New design for highly durable infrared-reflective coatings - ir reflectivity
The light is then focused on the eyepiece lens. This lens further magnifies the pre-magnified image coming from the objectives.
Seriously, if i am not grateful, i am lying. This note is really helpeful to me to differet ways to different methology.
Function of microscope
Ans. The magnification of a lens is defined as the ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object. Microscope magnification measures the total enlargement of the image of an object. Magnification power is the product of eyepiece lens power and objective lens power.
Thank you so much for the note that you have given to me i was so grateful to know that you are so bright people that extend your help to a student
What is eyepieceinmicroscope
Thank you very much it really helped me with my science home work since i in 8th grade and this my home work to draw a microscope label all the parts and the function thank may the holy father of holy spirits bless you and give more wisdom thanks love you all keep up the good work and thank you again bye.
1. which objective lens focuses closest to object 2. what controls the light entering the binocular lenses 3. how can you enhance the resolving power of a microscope 4. what is useful and false magnification PLEASE CAN YOU HELP ME IN ASWERING THOSE QUESTIONS
There are different types of microscopes like light microscope, dark-field microscope, phase contrast microscope, electron microscope, fluorescent microscope, etc.
Ans. A microscope is an optical instrument with one or more lens systems that are used to get a clear, magnified image of minute objects or structures that can’t be viewed by the naked eye.
A beam of light is passed through the condenser to the specimen. The light transmitted from the specimen enters the objective lens. While passing through the objectives, the transmitted rays are spread so that they appear to come from the bigger objects.
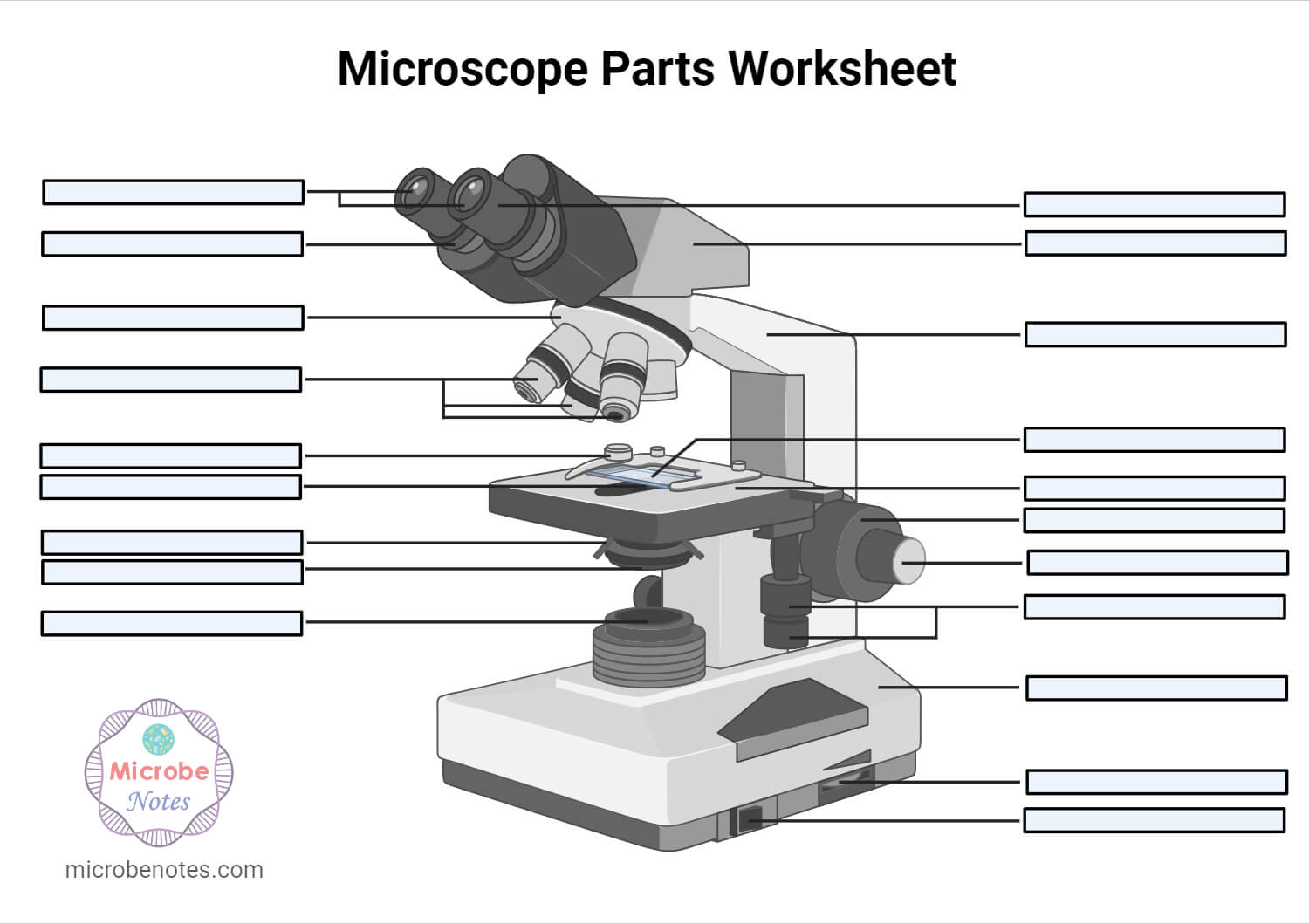
1. Ocular Lens (Eye Piece)2. Diopter Adjustment3. Head4. Nose Piece5. Objective Lens6. Arm (Carrying Handle)7. Mechanical Stage8. Stage Clip9. Aperture10. Diaphragm11. Condenser12. Coarse Adjustment13. Fine Adjustment14. Illuminator (Light Source)15. Stage Controls16. Base17. Brightness Adjustment18. Light Switch
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
I did NOT like this website sourse. Wanna know why I didn’t like it??? I don’t like it BECAUSE my school wants me to use this website sourse. My new science teacher wants us to answer those 10 questions. I think its pretty dumb. No Offensen to anyne out there, because I am a nice person not a mean one.
Function ofbody tube inmicroscope
Thanks much for this. We just did microscopy as a topic and the write-up has really helped me to understand better. Thanks again
this is a really good artical i used it to study my science i just wanted to point out to you that tere are a few spelling errors but other than that it is a 100% rating from me
Diagram of a fluorescence polarization assay. Rapidly rotating small molecule fluorophore gives low FP signal (low mP). The association of a relatively large molecule, such as a protein, with the small molecule fluorophore slows down the motion of the fluorophore, leading to increased FP signal.
Ans. Rack stop is included in the microscope for preventing the specimen slide from coming too far up and hitting the objective lens.
Function ofnosepiece inmicroscope
1. Illuminator (Light Source)2. Diaphragm (Iris)3. Condenser4. Condenser Focus Knob5. Rack Stop6. Stage7. Stage Control Knobs8. Nose Piece9. Objective Lens10. Tube (Head)11. Eyepiece (Ocular Lens)12. Diopter Adjustment13. Adjustment Knobs (Fine Adjustment Knob and Coarse Adjustment Knob)14. Arm15. Base16. Light Switch17. Brightness Adjustment
Thanks very much dear and please continue doing so, am Gerald M from Uganda East Africa doing diploma in nursing at Mulago school of nursing and midwifery
Ans. The coarse adjustment knob moves the stage up and down to bring the specimen into focus. The fine adjustment knob brings the specimen into sharp focus under low power and is used for all focusing when using high-power lenses.
Function ofstage inmicroscope
Microscopeparts and functions
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Ans. The eyepiece, also known as the ocular is the part used to look through the microscope. Its found at the top of the microscope. Its standard magnification is 10x with an optional eyepiece having magnifications from 5X – 30X. Objective Lens are the major lenses used for specimen visualization. They have a magnification power of 40x-100x. There are about 1- 4 objective lenses placed on one microscope, in that some are rare facing and others face forward.
it very good website i use in 4 grade right after i plai amog us and they vote me out using orang strat witch mad me sad 🙁
All Assay Guidance Manual content, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0), which permits copying, distribution, transmission, and adaptation of the work, provided the original work is properly cited and not used for commercial purposes. Any altered, transformed, or adapted form of the work may only be distributed under the same or similar license to this one.
Microscopes are instruments that are used in science laboratories to visualize very minute objects, such as cells and microorganisms, giving a contrasting image that is magnified.

What is the function ofarm inmicroscope
Having been constructed in the 16th Century, microscopes have revolutionized science with their ability to magnify small objects such as microbial cells, producing images with definitive structures that are identifiable and characterizable.
Microscopes are generally made up of structural parts for holding and supporting the microscope and its components and the optical parts that are used for magnification and viewing of the specimen images. Modern microscopes have additional electronics and display devices. This description defines the parts of a microscope and the functions they perform to enable the visualization of specimens.
Basemicroscope function
Thanks for helping me to know the parts and functions of a light microscope. THANKS AGAIN AND I HOPE THAT I WILL DRAW IT IN MY EXAM
The optical parts of the microscope are used to view, magnify, and produce an image from a specimen placed on a slide. These parts include:
Microscopes are made up of lenses for magnification, each with its own magnification powers. Depending on the type of lens, it will magnify the specimen according to its focal strength.
Ans. Condensers are lenses that are used to collect and focus light from the illuminator into the specimen. They are found under the stage next to the diaphragm of the microscope. They play a major role in ensuring clear sharp images are produced with a high magnification of 400X and above. Abbe condenser is a condenser specially designed for high-quality microscopes, which makes the condenser to be movable and allows very high magnification of above 400X. High-quality microscopes normally have a high numerical aperture than objective lenses.
Markossian S, Grossman A, Arkin M, et al., editors. Assay Guidance Manual [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; 2004-.

Thank you for the support u have done may the Holy Spirit from the Almighty shine upon you to have more knowledge 2 continue making more notes from various topics in microbiology????✍️
Thanks alot of your help and knowI can draw it well in my exams and write the functions.Thankyou very much for your help
Their ability to function is because they have been constructed with special components that enable them to achieve high magnification levels. They can view very small specimens and distinguish their structural differences, for example, the view of animal and plant cells viewing microscopic bacterial cells.
Thanks a lot for this wonderful note: It is really helpful, Really appreciate the way all the detail about microscope have been explained




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500