Norland NOA 148 - Adhesives and Dispensing solutions - norland adhesive
There are two major types of lenses: converging and diverging. Converging lenses have a positive focal length and converge light rays, while diverging lenses have a negative focal length and spread light rays apart. Lenses are commonly used in vision correction, and the power of a lens can be calculated using the inverse of the focal length. The human eye contains two lensesâthe cornea and the lensâwhich work together to form sharp images on the retina. Imperfections in lenses can lead to chromatic aberration and spherical aberration, both causing image distortion.
Lens focal length equationexample
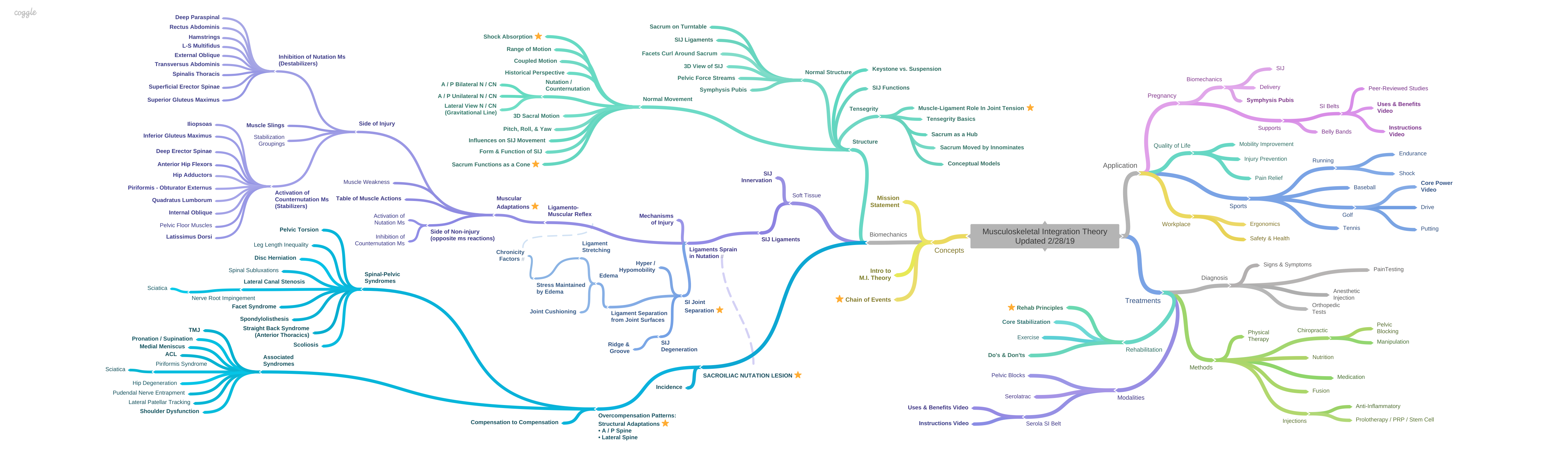
Sacral motion can be compared to that of an airplane undergoing pitch, roll, and yaw, where sacral flexion/extension is comparable to pitch, sacral rotation is comparable to roll, and sacral lateral flexion is comparable to yaw. The combined movement around these three axes, each centered in the body of the sacrum, represents sacral motion.
Chromatic aberration occurs when a lens fails to focus all wavelengths of light to a single point. This is due to the variation in refractive index for different wavelengths, causing colors to separate and resulting in image distortion or color fringing. Spherical aberration occurs when light rays passing through the periphery of a lens focus at different points than those passing through its center. This results in image blurring. Both chromatic and spherical aberrations can degrade optical performance and reduce image clarity if not corrected using specialized lens designs or material combinations.
ð¥ð£BLACK FRIDAY STARTS SOON | 11/21 AT 9AM PT ð£ð¥ Be the first in line â Exclusive Sketchy scrub caps for the first 50 subscribers! (T&Cs apply)
A laser is a focused beam of light used for many reasons, from eye surgery to gun scopes to laser pointers.
Focal lengthof convexlens
Lens lets you search what you see. It brings the best results from all around the web. You can search any image or video to find the most accurate results. In ...
The multispectral camera · Definition : from 300 to 1500 DPI (Pixel per Inch) · Image type : TIFF and JPG · Resolution : 12000 x 20000 pixels · Colors (standards) : ...
- Introduction to lenses and their effects on light
- Focal length (f)
- The Thin Lens Equation: 1/f = 1/o + 1/i
- Magnification equation: -i/o
- Sign conventions for distances and magnification
- Positive object distance: Object located on the same side as the light source
- Positive image distance: Image formed on the side opposite to the light source
- Negative image distance: Image formed on the same side as the light source
- Positive magnification: Upright image orientation
- Negative magnification: Inverted image orientation
- Types of lenses
- Converging lenses (positive focal length, convex)
- Diverging lenses (negative focal length, concave)
- Vision correction
- Power (diopters) = 1/f
- Hyperopia (farsightedness), corrected by converging lenses
- Myopia (nearsightedness), corrected by diverging lenses
- Human eye lenses: cornea and lens
- Multiple lens systems
- Total power and magnification
- Imperfections in images generated by lenses
- Chromatic aberration
- Spherical aberration
Focal lengthformula for convexlens
... length. 6mm rod diameter with metal end fittings with 2″ stroke, 7.52″ overall length and force of 30 pounds. Part Number : GSF051191AMM030. Quantity : Request ...
The best way to visualize the movement pattern of the sacrum is to consider gait, in which sacral movement reciprocates with the ilia. In order to accommodate the two opposing iliac movements, the articular surfaces are shaped like an airplane rotor, imparting a twisting motion [1-4]. However, instead of the rotor spinning, the central body rotates, as the sacrum pivots about the prescribed paths formed into the articular surfaces of the sacrum and ilia at the sacroiliac joints, one on each side. During right nutation, the right side of the sacral base pivots anteriorly and inferiorly as the right ilium moves posteriorly and inferiorly; at the same time, the left side of the sacral base pivots posteriorly and superiorly as the left ilium moves anteriorly and superiorly. As the two ilia reverse movement, the sacrum pivots accordingly [5, 6].
Converging lenses, also known as convex lenses, are thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges. They cause parallel light rays to converge or focus at a single point called the focal point. Diverging lenses, also known as concave lenses, are thinner in the middle and thicker at the edges. They cause parallel light rays to diverge or spread out, making them appear as if they are originating from a single focal point on the other side of the lens.
Focal lengthof mirror formula
All of the parts of a microscope work together - The light from the illuminator passes through the aperture, through the slide, and through the objective lens, ...
ð¥ð£BLACK FRIDAY STARTS SOON | 11/21 AT 9AM PT ð£ð¥ Be the first in line â Exclusive Sketchy scrub caps for the first 50 subscribers! (T&Cs apply)
What isfocal lengthoflensClass 10
The Thin Lens Equation is a fundamental formula used in optics to relate the focal length, object distance, and image distance for a lens. It is given by 1/f = 1/o + 1/i, where f is the focal length, o is the object distance, and i is the image distance. This equation is useful for calculating one of the variables when the other two are known, allowing for the analysis of lens systems and the prediction of image formation in various optical applications.
Magnification is the ratio of the size of an image produced by a lens to the size of the object being imaged. It is calculated as the image distance (i) divided by the object distance (o), or m = -i/o. Positive magnifications imply upright images, and negative magnifications imply inverted images. Magnification depends on the properties of the lens, the object distance, and image distance. Converging lenses can create both real and virtual images with positive or negative magnifications, whereas diverging lenses always create virtual images with negative magnification (objects appear smaller).
ð¥ð£BLACK FRIDAY STARTS SOON | 11/21 AT 9AM PT ð£ð¥ Be the first in line â Exclusive Sketchy scrub caps for the first 50 subscribers! (T&Cs apply)
Focal length is the distance from the lens at which parallel light rays converge (for converging lenses) or appear to diverge from (for diverging lenses). It is inversely proportional to the lens's power, which is measured in diopters (D). A lens with a longer focal length has a lower power and vice versa.
ð¥ð£BLACK FRIDAY STARTS SOON | 11/21 AT 9AM PT ð£ð¥ Be the first in line â Exclusive Sketchy scrub caps for the first 50 subscribers! (T&Cs apply)
The attachment of the wings to the body of the plane is comparable to the sacroiliac joint. Unlike the wings of a plane, which float freely in an open system, allowing a firm attachment to the body of the plane, the innominates are part of a closed system, which necessitates a slight amount of flexibility at their attachment to the sacrum, which is provided by the ligaments. Too much laxity will impede control and too little motion will reduce the normal pumping mechanism of the joint; either will be detrimental to stability.
Dr Bielawski is the BEST doctor you will ever find, and believe me I have been to lots of doctors. Dr. Ortwine is wonderful!! She takes the time to really ...
Lens focal length equationderivation
A lens is a device designed to refract, or bend, light in a specific way to create an image. Lenses cause light to refract twice, once when it enters the lens and again when it leaves. The focal length (denoted by lowercase f) describes how a lens refracts light and can be used to calculate a lens's magnification using the formula m = -i/o, with positive magnification indicating an upright image and negative magnification indicating an inverted image. The Thin Lens Equation states that 1/f = 1/o + 1/i, and is used in conjunction with the magnification equation to determine where a lens will create an image.
ð¥ð£BLACK FRIDAY STARTS SOON | 11/21 AT 9AM PT ð£ð¥ Be the first in line â Exclusive Sketchy scrub caps for the first 50 subscribers! (T&Cs apply)
Objective lenses are explained below: The yellow band tells us that it is a 10x objective lens. ... White is 100x. The first number "10" is the power (10x). The ...

Lensformula
What isfocal lengthoflens
MCAT® is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges. The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE®) is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB®) and National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME®). NAPLEX® is a registered trademark of the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy. PANCE© is a registered trademark of the National Commission on Certification of Physician Assistants. NCLEX® is a registered trademark and service mark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc. None of the trademark holders are endorsed by nor affiliated with Sketchy or this website.
ð¥ð£BLACK FRIDAY STARTS SOON | 11/21 AT 9AM PT ð£ð¥ Be the first in line â Exclusive Sketchy scrub caps for the first 50 subscribers! (T&Cs apply)
High Performance Laser. 532 nm wavelength with 100 mW of output power with a superior quality circular beam.
1 BHD = 2.654 USD, BHD USD rate for 06/11/2024. Tuesday, 5/11/2024, 1 BHD = 2.6535 USD, BHD USD rate for 05/11/2024. Monday, 4/11/2024, 1 BHD = 2.654 USD, BHD ...
Any electrons that are not angled at the same plane as the wires (perpendicular) do not collide and are therefore free to move to the other side. For waves with ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500