Monochromatisches Licht - Therapie - was ist monochromatisches licht
OCT can help an ophthalmologist see the different layers of the retina. This helps them map and measure the thickness of these layers.
Optical Coherence Tomographyppt
In its early stages, diabetic retinopathy usually does not cause symptoms. Some people may notice changes in their vision, such as problems seeing things that are far away.
The development of the microscope objective. Journal of the Optical Society of America 33: 123-128 (1943). Largely of historical interest, this review describes the invention of the microscope, early developments in lens design, correction for chromatic aberration, increasing numerical aperture, immersion objectives, and early progress in the design of apochromatic objectives.
Central serous retinopathy is a condition that occurs when fluid builds up under the retina. Medical professionals may also refer to this condition as central serous chorioretinopathy.
Researchers say the drug aflibercept performed better in a clinical trial than bevacizumab in helping wean people off treatments for wet age-related…
What can anOCTscan detect
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve. Glaucoma can lead to a person experiencing vision loss and blindness.
Proper alignment of the microscope. Methods in Cell Biology 56: 135-146 (1998). Addressed in this book chapter are the key components of optical microscopes and alignment for Köhler illumination. Among the topics discussed are the light source and collector, diffusers, condensers, stages, objectives, nosepiece, tube lens, eyepieces, and video adapters.
OCT can also help medical professionals diagnose optic nerve disorders. This is because an ophthalmologist can use OCT to spot changes to the fibers of the optic nerve.
By allowing an ophthalmologist to do all the above, OCT can help them diagnose certain eye disorders and guide specific treatments.
OCTeye test side effects
An ophthalmologist may use OCT to help confirm a diagnosis if a person is displaying symptoms of certain eye conditions. Below are the symptoms that may lead an ophthalmologist to use OCT.
Microscopy and Micrometry Methods in Microbiology 5: 1-103 (1971). A comprehensive 100-page review on all aspects of microscopy, including light and color, magnification, Abbe theory, image formation, resolution, depth of focus, objectives, eyepieces, and condensers, and configuration for illumination. Phase contrast is described in detail as are making measurements with stage micrometers and reticules.
During the scan, a person may focus on a target within the scanner. They may also see a red line appear during the scan.
OCTeye test price
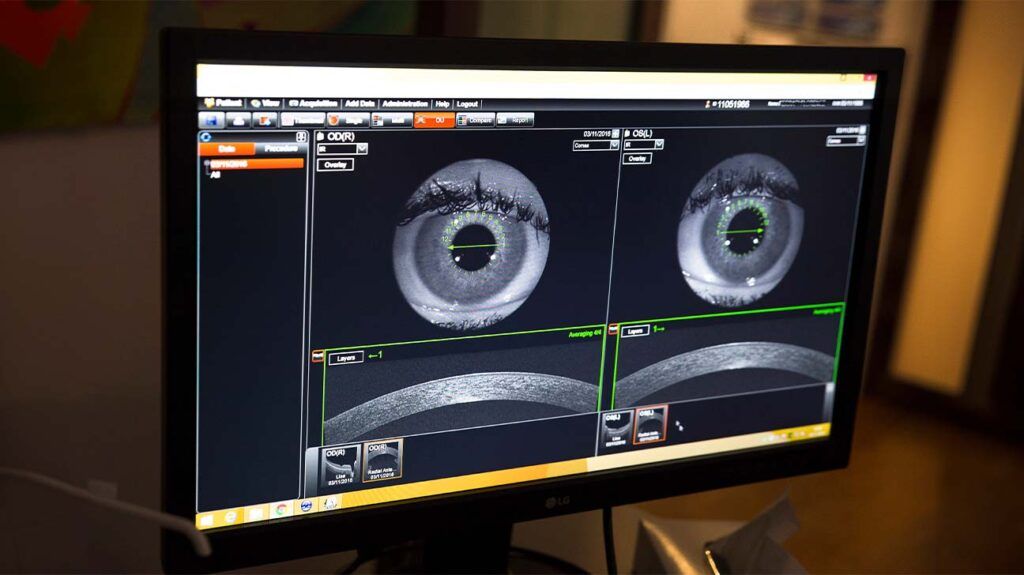
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a type of noninvasive imaging test. Ophthalmologists use OCT to create high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the inside of a person’s eye.
A medical professional can use OCT to help diagnose AMD. It can be suitable for helping diagnose both early and advanced-stage AMD.
A person may not experience any symptoms if they have early stage glaucoma. Over time, a person may slowly experience vision loss.
Optical coherence tomographyangiography
Read on to learn more about how OCT works. This article also explains the conditions that OCT can help with and what happens during the procedure.
There is no research to prove that exercises can help with drooping eyelids. Learn more about this here and find out about other treatment options.
OCTeye test results
During a CT scan, a medical professional aims the X-rays at a part of the person’s body and quickly rotates them around the body. The CT scanner processes the signals that these X-rays produce. The CT scanner then creates cross-sectional images.
Optical Microscopy. Encyclopedia of Condensed Matter Physics: 175-182 (2005). A thorough review of microscope system optical components, including light sources, condensers, filters, objectives, eyepieces, the stage, stand, resolution, and depth of field. Also covered are various imaging modes, such as brightfield, oblique illumination, darkfield, polarized light, and DIC microscopy.
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that causes damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Learn about its causes, symptoms, and…
Without treatment, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness. OCT can help a medical professional diagnose diabetic retinopathy.
OCTin Cardiology
They must then remain still and follow the instructions of the person carrying out the procedure. These instructions will direct the person to look in certain directions throughout the scan.
PVD can cause a person to develop vitreous traction. This is a condition that occurs when part of the vitreous remains stuck to the macula during PVD. This part of the vitreous then pulls on the macula, causing symptoms of vitreous traction.
Microscopy overview. Encyclopedia of Analytical Science: 32-41 (2005). The authors provide a comprehensive review of all phases of the optical microscope. Addressed are lenses, magnification, simple and compound microscopes, numerical aperture, illumination, reflected light microscopy, diffraction, resolution, aberrations, contrast, confocal microscopy, and limitations of the microscope.
Optical Microscopy Encyclopedia of Imaging Science and Technology 2:1106-1140 (2002). A thorough review of microscope optical systems and contrast-enhancing techniques. Eyepieces, condensers, and objectives are discussed in detail, as are finite and infinity optical systems. Included contrast techniques are phase, DIC, polarized light, Hoffman modulation contrast, and fluorescence.
Basic principles of microscope objectives. BioTechniques 33: 772-781 (2002). The authors describe the properties of microscope objectives, including resolution and numerical aperture, effects of design on magnification factors, correction for various degrees of aberration, infinity optical systems, and oil immersion fundamentals.
The compound microscope: Optical tube length or parfocalization? European Journal of Physics 26: 1101-1105 (2005). A theoretical study of standardized distances in compound microscopes. The authors examine the optical tube length with regards to requirements of parfocalization and discuss the German and Japanese industry standards employed for standardization of specimen-to-intermediate image distance.
The microscope optical train typically consists of an illuminator (including the light source and collector lens), a condenser, specimen, objective, eyepiece, and detector, which is either some form of camera or the observer's eye. Research-level microscopes also contain one or more of several light-conditioning devices that are often positioned between the illuminator and condenser, and a complementary detector or filtering device that is inserted between the objective and the eyepiece or camera. The conditioning device(s) and detector work together to modify image contrast as a function of spatial frequency, phase, polarization, absorption, fluorescence, off-axis illumination, and/or other properties of the specimen and illumination technique. Even without the addition of specific devices to condition illumination and filter image-forming waves, some degree of natural filtering occurs with even the most basic microscope configuration.
OCT is not the same as a computed tomography (CT) scan. OCT uses light rays to create images, and CT scans use X-ray beams.
Microscope Basics. Methods in Cell Biology 81: 1-10 (2007). Drs. Sluder and Nordberg review finite and infinity microscope optical systems, objectives (including mixing and matching), coverslip selection, empty magnification, camera pixel number and resolution, mounting cameras on the microscope, and many of the basic fundamentals of digital cameras.
The macula is a small area in the center of the retina. It plays a role in helping people clearly see the details of objects.
If a person has received dilating eye drops during OCT, their eye may be sensitive to light for several hours after the procedure.
OCT can help an ophthalmologist diagnose a number of medical conditions including problems with the macula, AMD, glaucoma, and different types of retinopathy.
During OCT, an ophthalmologist uses a beam of light to scan an area of a person’s eye. The OCT device then measures the light that the structures within the eye have reflected back.
Measuring the thickness of the different layers of a person’s retina can help an ophthalmologist diagnose a number of medical conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and glaucoma.
Vitreous is the substance that fills the middle of the eye. Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) occurs when the vitreous pulls away from the retina.
Optical coherence tomographymachine
Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage the retina. This occurs when diabetes damages the blood vessels that supply the retina with blood.
The OCT device then uses these measurements to create images of a person’s retina that are cross-sectional and three-dimensional.
In some cases, an ophthalmologist may administer dilating eye drops before the procedure. This is to help widen the pupil to make imaging easier.
Choosing objective lenses: The importance of numerical aperture and magnification in digital optical microscopy. Biological Bulletin 195: 1-4 (1998). A comprehensive discussion of microscope objectives focused on the critical aspects of objectives for imaging. Included are basics of image formation and an overview of objectives for widefield and confocal fluorescence microscopy.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a form of noninvasive imaging test that creates high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the inside of a person’s eye.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500