Multispectral vs Hyperspectral in agriculture | by Ivanov Igor - multispectral vs hyperspectral imaging
Bei dieser so genannten endlich-unendlichen Abbildungsbedingung wird der beleuchtete Spalt oder das Fadenkreuz direkt in der Objektebene der Probe bewegt. Bei der häufiger anzutreffenden unendlich-unendlichen Abbildungsbedingung ist der beleuchtete Spalt oder das Fadenkreuz Teil eines Kollimators, der das Ziel ins Unendliche projiziert. Der Kollimator wird dann in verschiedenen Off-Axis-Winkeln ausgerichtet, um die MTF in den entsprechenden Bildfeldern zu charakterisieren.
MTFtrans
Die Modulationsübertragungsfunktion (MTF) ist der allgemein anerkannte und grundlegende Parameter für die Charakterisierung optischer Systeme weltweit. Die MTF ist ein quantitatives Maß und ein objektives Kriterium für die Abbildungsqualität von Optiken.
Die MTF ist ein Werkzeug für Optikdesigner, um die Gesamtabbildungsleistung eines Systems in Bezug auf Auflösung und Kontrast zu quantifizieren. Die Kenntnis der MTF-Kurven der an einem optischen System beteiligten Objektive und Kamerasensoren wird zur Optimierung der Leistung des optischen Systems verwendet.
Mit den drei Neuentwicklungen der ImageMaster® PRO Serie unterstreicht TRIOPTICS seine Technologieführerschaft auch für die Produktion zukünftiger Handy-Kameraoptiken.
Die MTF wird für eine Vielzahl an Optiken von einfachen Komponenten wie sphärischen Einzellinsen bis hin zu komplexen Objektiven verwendet. Beispiele sind neben fotografischen Optiken auch fotolithografische Optiken, Intraokularlinsen, Endoskope, Zielfernrohre, Teleskope, Spektive, Ferngläser, AR/VR-Optiken, Cine-Objektive, Automobilobjektive und viele andere mehr.
Die Modulationsübertragungsfunktion (MTF), die die Auflösung und Leistung eines optischen Systems beschreibt, ist das Verhältnis des relativen Bildkontrasts zum relativen Objektkontrast.
Die in der Abbildung gezeigten Gitter werden eigentlich nicht mehr zur Messung der MTF verwendet. Moderne MTF-Tester wie der ImageMaster® verwenden als Objekt einen einzelnen beleuchteten Spalt auf einem undurchsichtigen Hintergrund. Aus mathematischer Sicht kann ein einzelner Spalt als Summe über alle Raumfrequenzen betrachtet werden (Fourier-Synthese). Alle Frequenzen tragen mit der gleichen Amplitude (=1) zu diesem Spalt bei, wobei die endliche Spaltbreite bei dieser Beschreibung nicht berücksichtigt wird. Dieser einzelne Spalt wird in der Bildebene der Probe abgebildet. Aufgrund von Beugung und Abbildungsfehlern gibt es in dieser Ebene kein perfektes Spaltbild, sondern das Spaltbild ist verbreitert. Es stellt die Linienausbreitungsfunktion (LSF) dar.
Chromatic aberrations, on the other hand, result from different wavelengths of light being refracted at different angles. The extent of this is determined by the lens properties. This is especially important to consider when using a polychromatic light source, like an incandescent bulb. In this case, the light source consists of the entire visible light spectrum, and the red wavelengths will refract at different angles than the blue wavelengths. Chromatic aberrations are harder to correct since they stem from the natural property of the lens material. However, most applications for Fresnel lenses do not require this step so chromatic aberrations are expected and tolerated.
When visiting lighthouses built in the 19th century, you may notice a strange hive like glass cage around the lamp. These are the Fresnel lenses, originally designed by Augustin Fresnel*. At the time, lighthouses were starting to use lenses to extend the distance of the light beam. However, they faced a problem with traditional lenses, which were heavy and lost a lot of light. Fresnel realized that a lot of bulk glass could be removed and designed the strange lens with concentric stepped rings and a flat back. This new design collimates the light and reduces the loss. Today, they have many applications from bike lights to magnifying text. In this article we will learn how they work and how they can be used.
Since many applications focus on the visible light wavelength range, they can be made of plastics, which reduce the cost and weight even more. This was first done with a mold, though today there are many techniques for creating structures on material surfaces. This is possible because many plastics are transparent to visible light. However, UV or IR wavelengths requires lenses to be made of a different material.

Die MTF-Messung kann bei einer einzigen Wellenlänge oder in einem Spektralbereich durchgeführt werden, der ein endliches Band von Wellenlängen abdeckt. Die resultierenden Messdaten werden als monochromatische bzw. polychromatische MTF-Werte bezeichnet.
Normalerweise wird die MTF in ihrer eindimensionalen Form verwendet, die für einen azimutalen Schnitt durch die Bildebene berechnet wird. Der Azimut (Schnittebene) des Objektmusters wird als sagittaler Azimut bezeichnet, wenn die Verlängerung des Spalts oder des Objekts durch die Bezugsachse verläuft. Wenn die Verlängerung des Spaltmusters senkrecht zur Bezugsachse verläuft, wird der Azimut als tangentialer Azimut bezeichnet.

MTF bedeutungFeuerwehr
The central light source radiates light in every direction and is very close to the lens, especially compared to the kilometer length scale the transmitted beam travels. As a result, the lens needs to have a short focal length so the light will focus into a collimated beam. Choosing the right focal length is important to ensure the light reaches its maximum range.
TransMtF bedeutung
Der Beitrag der einzelnen Ortsfrequenzen zur LSF kann auf der Grundlage der Fourier-Analyse berechnet werden. Die Amplitude jeder Ortsfrequenz ist gleich dem Kontrast bei dieser Frequenz. Die Fourier-Analyse der Line Spread Function entspricht der MTF der Probe. Die Aufnahme eines einzigen Bildes der LSF enthüllt die vollständige MTF.
Dieser Artikel hat Sie inspiriert? Sind Sie auf der Suche nach weiterem Wissenstransfer? Dann könnten Sie auch an folgenden Themen interessiert sein …
With the need for alternative energy sources, solar energy is gaining a lot of attention. One of the main drawbacks for solar energy is the inefficiency of many solar cells. They are unable to make full use of the solar energy entering our atmosphere. Fresnel lenses offer a solution, by concentrating light at the solar cell surface.
A traditional converging lens consists of at least one convex face. This face usually has spherical curvature, though other shapes are also used. For instance a parabolic lens will have fewer aberrations, but will be much more expensive. Other lens shapes include conical and cylindrical. Further, the way the lens is arranged will impact the way a lens focuses. For instance, having two convex surfaces will create a diverging lens in which the focal point lies behind the lens. On the other hand, prescription glasses usually have a meniscus shaped lens, where one side is convex and the other is concave. In all cases, the curvature of each surface can differ. These parameters all affect the focal length and magnification of the lens.
FTMbedeutung
Vereinbarungsgemäß ist die Modulationsübertragungsfunktion bei einer Ortsfrequenz von Null auf Eins normiert. Bei niedrigen Ortsfrequenzen liegt die Modulationsübertragungsfunktion nahe bei 1 (oder 100 %) und nimmt im Allgemeinen mit steigender Ortsfrequenz ab, bis sie Null erreicht. Die Kontrastwerte sind, wie oben gezeigt, bei höheren Ortsfrequenzen geringer. Mit zunehmender Ortsfrequenz sinkt die MTF-Kurve, bis sie den Wert Null erreicht. Dies ist die Auflösungsgrenze für ein bestimmtes optisches System oder die so genannte Grenzfrequenz (siehe Abbildung unten). Wenn der Kontrastwert den Wert Null erreicht, wird das Bild zu einem einheitlichen Grauton.
Als zwei weitere wesentliche Zukunftstreiber kommen die hochauflösende, professionelle Fotografie sowie die Zoomfähigkeit der Kameras hinzu. Alle drei Trends stellen neue Herausforderungen an die Messtechnik, für die TRIOPTICS jetzt maßgeschneiderte Messlösungen für die Prüfung der Bildqualität herausbringt.
The top and bottom of the hive like structure are engineered to reflect the light that would otherwise be lost. These panes have a stepped edges on both sides of the material, instead of just the outer surface and employ total internal reflection, which occurs when light hits a surface at or above the critical angle. The angle of the reflector’s grooves is specifically designed with this critical angle in mind. The light rays from the source have a small incident angle so they are captured by the prism
What doesMTFmean on instagram
Die Produktfamilie ImageMaster® PRO setzt seit Jahren weltweit den Standard bei der Prüfung der Abbildungsqualität von Handy-Kameralinsen in der Massenproduktion.
While Fresnel lenses work very well for collimating a bright central light source, they can also be used to focus incoming collimated light. However, the placement of the lens needs to be precise to minimize the amount of aberrations that occur. The two most notable aberrations are spherical and chromatic. In both cases, the aberrations can be fixed with a multi-lens system, where light passes through more than one lens, whose curvature, focal lengths, and material properties can be specifically chosen.
Wir bieten eine umfassende Produktlinie zur softwaregestützten vollautomatischen Messung der Modulationsübertragungsfunktion (MTF) sowohl für die Forschung und Entwicklung als auch für die Produktion bzw. Optikfertigung.
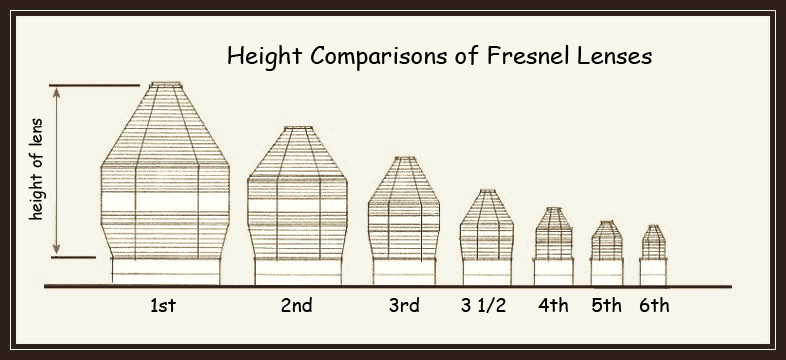
As a result, Fresnel created a 6 order system, detailing the size of each component, the focal lengths, where to use each order, and even the number of wicks for the central light source. This list was expanded later to include a few larger and smaller lenses. The first order, and originally the largest, Fresnel lens has a focal length of 92 cm and an approximate visibility of 35 km. On the other end, the sixth order Fresnel lens has a focal length of 15 cm and a visibility of 8 km.
*Note: Fresnel was not the first to try to split traditional lenses to reduce their weight, but he came up with a practical and affordable design for use in Lighthouses.
MTF BedeutungOptik
Though they were originally deigned for use in lighthouses, Fresnel lenses are useful anywhere a concentrated beam of light is needed. Today, many bike lights use a Fresnel lens to increase visibility for a biker and for vehicles around them. Plastic Fresnel lenses provide extra magnification when reading, though there is often distortion, especially near the edges. Examples of Fresnel lenses, available for purchase can be found here.
Die ImageMaster® Serie wurde speziell für die Messung der MTF entwickelt, um die Abbildungsqualität von Objektiven und optischen Systemen präzise bestimmen zu können. Dabei werden neben der MTF als allgemein anerkannte Methode zur Bestimmung der Abbildungsqualität eines Objektivs eine Vielzahl weiterer optischer Parameter gemessen.
MTF bedeutungmedizin
Objektive können während der Produktion in ihrer Abbildungsqualität variieren. Um die oftmals hohen Anforderungen an die Abbildungsleistung zu erfüllen, werden Objektive anhand der MTF als wichtigstem Parameter charakterisiert und bewertet. Die MTF liefert eine aussagekräftige Qualitätsfunktion für die objektive Bewertung optischer Systeme in der optischen Industrie.
TRIOPTICS bietet ein breites Produktportfolio im Bereich MTF-Messung. Dazu gehören auch Modellvarianten für Messanforderungen, die sich durch die neuesten Technologietrends für Kameraoptiken von Smartphones ergeben.
An example of a first order Fresnel lens used by lighthouses, which is on display at the San Francisco Maritime Museum. Courtesy of National Park Service
Alternativ ist es auch möglich, ein Kreuz (d. h. zwei senkrechte Schlitze) für das Ziel zu verwenden. Dadurch kann der ImageMaster® die MTF in zwei Bildrichtungen gleichzeitig messen, sofern eine CCD-Kamera für den Bildanalysator verwendet wird. Und schließlich kann auch ein Pinhole-Target als Objekt verwendet werden. Das Bild eines Pinhole-Targets wird als Point Spread Function bezeichnet. Diese Funktion enthält die vollständige MTF-Information in allen Bildrichtungen. Die grundlegenden Begriffe und mathematischen Beziehungen, die für die MTF verwendet werden, sind in der Norm ISO 9334 beschrieben.
Aside from spherical and chromatic aberrations, Fresnel lenses also suffer from distorted images. This means the image seen after light passes through the Fresnel lens will not be a perfect replica of the original object. When using a Fresnel lens to magnify text, the letters and words may be harder to distinguish especially at higher magnifications. This trait limits the effectiveness of Fresnel lenses as a tool for magnification. Of course, this has no impact on a bright white light like a lighthouse.
Infolgedessen erscheinen helle Lichter im Bild nicht so hell wie im Objekt, und dunkle oder schattige Bereiche sind nicht so schwarz wie in den Originalmustern. Im Allgemeinen kann ein beleuchtetes Ziel durch seine räumliche Häufigkeit (Anzahl der hellen und dunklen Bereiche pro Millimeter) und den Kontrast (den scheinbaren Helligkeitsunterschied zwischen hellen und dunklen Bereichen des Bildes) definiert werden.
Um die Abbildungsleistung eines optischen Systems vollständig zu charakterisieren, muss die MTF an verschiedenen Positionen innerhalb des Sichtfelds gemessen werden. Die MTF-Messung innerhalb des Sichtfeldes wird als Off-Axis-Messung bezeichnet. Für eine Off-Axis-Messung wird das Messobjekt im Sichtfeld an die gewünschte Objektposition und der Bildanalysator an die entsprechende Bildposition bewegt.
MTFGeschlecht
Die Modulationsübertragungsfunktion variiert in Abhängigkeit von der Ortsfrequenz und auch von der Position im Sichtfeld. Die MTF-Messung entlang der Symmetrieachse des optischen Systems wird als achsnahe Messung bezeichnet.
Wenn ein Objekt (beleuchtetes Ziel oder Fadenkreuz) mit einem optischen System beobachtet wird, wird das resultierende Bild aufgrund von unvermeidlichen Aberrationen und Beugungserscheinungen etwas beeinträchtigt sein. Darüber hinaus stimmt ein reales Objektiv nicht vollständig mit den Konstruktionsdaten überein. Herstellungs-, Montage- und Ausrichtungsfehler in der Optik verschlechtern die Gesamtabbildungsleistung des Systems.
Die Modulationsübertragungsfunktion (MTF) ist ein wichtiges Hilfsmittel zur objektiven Bewertung der Bildgebungsvermögens optischer Systeme. Nicht nur, dass die MTF auch ein Mittel ist die Abbildungsqualität optischer Systeme objektiv und quantitativ auszudrücken, sondern sie kann aus den Konstruktionsdaten des Objektivs berechnet werden. Auf diese Weise können Optik- und Systemdesigner die Leistung der optischen Systeme zuverlässig vorhersagen. Hersteller können die Abbildungsqualität der gefertigten Objektive mit den Design-Erwartungen vergleichen.
Using Snell’s Law, you can calculate how much a light ray will bend based on the refractive index of the materials, and the incident angle. If the surface is curved, like in a lens, then the amount of refraction of the incident light will depend on the distance of the incidence point from the optical axis. Parallel light rays incident on a convex surface will bend towards the optical axis, and converge at a focal point.
Eine neue Technologie im Mobiletelefon-Markt ist die Under-Display-Kameratechnik – Kameraoptiken sind nahezu unsichtbar unter vollflächiger Displayoberfläche verborgen.
TRIOPTICS ist mit der Produktreihe ImageMaster® Marktführer für MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) Messgeräte zur hochgenauen Messung der Abbildungsqualität.
When looking at a Fresnel lens from a lighthouse, you’ll notice two distinct parts. The first is the set of rectangular pieces that sit around the center of the lens. This is what a typical Fresnel lens looks like, and is the main part of a Fresnel lens. Unlike a traditional lens, the surface of a Fresnel lens is broken up into rings that are arranged like a sawtooth when viewed from the side. This can be seen in the image above.
Wenn es darum geht, ein Objekt mit der gewünschten Genauigkeit abzubilden, liefern MTF-Daten die benötigte Grundlage für das Optikdesign. Von besonderer Bedeutung sind dabei Auflösung und Kontrast. MTF-Daten können die Auswahl des geeigneten Objektivs für eine Anwendung erheblich vereinfachen.
Spherical aberrations occur when the light rays at the edge of the lens are focused at a different location than the rays near the center. This is caused by the shape of the lens, which most often has a spherical curvature. Changing the lens shape to have a parabolic curvature can correct the aberration, but will cost much more. A more cost effective route is to increase the radius of curvature of the lens, so the rays at the edge and the center are focused to the same point. However this increases the focal length of the lens.
The key element for lenses is the refractive index of the material they are built out of. This is a property of the material that makes up a lens. For example, air has a refractive index of 1 (it’s actually slightly greater than 1 but is often rounded down for simplicity) and glass has a refractive index of 1.52. When a beam of light travelling in air is incident on a glass surface, it will refract.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500