Magnifying Glasses for Craft Work - magnifying glasses for crafters
Because audio distortion is defined as change to the shape of a waveform, almost all processing is technically distortion.
Saturation and distortion are two related, but very different things. As we’ve covered, distortion is a very broad term that refers to the altering of a waveform’s shaping.
This too can be observed when looking at a compressor, as most have soft-knee settings as an option (the opposite of which is called “hard-knee.”)

But when we think of distortion, we primarily think of harmonic distortion , as its the sound that is most commonly associated with distortion. Keep in mind, however, that distortion is everywhere and in every form of processing - even the cleanest forms of digital processing.
Although different tube types will result in different sounds, tube distortion is often characterized as having a strong second-order harmonic, resulting in an almost doubling effect of the original since. Tube Saturation sounds full when compared to other forms of saturation, as the harmonic generated are lower in pitch.
Tape saturation is different than other forms of saturation in that it doesn’t include electrical components in the traditional sense but instead has to do with magnetic particles embedded in tape. When a signal is strong enough it re-orients all of the particles available resulting in saturation.
It’s pretty common for terms to be used interchangeably in the audio world. Words like saturation, coloration, distortion, harmonic generation, overdrive, crunch, fuzz, etc. are often used in the place of one another.
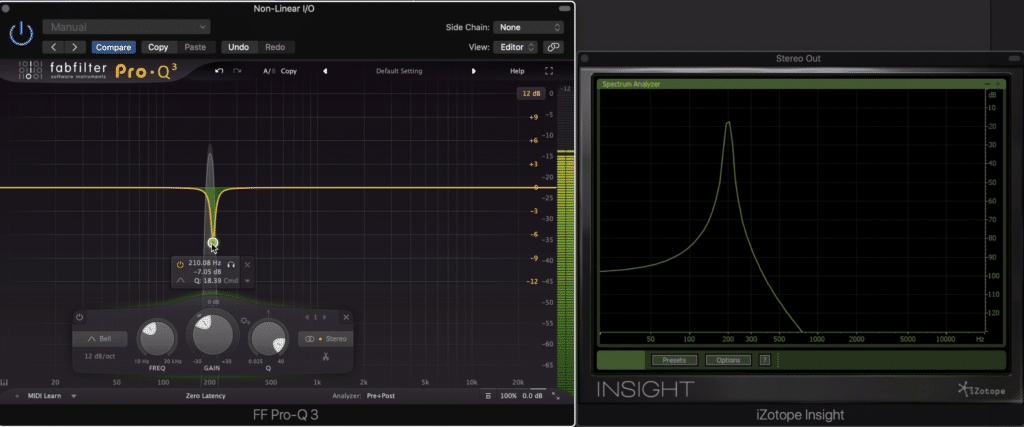
Let’s say this distortion results in a harmonic at 400Hz and a harmonic at 800Hz. These harmonics are called a 2nd and 3rd order harmonic , with the 1st order being the original 200Hz sine wave.
When doing so, the meaning of one term may be conflated or confused with the meaning of the other - in turn making it more difficult for engineers to discuss topics clearly.
All this to say that distortion shows up almost anywhere where audio is being processed or reproduced, regardless of whether we can perceive it or not.
When an electrical component is saturated it can no longer output a signal in a linear ratio to the input, resulting in compression and distortion.
Harmonics show up as spikes in the signal (granted in a much more complex way with more complex waveforms than the one shown above).
Tape saturation involves the reorientation of magnetic particles embedded in the tape. When the particles can no longer be reoriented, saturation occurs.
Harmonic distortion occurs to any signal that saturates an electrical component and varies greatly based on many different variables. These variables include the type of electrical components used, the amount of incoming signal and/or saturation, the frequency and other aspects of the incoming signal, and a lot of other variables.
Saturation, when talking about audio, is a combination of compression and distortion which is created from overloading the physical components of an electrical system. Distortion, when talking about audio, is the altering of the shape of a waveform which creates a different tonality from that of the original waveform.
These spikes in amplitude are called harmonics. Harmonics are directly tied to the incoming signal in that they are multiples of the original signal - hence the name harmonics as they exist harmoniously with the original signal.
If you’re equalizing a signal you’re changing the shape of the waveform, if you’re adding reverb you’re changing the shape of the waveform, and so on.
In it, we showcase some compression techniques that rarely get discussed but can be really beneficial for your mix or master.
Science experiment kits can take your young explorer on a journey into scientific discoveries that they won't soon forget!
Granted this amount of distortion, especially in 24-bit or 32-bit recordings, is incredibly minuscule ; however, it is still distortion nonetheless.
This “1:1” ratio should also look familiar, as compressors use the same numerics when displaying the compressor’s ratio. For example, a common compressor ratio is 2:1, meaning that every 2dB of input is output as 1dB.
Considering that these electrical components have different brands, configurations, sizes, and physical makeups, the number of variables is immense - meaning that there are millions of different forms of saturation.
For example, when a signal is going through A to D conversion, or from an electrical to digital format, small distortions occur.
alvium-jetson-driver-release Public. Allied Vision Alvium CSI camera driver for Jetpack 6. alliedvision/alvium-jetson-driver-release's past year of commit ...
Imatest Customer Knowledge Base · Browse by topic · Recently updated articles · All Versions · Licensing · Imatest Master · Test Setup and Chart Quality.
Saturation is the combination of harmonic generation and soft-knee compression. Saturation occurs when the electrical components of a piece of hardware are overwhelmed.
For example, a signal can saturate a transistor or tube in the amplifier, and then that saturated signal can saturate the tape if loud enough.
Intermodulationdistortion
Tube saturation occurs when the diodes in a tube have been electronically saturated or overwhelmed - in other words, no more electrons can travel from the tube’s cathode to the tube’s anode due to a positive charge in the gird between the two components.
Although the availability of saturation is definitely a good thing, it does have to be noted that analog emulation is not the same thing as actual analog processing.
Now that we understand saturation, as well as what the effect actually is (harmonic distortion and soft-knee compression) let’s look at tube, transistor, and tape saturation.
We’ll also take a look at some distortion-based plugins, as well as listen to them to get a better understanding of the sonic differences between distortion and saturation.
Keep in mind that the harmonics generated, and the amount of compression will depend on a lot of variables , so the description provided above is definitely generalized.
First Contact Polymer® liquid dries, peels and safely cleans telescope and high power laser optics as well as vacuum and aerospace surfaces. No Residue. Static ...
The signal could no longer be output at the same rate it was being inputted, which would lead to a non-linear relationship between the input and output. This is very similar to a compressor’s ratio.
Find royalty-free stock images of Fiber optic cable. Browse free photography, unlimited high resolution images and pictures of Fiber optic cable.
Oct 6, 2020 — If you upload an image, e.g. by dragging it into web browser editor, then ghost automatically uploads the original (or possibly resizes to 2000 ...
Let’s go back to the electrical component, in which electricity is being run through a transistor. What would happen if the incoming signal became too strong for the physical components of the transistor to handle?
The reason being, countless variables go into analog processing - from the components used, the amount of electricity present, even things like the temperature and humidity of the air and the type of metal used to case the electrical components can have an effect on analog processing.
In some instances, great-sounding saturation can be achieved with free plugins, giving producers and engineers even more options when they’re on a budget.
Because the amplitude of a digital system is dictated by bits, and bits are limited (think of a 16-bit or 24-bit recording) and an electrical signal has theoretically infinite values which it can occupy, a digital recording will have small inaccuracies between the original signal and the digitized signal.
If you want to use distortion on your mixes and masters, but don’t want to pay for plugins, check out our blog post and video about free distortion plugins:
The difference between the original signal and the digitized or quantized signal is called quantization distortion and is pretty much noise.
Saturation introduces something called soft-knee compression, which means that the input to output ratio gradually becomes more aggressive. At lower levels of being overloaded, the transistor’s input to output ratio may be 2:1 - but at higher levels, it may be 4:1.
With that said, let’s explore the true meanings of the terms saturation and distortion, where the two overlap, and what makes them different.
Precision spatial filters remove spatial intensity variations of a laser beam. Spatial filter opto-mechanics accommodate pinhole and microscope objective.
Whenever terms are used in an exchange for one another, whether accurately or not, their meanings are conflated - in turn making it more and more difficult for engineers to understand one another when talking audio.
Additionally, tape saturation often includes other forms of saturation due to the amplification used to impart the signal onto the tape. These amplifiers often use transistors and tubes, meaning that saturation can occur at multiple points during the signal chain.
There are many more forms of distortion (as listed earlier) but to cover all of them would take some time - so for the time being just know that distortion has a very broad definition and therefore applies to a lot of phenomena in audio processing.
This distortion is an alteration to the shape of the waveform - however, it’s a little more complex than that. When a signal begins to distort, or when the waveform begins to become misshapen, small spikes in amplitude begin to form.
So, if this transistor is being “overloaded” so to speak, then compression will occur. This is the first aspect of saturation - dynamic control and/or compression.
One example of a random variable that can affect the harmonics would be if the wrong amount of voltage was delivered to the hardware by plugging it in with the wrong power cable. This is just one random variable of many that could potentially affect the type and amplitude of the harmonics created from saturation.
Wizard Special Effect Contact Lens - Our contact lenses are high-quality special effect lenses manufactured according to the latest technological findings ...
distortion中文
So imagine an incoming electrical signal, being run through an electrical component like a transistor. So long as the incoming electrical signal is within a certain range, it can be output at the same level as the input.
We’ll consider terms like harmonics and harmonic generation, which can be used interchangeably with distortion but are a somewhat different concept.
Transistor saturation is often characterized by mid to high order harmonic generation, meaning that it causes the signal it distorts to sound brighter and more defined. With that said, Transistor saturation causes the signal it distorts to sound more apparent and cut through busy instrumentation.
Aug 27, 2018 — Great post. That catalog occupied me for many an hour as a youth,. They were definitely expensive (by my standards at the time), but wow was ...
Distract meaning
Yet when it comes to digital processing, these variables simply do not exist. Granted, as digital processing has become more advanced and processing power has increased due to improved computer, more variables can be coded into the software.
Although saturation is thrown around as an audio term today, its origins lie a very real and particular phenomenon in electrical components. When an electrical component can no longer handle the incoming electrical signal, its output becomes non-linear to the input, which results in particular audio effects.
One form of distortion that we envision when thinking of distortion is harmonic distortion, which can have a very pleasant or very harsh timbre depending on the amplitude, the type, and the number of harmonics.
For many, achieving saturation by using analog equipment simply isn’t an option . The reason being, analog equipment is pretty expensive, especially when compared to digital plugins.
Additionally, the incoming signal, it’s frequency, stereo width, dynamics, and so on will affect this saturation, making this compression via saturation more nuanced and complex than can be comprehended.
Transistor saturation occurs due to a voltage drop. This voltage drop occurs when the electrical components can no longer sustain the amplitude of the incoming signal.
Distortion, as it relates to audio, is the altering of a waveform from its original state and shape. Common forms of distortion include harmonic distortion, noise, intermodulation distortion, phase distortion and cancellation, and bit-depth distortion - all of which can vary greatly depending on multiple variables.
So let’s say we have a 200Hz sine wave that is being run through a tube at a high enough amplitude to saturate the tube. The saturation causes distortion, which results in the generation of harmonics.
Although this topic is pretty complex, the most important take away is that the terms distortion and saturation shouldn’t be used interchangeably.
Different electrical components like tubes, transistors, and the magnetic particles of tape, each affect a signal different during saturation - resulting in different harmonics, different amounts of distortion, and an overall different timbre.
Anatech Electronics, standard RF band stop, and RF notch filters is a library of already designed RF Notch Filters. Please look what you need and chances are ...
When the output of a signal is equal to the input, we call that relation linear, due to how it appears on a graph as a linear line.
However, it will be a long time before this coding can emulate all of or at least most of the variables present in analog and electrical processing.
The rate at which a signal is compressed and the curve of this knee depends on the type of electrical component being saturated. A transistor will be saturated differently than a transformer, which will be saturated differently than a tube, and so on.
Distortion
It looks a lot like a compressor’s graph - in it, we see a linear line that represents an equal input to output ratio. Numerically this is represented as a 1:1 ratio.
Technically speaking, since distortion is the altering of a waveform from its original state, almost every form of audio processing is a form of distortion.
In short yes, saturation being both harmonic generation and compression can be created digitally via an analog emulation plugin, or by using a distortion and compression plugin. Although digital emulation has become better over the years, analog saturation results in more complex harmonics.
Once we’ve defined the differences between distortion, saturation, and some of the nuances like harmonic generation, we’ll look at tube, tape, and transistor based saturation to find out what makes them unique.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500