) to allow for different distances between the eyes of different individuals.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500