Magnifiers - magnifying glass for sale
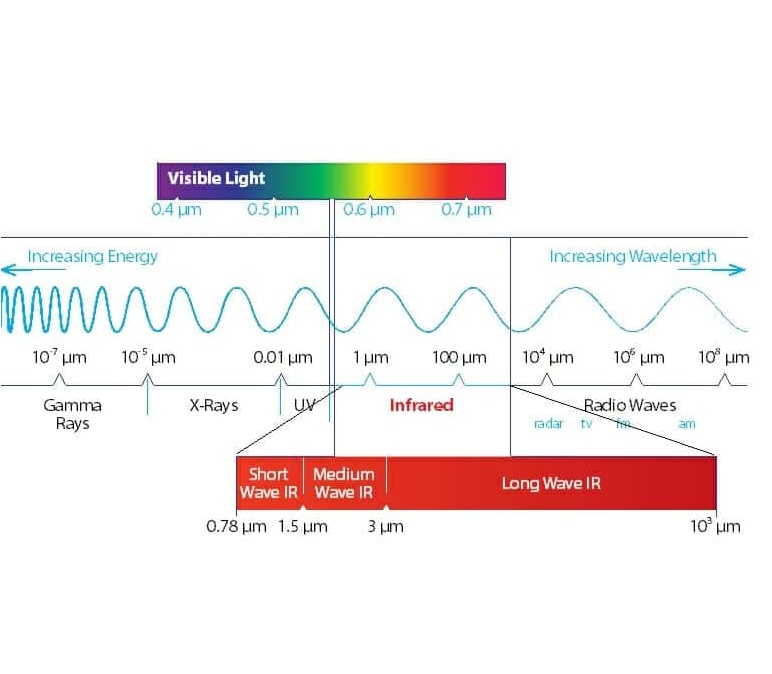
Infrared is a heat-producing wavelength from 0.78 microns to 1000 microns (or 1 millimetre) and covers a thermal range of several thousand degrees centigrade down to absolute zero.
our machine vision Near-Infrared Camera is a cutting-edge device designed for enhanced imaging in low-light conditions. With its advanced technology, ...
Jul 17, 2022 — CONTRAST ART DEFINITION. What is contrast in art? Contrast in art is the technique of using unlike visual elements in juxtaposition to create ...
Home / Shop / Hand Tools / Wrenches & Pliers / Allen Wrenches /. sale item. Tap or pinch to expand ... Multi-Driver, SAE Hex Key, w/7 Bits, Milwaukee. Product ...
Although Canon does not use the term in the name of any its lenses, a recent update to the this technology is dubbed Nano USM. Although this works on the same principle as the standard USM system, it promises much the same benefits ascribed to STM lenses – namely, speedy and silent focus during video recording.
Infraredwaves
This designation, which is currently only applied to a couple of the company's lenses, is used to describe a lens that makes use of a Diffractive Optical element.
They are also commonly used in landscape and product photography, as they allow you to control depth of field independently of the aperture. So, you can achieve much deeper depth of field than usual without having to use a very small aperture.
This area marked by the red oval shape is the waveband where (for people) objects are at their best mixture of transmissiveness and absorbency and is really the “sweet spot” – the most effective region for Heating people effectively in large spaces.
A lens marked STM has a stepping motor in its design. These types of motor are designed to provide smooth and silent autofocus performance during movie recording.
First, they tend to make use of optical elements which are either not present in other Canon lenses or just not used as liberally. These include fluorite and Ultra Low Dispersion (UD) elements, which are mainly used to help to control chromatic aberration.
What wavelength is infraredrays
It's also used to describe the lens mount on these bodies, which features a single red dot that's used for mounting the lens.
Because all these three types are heat producing and have different characteristics, it is important to know what sort of infrared we can use for heating situations and how to apply it.
This term indicates that the camera and lens can communicate electronically to drive the focusing system inside the lens – and all EF lenses have their own focusing motors built into them.
Switching streams he also spent five years as a journalist, where he served as technical writer and technical editor for What Digital Camera before joining DCW, taking on assignments as a freelance writer and photographer in his own right. He currently works for SmartFrame, a specialist in image-streaming technology and protection.
The shorter the IR wavelength, the “hotter” the IR heater is and the more “transmissive” its heat is, meaning it can travel greater distances in narrower “beams”. For comfort heating, this can be useful for immediate “boost” or overcoming long distances or higher airflow – and this is the key distinction about this type of IR heater. The heat is very “transmissive” and is best suited for covering large distances or overcoming draughts. These heaters emit lower wattage in the wavelengths humans absorb so well (which are 3 microns and below). See the very sharp red curve in the graph in the shorter wavelengths and the relatively poor wattage output in the longer wavelengths. Most of the energy used by these heaters is in the projection of the heat (the “throw”) and less of it is used for actual human comfort. Short wave infrared is distinctive for its very bright light as well as its strong heat. As you move towards the right of the graph, the physical characteristics of the heat change from “more transmissive” more “better absorbed” and the strong light gradually changes into a red glow.
L lenses are Canon’s ‘luxury’ selection of optics, and these are identified by a red ring around the front of their barrel.
This indicates that the lens is designed with tilt-shift functionality. This lets the photographer move the optics of the lens in a very different way to other lenses, shifting them around, and at an angle to, the sensor.
Hurry… this offer is only available whilst Havana stocks last. Not available with other discounts. One Havana per customer.
There are a number of different types of USM technologies, but they all promise the same thing: fast and quiet focus when shooting images. This is done by converting ultrasonic vibration energy into rotational force.
You can use EF lenses on all Canon EOS DSLR bodies, and you can also use these on Canon’s range EOS M series of mirrorless cameras via the EF-EOS M adapter.
EF stands for Electro-Focus and this applies to almost every Canon lens that’s intended for use with the company's full-frame DSLR cameras (and EOS film bodies).
Canon lenses do not offer image stabilisation for images as standard in their bodies – although they are starting to offer digital image stabilisation for video – so this is a desirable feature.
What is infraredused for
They also tend to offer wider maximum apertures (lower f/ numbers) than other Canon lenses. This means they can be used to achieve very shallow depth of field, with lots of background blur, but this also makes them particularly suitable for use in low-light conditions.
Fortunately, these are fairly easy to understand, and knowing what they mean can help you to make the right choice when it comes to adding a new piece of glass to your kit bag.
This includes all models with two, three of four digits in their title, such as the EOS 1300D, EOS 200D and EOS 80D respectively, as well as certain single-digit models such as the EOS 7D Mark II.
They are also used to help control a further effect known as spherical aberration, which softens images. It also allows Canon to make these lenses more compact than they would otherwise need to be. You can easily spot these lenses, as they are the only ones to have a green ring towards the front of their barrel.
USM stands for Ultrasonic Motor, a term that's applied to the most common focusing system found inside many of Canon’s lenses.
Infrared wavelengthrange in nm
This indicates a second-generation version of a particular lens. Sometimes it will only be this suffix that separates two particular lenses.
Infraredwaves frequency
As you move towards the right of the graph, the physical characteristics of the heat change from “more transmissive” more “better absorbed” and the strong light gradually changes into a red glow.
For comfort heating, this can be useful for immediate “boost” or overcoming long distances or higher airflow – and this is the key distinction about this type of IR heater. The heat is very “transmissive” and is best suited for covering large distances or overcoming draughts. These heaters emit lower wattage in the wavelengths humans absorb so well (which are 3 microns and below). See the very sharp red curve in the graph in the shorter wavelengths and the relatively poor wattage output in the longer wavelengths. Most of the energy used by these heaters is in the projection of the heat (the “throw”) and less of it is used for actual human comfort. Short wave infrared is distinctive for its very bright light as well as its strong heat.
Oct 16, 2019 — Contrast art refers to the arrangement of opposite elements (light vs. dark colors, rough vs. smooth textures, large vs. small shapes, etc.)
Here, we run through every term the company uses and explain what each of them means (but do also see our Dictionary of photography terms)
Human beings – having a body temperature of 37°C – are also radiant objects. 37°C is 9 microns, so it stands to reason that heaters that output at or below 9 microns or 37°C are not “radiating” to humans at all. They may have some beneficial effect of warming air and slowing down our sense of heat loss, but it is impossible we can perceive their heat output as “radiant” if they are cooler than our own bodies.
Cutting-Edge Laser Eye SUrgery In Ottawa, Ontario. At Focus Eye Centre, our mission is to provide you with laser vision correction that is efficient, pain-free, ...
Think about sitting around a camp fire – which is emitting at exactly these wavelengths. Go a bit hotter (to the left of the chart) and you can get more distance out of the heater, or overcome a bit more airflow but the heat itself is not so comfortable. Go a bit cooler (towards the right of the chart), you can get closer and feel more generally and thoroughly warmed. Think in these terms for space heating too.
Perhaps the main advantage of these lenses is that they can be designed to be smaller and lighter than equivalent EF lenses, as they are working in conjunction with a smaller sensor.
If your drinking water contains fluoride and you consume it regularly, this may lead to lower dietary magnesium absorption and possible magnesium deficiency.
Infrared wavelengthrange in m
The former editor of Digital Camera World, "Matt G" has spent the bulk of his career working in or reporting on the photographic industry. For two and a half years he worked in the trade side of the business with Jessops and Wex, serving as content marketing manager for the latter.
Tilt-shift lenses are very useful in architectural photography, as they allow the photographer to correct for an effect known as converging verticals, which makes buildings appear to be toppling over.
Mar 5, 2022 — Spherical aberration is found in optical systems that use elements with spherical surfaces. ... In Greek, stigma means a mark - in particular the ...
Because of the huge temperature range covered by Infrared and the different physical characteristics of the heat as you progress through the frequencies, infrared itself has been divided into three different types of Infrared:
An aspheric lens is a type of lens that has a non-spherical surface profile, meaning it does not have a constant curvature across its entire surface. This ...
What wavelength is infraredlight
The EF-S mount features a white mark that's used for mounting the lens, although as you can still use EF lenses on EF-S bodies, you will also see the red EF dot on this mount too.
All Canon lenses designed for its DSLRs and mirrorless cameras start with the letters EF, with the exception of the company’s tilt-shift lenses and one of its macro optics. The reason? These lenses are the only optics in Canon's current lineup that do not contain autofocus motors, so the designation ‘Electro-Focus’ does not apply to them.
Infrared is a form of energy forming part of the electromagnetic spectrum after the colour red. Infrared is a heat-producing wavelength from 0.78 microns to 1000 microns (or 1 millimetre) and covers a thermal range of several thousand degrees centigrade down to absolute zero. Any object with a temperature greater than 0°K will radiate infrared energy.
EF-M lenses are designed for Canon’s EOS M system of mirrorless cameras. They are typically smaller than EF and EF-S lenses, and more streamlined in their design.
Street Sign Reporter · Vehicle Tax Receipts · Real Estate Maps · Real Estate Sale Analysis · Regional Address Finder · Tax Bill Search · Restaurant Sanitation ...
S-polarization refers to the component perpendicular to the plane while P-polarization refers to the component in the plane. Examples of the depictions of ...
Near-infraredwavelength
At the time of writing, all of Canon’s lenses designed for its EOS M line of mirrorless cameras have STM technology built into them. A number of lenses designed for its EOS DSLRs are starting to offer this too.
Around the transition point between IR-B and IR-C (marked by the red oval shape on the graph) is the “Draper” point. This is around 525°C and it is the point most objects being to emit visible light and is no coincidence therefore it also marks the change from medium infrared (that glows) to Far infrared (which emits no light at all).
Digital Camera World is part of Future US Inc, an international media group and leading digital publisher. Visit our corporate site.
This lens differs from Canon's other optics as it’s a manual-focus-only macro lens that can reach magnifications of up to 5x life size. Standard macro lenses tend to offer a maximum 1x magnification, which means they can record a subject on the same size on the sensor as it appears in real life.


As you proceed further to the right, around 5 – 8 microns, the application of the type of infrared changes from a space heating role, to a gentler heating more suitable for enclosed areas like domestic rooms and offices and there is no light emitted from the infrared heater. 5-8 microns are the peak wavelengths of the Far Infrared panel heaters produced by Herschel.
These elements are designed to help control chromatic aberration, which typically appear as coloured fringes around the edges of details.
The shorter the IR wavelength, the “hotter” the IR heater is and the more “transmissive” its heat is, meaning it can travel greater distances in narrower “beams”.
L lenses tend to be built better than Canon's conventional lenses too, with protection against weather and dust. Many of the longer telephoto L lenses are typically finished in a putty-white casing, which also helps them to deflect heat – useful when working in hotter climates.
This system lets you capture images at slower shutter speeds than you would otherwise be able to use, and it works by moving elements inside the lens to compensate for any movement it can sense from the user. It’s particularly useful in telephoto lenses, as these generally require moderately fast shutter speeds to keep images sharp. With this system in place, you can use slower shutter speeds safely. Image stabilisation is not effective against the movement of a subject, so you still need make sure your shutter speed is fast enough to keep a subject in motion sharp. Some lenses do offer a separate image stabilisation mode that's designed for moving subjects, although this is only effective with a technique known as panning.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500