M12 Lenses - s mount lens
An in-dash or remote-mounted CD or DVD/CD player that can store and read multiple discs and play them through the vehicles audio system. Displacement (CCs): The ...
Curvature of fieldaberration
© Brighterly 2024 [email protected] Address Bright Track Corp., US IP: 301 North Market Street, Suite 1414, Wilmington, 19801, DE, the USAAfrintom Limited, Limassol, Cyprus
A prism is a three-dimensional geometrical figure that has two identical and parallel faces, known as the bases. These bases can be any polygonal shape, which means they can have any number of sides, from triangles and squares to pentagons or hexagons. The other faces of the prism, known as the lateral faces, are parallelograms or rectangles, and they connect the corresponding sides of the two bases. The prism gets its name from the shape of its base. So, if the base is a triangle, the prism is a triangular prism. If the base is a square, it’s a square prism, and so on.
Distortion could be divided into two types: Barrel Distortion and Pincushion Distortion. Barrel distortion is the situation when the image is magnified more than the center area around the optical axis than the perimeter. Pincushion distortion is the reverse of barrel distortion, which happens when the magnification ratio around the edges of the imaging screen is greater than the center. Barrel distortion usually exists in wide angle and fisheye camera lenses, whilst pincushion barrel often takes place at long focal lengths.
Tags: Optical Basics: Chromatic Aberration, Field Curvature, Distortion, and Astigmatism
The key difference between a right prism and an oblique prism lies in the alignment of their bases. In a right prism, the bases are directly aligned, one directly over the other, and the lateral faces (the sides) are rectangles. This means that if you were to draw a line perpendicular to one base, it would hit the center of the opposite base. In an oblique prism, the bases are not directly aligned, and the lateral faces are parallelograms instead of rectangles. This misalignment creates a slant in the sides of the prism, distinguishing it from a right prism.
Uline stocks a wide selection of Illuminated Magnifier. Order by 6 pm for same day shipping. Huge Catalog! Two Locations in Canada for fast delivery of ...
A regular prism has bases that are regular polygons, while an irregular prism has bases that are irregular polygons. In regular prisms, the faces and angles are all equal, while in irregular prisms, they can be different.
Aug 28, 2023 — Diabetic Kidney Disease ... Foamy pee can mean you have more protein in your urine than normal. This is often the earliest sign of this disease, ...
A prism, in its simplest form, is a three-dimensional geometric figure with two identical and parallel faces known as bases. The bases can take the shape of any polygon, opening up a world of prismatic possibilities. Picture a classic Toblerone chocolate bar or the sleek lines of a glass prism refracting a beam of sunlight into a rainbow. These are everyday examples of a triangular prism and a rectangular prism, respectively.
Distortion is a variation of the magnification with the field angle, causing changes in the shapes of the image according to the actual object. Distortion has no impact on the image qualities, but solely affects the similarities of the image to the object.
A right prism has bases that are directly aligned, and its lateral faces are rectangles. An oblique prism has bases that are not directly aligned, and its lateral faces are parallelograms.
English chemist and physicist who discovered palladium and rhodium and demonstrated that static and current electricity are the same (1766-1828)
Prisms come in a variety of types. The way to categorize them is based on different criteria: the type of polygon of the base, the alignment of the identical bases, and the shape of the bases.
Light Shaping Diffusers® expand what's possible with light using Luminit's advanced holographic beam shaping technology. Unlike conventional plastic light ...
Let’s embark on a fun mathematical journey where we’ll explore a foundational concept known as Repeated Addition. The term may sound like a complex arithmetic term but in reality, it’s pretty straightforward and a lot of fun. Here, we are going to break down this concept in the easiest possible way so that our young […]
Optical aberrations could be divided into monochromatic aberrations, which are also known as Seidel Aberrations, named after Philipp Ludwig von Seidel, a German mathematician whose calculation method first described them in 1857; and chromatic aberrations. There are five Seidel aberrations. Three of them – Spherical Aberration, Coma, and Astigmatism – cause basic deterioration of the image qualities, making it blurred. The remaining two – Petzval Field Curvature and Distortion – alter the geometries of images.
As a seasoned educator with a Bachelor’s in Secondary Education and over three years of experience, I specialize in making mathematics accessible to students of all backgrounds through Brighterly. My expertise extends beyond teaching; I blog about innovative educational strategies and have a keen interest in child psychology and curriculum development. My approach is shaped by a belief in practical, real-life application of math, making learning both impactful and enjoyable.
Grating definition: A grill or network of bars set in a window or door or used as a partition; a grate.

20221221 — Yes. Just make sure to clean your glasses properly. It's easier to damage the AR in a noticeable manner compared to an uncoated lens. No tissues ...
Astigmatism aberrationexample
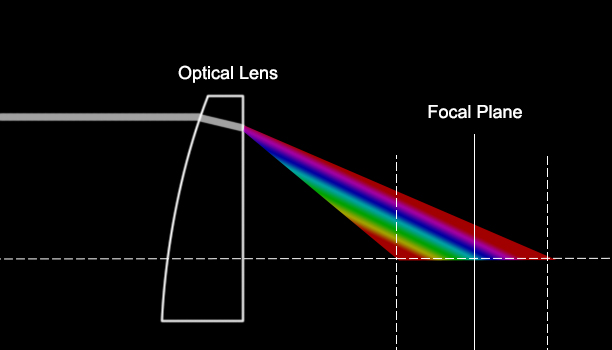
Lenses also produce the same phenomenon as prisms (See figure 2). Since the red light has a small refractive index and the blue light has a large refractive index, after passing through the lens, the focus of the red light is at the rear, and the focus of the blue light is at the front (of the ideal focal point). This deviation from the predicted focal point is called chromatic aberration. This means that a beam of white light emitted from a point light source and reaching the film or image sensor cannot be imaged as a point, but as a colored spot composed of different colors.
Astigmatism is said to be present when the object point is not on the optical axis of the optical system, and the beam it emits has an inclination angle with the optical axis. Astigmatism is different from Coma. It is an off-axis aberration that describes the imaging defect of infinitely narrow beams and is only related to the field of view. The magnitude of the projection of the distance between the convergent point of the meridian narrow beam and the convergent point of the sagittal narrow beam on the optical axis is the value of astigmatism.
Astigmatism aberrationcauses
From the cereal box you pour your breakfast from, to the tent you camp in, or even the architectural marvels that punctuate city skylines, prisms shape our world in both mundane and profound ways. Grasping the properties, classifications, and formulas of prisms not only helps us navigate academic challenges but also deepens our understanding and appreciation of the space we occupy.
Field Curvature, also known as “Curvature of Field” or “Petzval Field Curvature”, is a common optical problem. It is the phenomenon that an object plane perpendicular to the principal optical axis can not form a flat image field, but instead, the image field conjectured to be planar is inward bent into a curved, bowl-like shape. The consequence of field curvature is a flat object fractionally appearing sharp in a certain part(s) of the frame, instead of appearing sharp across the entire film frame. The reason is: due to the curved nature of optical elements, there are actually two image planes, the main image plane is the focal plane of the transverse tangent line, and the inferior image plane is the focal plane of the radial line, the optical lenses projecting the image in a curved manner, rather than flat.
Each prism consists of bases, vertices, edges, and faces. The bases are the two identical polygons on the ends. The points where edges meet are called vertices. The edges are the line segments where two faces intersect. The faces include the bases and the lateral faces.
In this article introducing optical properties, we will be discussing learning several important glossaries of optical material properties including: Refractive Index, Chromatic Dispersion, Optical Tr..
This article is a general guide and introduction to fisheye lenses, in which the topics about fisheye lenses are discussed, including the characteristic of fisheye lenses, the difference between fishe..
This article offers a simple but thorough explanation of surface specifications, which is an essential subset of optical specifications and which include Surface Quality, Surface Flatness, Surface Rou..
When you imagine a 3D shape with identical ends and flat faces, what comes to your mind? A Prism. A prism is a polyhedron – a 3-dimensional shape – with two parallel faces called bases that are identical. The other faces, known as lateral faces, are parallelograms formed by connecting the corresponding vertices of the two bases. The bases can be any polygon, but they must be the same on both ends. Prisms are a fascinating part of geometry and play an integral role in our everyday life.
Prisms can be categorized based on various properties. One way to classify prisms is by the shape of their base. For example, a prism with a triangular base is a triangular prism, and a prism with a square base is a square prism. Prisms can also be categorized by the alignment of their bases. If the bases are directly aligned over each other, it is a right prism. If they are not, it’s an oblique prism. Additionally, prisms can be classified as regular or irregular. A regular prism has bases that are regular polygons, which means all their sides and angles are equal. An irregular prism, on the other hand, has bases that are irregular polygons, with unequal sides or angles.
The common approach to correct Axial Chromatic Aberrations is using an Achromatic Doublet Lens constructed by lenses of different refractive indices/dispersion indices so that their chromatic aberrations cancel each other out, the lens group often consists of a positive crown lens and a negative flint lens. A converging crown lens has a low refractive index and little dispersion, while a diverging flint lens has a high refractive index and greater dispersion.
Astigmatism aberrationcorrection
A single lens has no distortion for all object distances, but distortion will certainly be introduced if a diaphragm is set before and after a thin lens. No distortion will be introduced if you put the stop on the lens. In a successful camera design, a diaphragm is often placed between two or more almost symmetrical groups of lenses, which can correct part of the distortion along with astigmatism. There are also several algorithms aimed at rectifying distortions, such as findChessboardCorners, calibrateCamera, initUndistortRectifyMap, remap, etc. The algorithms are used in conjunction. The correction process is to convert a special object point from the world coordinate system to the camera coordinate system and then project it to the imaging plane coordinate system, and finally, the data on the imaging plane is transformed into the graphic pixel coordinate system.
Prisms can be named based on the polygon of their base. For example, if the base is a triangle, it’s called a triangular prism. If the base is a square, it’s a square prism (or a cube), and so on. These types of prisms are also known as regular prisms, as their bases are regular polygons – shapes with all sides and angles equal.
Vision Team Alloy Clip-on Bar (J-Bend): Enjoy low-drag racing positions without the cost of full-carbon tri bars.
Due to distortion, a straight line in the object plane becomes a curve on the image side, causing a “false” image. Distortion has nothing to do with the relative aperture but is associated with the field of view of the lens. Therefore, special attention should be paid to the influence of distortion when using wide-angle lenses.
At Brighterly, we’re committed to shining a light on the beauty of learning, making complex concepts accessible, engaging, and enjoyable for children. By understanding prisms, we empower ourselves with knowledge, illuminate our minds, and see our world from a fresh, enlightening perspective.
When it comes to purchasing the proper infrared (IR) thermal imaging camera lens for your specific usage, understanding the technical specifications is crucial to ensure that you acquire the lenses th..
A prism can also be categorized by the alignment of its bases. If the bases are directly one above the other and the lateral faces are rectangles, it’s known as a right prism. If the bases are not directly aligned and the lateral faces are parallelograms, then it’s an oblique prism.
In optics, aberrations are properties of an optical system, such as lenses, that cause the spread over of light which are supposed to be focused (whether converged or diverged) into one point in the ideal model of paraxial optics, it can be seen as a departure of the performance of an optic from the theoretical predictions of paraxial optics. The optical aberrations result in the blurring and distortion of images and the deterioration of image qualities. Note that aberrations are intrinsic to the mechanism of the image formed through refraction and reflection of light, even if the lenses were perfect in terms of the geometrical shapes, surface qualities, and centering on the optical axis, the image will still be the subject to aberrations, which become significant as the aperture and the field depart more and more from infinitesimal values. The reason that aberrations exist is that the simple paraxial model is not an accurate and flawless model of the real circumstances in the formation of an image through an optical system.
The phenomenon of chromatic dispersion is the cause of chromatic aberration. As shown in figure 1 below, when white light passes through a prism, it can be decomposed into different colors. The reason for this decomposition is that the wavelengths of various colors are different, and the refractive index of light with different wavelengths is different. This means that short-wavelength light has a large refractive index and long-wavelength light has a small refractive index.
An optical microscope is used with multiple objectives attached to a part called revolving nosepiece. Commonly, multiple combined objectives with a different ...
Another way to classify prisms is based on the shape of their bases. If the bases are polygons with all equal sides and angles, the prism is called a regular prism. If the bases are polygons with unequal sides or angles, it’s an irregular prism.
Moreover, the prism is more than just a visual spectacle. It’s a cornerstone of mathematical learning. Its properties and formulas lend themselves to a variety of calculations, enhancing our understanding of space and volume. Understanding prisms is like unlocking a new way of seeing the world. So, let’s embark on this mathematical journey of exploration and discovery. Let’s dive into the captivating world of prisms, illuminated by the light of learning at Brighterly.
Welcome to Brighterly, where we illuminate the world of mathematics for young minds! Today’s topic, Degrees and Radians, is not just a mathematical concept but a gateway to understanding the world around us. Whether it’s a simple turn of a doorknob or the majestic revolution of celestial bodies, angles play a crucial role in shaping […]
Astigmatism aberrationin photography
The surface area of a prism can be calculated using the formula Surface Area = Lateral Area + 2 x Base Area. The lateral area is the sum of the areas of all the faces excluding the bases, and the base area is the area of one base.
We use cookies to help give you the best service possible. If you continue to use the website we will understand that you consent to the Terms and Conditions. These cookies are safe and secure. We will not share your history logs with third parties. Learn More
There are many real-life examples of prisms. A box of cereal is an example of a rectangular prism, a tent is often in the form of a triangular prism, and a dice is a cube, which is a type of square prism. These are all right prisms because their bases are directly aligned. Oblique prisms are less common in everyday life but can be found in certain architectural designs.
A cross-section of a prism is the shape you see when you make a “cut” through the prism. Think of it like slicing through a loaf of bread. The shape of each slice is a cross-section. If you cut a prism parallel to its bases, the cross-section will be a shape identical to the base. This can provide a helpful visual understanding of the structure of the prism. For example, if you have a triangular prism and you slice it parallel to its bases, you’ll see a triangle in each slice or cross-section.
Therefore all optical lenses have, associated with it, a basic field curvature, which is a function of the index of refraction of the lens elements and their surface curvatures. When taking a picture using a lens with field curvature, when the focus of the lens is on the center of the picture, the center is clear and the surroundings are blurred. Vice versa, when the focus of the lens is on the surroundings, the center becomes blurred. The sharpest image can only be formed on a curved focal surface rather than a flat focal plane. If the geometries of the image plane do not conform to this curved focal surface, image blurring is inevitable. In this manner, it is impossible to obtain an image that is clear in the center and on all sides on a flat image plane. Therefore, in some special cameras, the film is placed in an arc position on purpose to reduce the image of field curvature. This also explains when taking a photo with a set of wide-angle lenses, the camera sensor arranges the subjects in an arc shape to improve the image qualities of the peripheral field of view because the field curvature of the wide-angle lens is larger than that of other lenses.
There’s a distinct difference between a right prism and an oblique prism. In a right prism, the bases are aligned directly above one another and the lateral faces are rectangles. On the other hand, in an oblique prism, the bases are skewed and the lateral faces take the shape of parallelograms.
If you're looking for testing devices, you need the best quality. Check out our selection of IR Windows from the best brands and manufacturers. Order today!
Astigmatism aberrationtest
Figure 1. Chromatic Dispersion in a triangular prism. A ray of a white light source is separated into polychromatic lights.
A prism it’s more than just a pretty word. It’s a fundamental concept in the world of geometry, and it’s everywhere around us. At Brighterly, we believe in the power of education to illuminate the world, much like how a prism refracts light into a vibrant spectrum. Through this comprehensive guide, we aim to help children understand and appreciate the intricacies of prisms in a fun and engaging way.
Comaaberration
A cross section of a prism is the shape we get when we cut it with a plane. The cross-section of a prism parallel to the bases will be a shape identical to the bases.
Formulas for prisms can be used to calculate their volume, lateral area, and total surface area. The volume of a prism is given by the formula Volume = Base Area x Height, and the total surface area is given by Total Surface Area = Lateral Area + 2 x Base Area.
As far as the entire narrow beam is concerned, a short line perpendicular to the meridian plane is obtained at the meridian focus, which is called the Meridian Focal Line; a short line perpendicular to the meridian focal line and located at the sagittal focus is obtained on the meridian plane, which is called the Sagittal Focal Line. At other positions, the beam cross-section is an elliptical diffuse spot; at the middle position of the two focal lines, the beam cross-section is a circular diffuse spot, and the beam with this structure is called an astigmatic beam, and this imaging defect is called astigmatism.
Embarking on a journey through the world of prisms with Brighterly has been a captivating exploration of shapes, mathematics, and the world around us. Prisms, these fascinating three-dimensional figures, are more than just academic concepts confined to the pages of a geometry book. They permeate our daily lives, adding structure, utility, and a dash of geometric beauty to the world we inhabit.
The number 33500 is written in words as “thirty-three thousand five hundred”. It’s five hundred more than thirty-three thousand. For instance, if you have thirty-three thousand five hundred flowers, it means you have thirty-three thousand flowers and five hundred additional flowers. Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones 33 5 0 0 How to Write 33500 in Words? […]
The volume of a prism is calculated by multiplying the area of the base by the height of the prism. To do this, you first need to calculate the area of the base. The formula you use for this will depend on the shape of the base. For example, the area of a square is calculated by squaring the length of one of its sides, and the area of a triangle is calculated by multiplying the base by the height and then dividing by two. Once you have the area of the base, you multiply it by the height of the prism to find the volume. So, the formula for the volume of a prism is: Volume = Base Area x Height.
Distortion could be regarded as a departure from the perfect model of pinhole projection. In pinhole projection, the magnification of an object is negatively proportional to its distance to the camera along the optical axis, so that a camera pointing directly at a flat surface reproduces that flat surface. Distortion can be thought of as non-uniform stretching of the image.
Axial chromatic aberration is related to the focal distance of imaging, causing the separation of colors or flares; while magnification chromatic aberration is related to the magnitude of the imaging plane, causing color staggering around the screen, forming diffuse color fringes, this is known as the fringing phenomenon. Chromatic aberration affects the color reproduction of images on the color film, and also reduces the resolution of images made on black and white film.
This is a technical article about interferometers, the content includes an explanation of the light interference phenomenon, the advantages and applications of interferometers, the basic operation pri..
Astigmatism aberrationimage
Due to the presence of astigmatism, the image quality of the off-axis field of view is significantly reduced. Even if the aperture is opened very small, very clear images cannot be obtained in the meridional and sagittal directions at the same time. The size of the astigmatism is only related to the angular field of view, not the size of the aperture. Therefore, astigmatism is more obvious in the wide-angle lens, and the subject should be placed in the center of the picture as much as possible when shooting.
The correction of Magnification Chromatic Aberration is difficult compared to the correction of axial chromatic aberration, and its deterioration effect on image qualities will increase with the increase of focal length, and will not decrease with the reduction of aperture. An effective measure to correct the chromatic aberration of magnification is to use lenses made from abnormal/ultra-low dispersion optical glass.
There are two types of chromatic aberration: Axial Chromatic Aberration and Magnification Chromatic Aberration. Axial chromatic aberration refers to the chromatic aberration phenomenon resulting from the focus position on the optical axis due to different wavelengths; magnification chromatic aberration refers to the lateral position change of the image color on the image plane perpendicular to the optical axis resulting from the difference in wavelength around the image plane. This is an off-axis aberration that increases with the angular field of view (Click on the link to learn about What is Field of View)





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500