Metering mode - light metering
May 2, 2024 — Leveraging the Parabolic Mirror Advantage: Parabolic mirrors, commonly used in astronomical telescopes, offer a unique advantage with their ...
When light shines, nearly everything it shines on will reflect at least some of it back. Kids can understand that our eyes gather that light. The light travels through the clear outer layer of the eye, called the cornea, to the crystalline lens. The cornea and lens work together to focus the light onto the back of the eye, where the retina converts the light to electric signals that travel along the optic nerve to the brain. The brain then interprets the signals as an image.
Infraredfrequency
It is a coating added on to lenses. It can be added to lenses that are already made, or on to lenses that have yet to be cut to the frame.
In addition to simply capturing reflected light to render an image, the objective lens of a microscope magnifies the image. Many stationary microscopes have several objective lenses that the user can rotate to view the object at varying levels, or “powers,” of magnification.
Spectral Devices Inc offers a wide range of hard-coated optical filters that cover the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, and short-wave infrared spectral ...
Infrared radiation was discovered by William Herschel in 1800. He was studying the heating effect of different colours of light by using a prism to produce a spectrum of colours and thermometers to measure their heating effect. He noticed that the heating effect got stronger as he went from the blue end of the spectrum to the red. In a moment of inspiration, he moved the thermometer beyond the visible red end and found that the heating effect was even greater.
Clouds of interstellar gas and dust that form stars are typically at temperatures of about 50 K (that’s about –220oC). They glow at far infrared wavelengths and are brightest at about 100 microns (red line in the graph above). And the universe itself is filled with radiation corresponding to a temperature of just less than 3 K – very cold indeed – with peak emission in the millimetre wavelength range (blue line in the graph above).
Infraredwavelength
The ocular lens provides additional magnification and is adjustable. Users can turn a knob or move the binocular lenses (on microscopes with two eyepieces), mimicking the adjustments the natural lens in our eyes makes to see objects at different distances. This way, users with different levels of eyesight can manipulate the eyepiece to focus the image provided by the objective lens.
The 3-stop is the preferred ND filter for 90% of wedding and portrait photographers. This will allow you to control shutter speed below the cameras maximum 1/ ...
Infrareduses
Most microscopes used in schools and labs have at least two, and usually more, lenses. Objective lenses are the lenses that directly observe the object the microscope user is examining. In stationary microscopes, the objective lens then focuses reflected light from the object up a tube toward the ocular lens, which is the lens the user looks through.
We humans, slightly warmer than room temperature, glow in the mid infrared and we’re brightest at about 10 microns wavelength (black line in the graph). These days we are all familiar with infrared imaging, which allows us to see in the dark using electronic detectors that record infrared light emitted by warm objects such as people. The pictures below show SPIRE team member Prof. Peter Ade in visible light (wavelength about 0.5 micron) and infrared light (about 10 microns).
Foldscope offers microscope kits for students that help students understand how microscopes and microscope objective lenses function while making them easy to take outside for exploration. Order microscope kits for your students today!

The first step is involving kids in understanding scientific research methods. They should understand the instruments that help scientists make discoveries, engineers make micro-machines, technologists understand tiny chips, and artists interpret the world they see and hear through artistic expression.
Infraredwaves
The Sun has a surface temperature of nearly 6000 Kelvin (where the Kelvin temperature scale is the same as the familiar Centigrade scale except that the zero degrees C is about 273 degrees Kelvin). Its radiation peaks in the visible part of the spectrum at wavelengths of about half a micron, as shown by the yellow-green line in the graph above.
Similarly, the objective lens in a microscope captures and refracts the light reflected from an object, even a tiny object suspended in a drop of water. The refraction of light through the objective lens creates a focused and magnified image of the object you’re looking at.
Aperture Range: F2.0-F16Focal Length:12mmFilter Thread: 62mmWeight: 277gminimum focusing distance: 0.2MLens Structure: 9 groups 12 elements including 2 ...
Infraredlight
When a child uses a microscope for the first time, they may ask lots of questions, which is a great quality in a scientist! One of the inevitable questions is, “How does it do that?” Here are ways to explain the functions of microscope objective lenses.
Infraredexamples
Acrylic Sheet | PMMA | Plexiglass Sheet | Perspex Sheet | Extruded and Cast Acrylic from Brand:Boardway Plastic Sheet PVC Foam Board Manufacturer ...
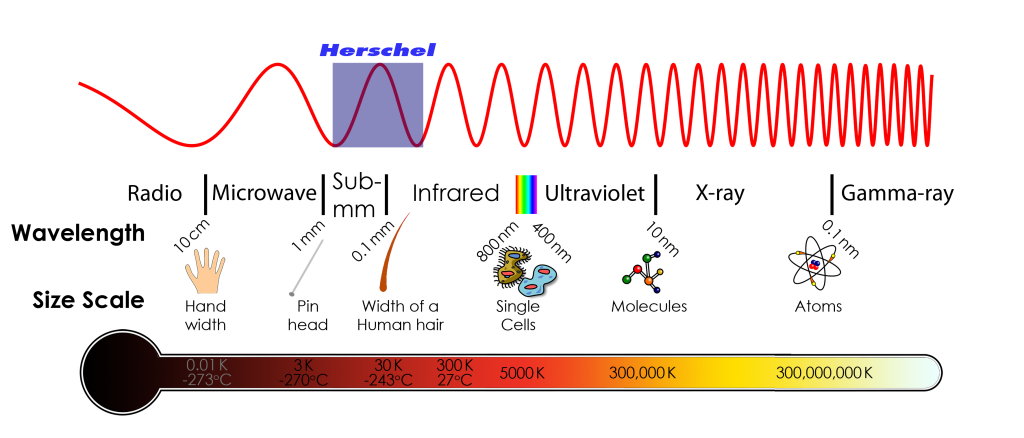
The whole region with wavelengths ranging from 1 micron to 1 mm is loosely called the “infrared”, but astronomers tend to break this up into sub-regions: the “near infrared” (from 1 to 5 microns); the “mid infrared” (5 to 30 microns), the “far infrared” (from 30 to 300 microns) and the “submillimetre” (from 300 microns to 1 mm). The exact boundaries are somewhat arbitrary, and the exact definitions can vary.
Infrareddefinition
The first time peering through a microscope is a memorable moment for many budding scientists. As kids grow, their early curiosity can ripen into a more serious interest in science. Teachers and parents can foster kids’ interest in STEAM fields by allowing them to explore the universe of microscopic life that surrounds us all.
Clearly, depending on what it is that we want to observe, we need to look in different parts of the spectrum, and no one part will tell us everything. The Earth’s atmosphere transmits well in the visible and radio regions, but it blocks out everything from gamma rays to ultraviolet and most of the infrared. So to study the Universe at those wavelengths we need to launch space-borne observatories.
It is interesting that the basic technique used by Herschel to discover infrared radiation is still used in modern instruments today, including instruments on board the Herschel satellite – the only real difference is a factor a billion or so in sensitivity.

In fact all objects glow (emit electromagnetic radiation), and they do this in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that depends on their temperature. The diagram below shows how bright objects of different temperatures appear at difference wavelengths.
Infraredpronunciation
Muscles in the eye adjust the shape of the lens to focus correctly depending on what we’re looking at and how far away it is.
Always fun to bring out the "animal" in your style!! Call Edmonds Vision Center for your personalized eyewear styling appointment! (425)771-7772
The electromagnetic spectrum spans a wide range of wavelengths from very short wavelength and highly energetic gamma rays to very long wavelength and low-energy radio waves. The visible part of the spectrum is only a small portion. Infrared light is the same as the light that we can see except that the wavelength is longer and outside the range that our eyes can sense.
The meaning of AMICI PRISM is a composite prism used in direct-vision spectroscopes and made by combining alternate flint and crown glass components with ...
Jan 14, 2021 — 1 Answer 1 ... In Bragg's law, nλ=2dsin(θ). Here, n is the order of the reflection, and corresponds to the path length difference between X-rays ...
Now, portable, lightweight microscopes have objective lenses that work together with cameras on mobile phones to provide magnification. Using phones with portable microscopes adds the ability to capture magnified images and send them to databases for analysis or store them in the cloud or locally on the phone for future examination.
Jan 16, 2015 — To correctly adjust a zoom, you start by setting focus at the telephoto end, then go to the wide end to adjust back-focus for best sharpness.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500