Light Diffusing Film - light diffuser
202429 — JoVE Confocal and Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy (LSFM) Imaging of Cleared Mouse Kidneys.
For a tightly focused laser beam (w0 = 10 µ) and a 1 µm wavelength, we find ZR = 314 µm and a divergence (half-angle) of 1,8 degrees.
Gaussian beamq parameter
The main basic expressions related to Gaussian beams were mathematically obtained in the previous paragraph. We will now describe their physical signification.
Besselbeam
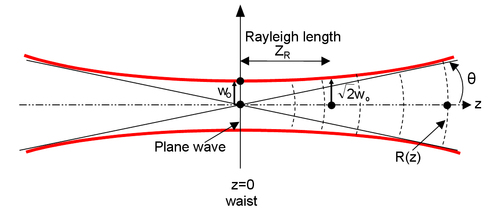
The size of the beam at the origin, w0, is minimal : the beam will diverge from this point (see figure 11). This minimal dimension is called “beam waist” (the waist is the radius of the spot. The diameter is of course given by 2 w0).
The divergence of a Gaussian beam is inversely proportional to the size of its waist. In the framework of Gaussian optics, “collimating a beam” is the same thing as “having a big waist”.
If we consider a “big” waist (1 mm), we find ZR = 3,14 m and a divergence (half-angle) of 0,018 degrees. We then obtain a so-called “collimated beam”.
The Standard Circular Polarizer filter blocks 1.5 stops of light and is one of those must have filters. Linear Polarizer. Polarizing filters provide color and ...
Addition of microlens arrays to CCD photodiodes can increase the optical fill factor by up to three times that realized without the tiny optical components. Increasing the fill factor yields a corresponding increase in the sensitivity of the photosite. Microlens arrays provide a substantial increase in performance of interline-transfer CCD imaging arrays that have lateral overflow drains and a sizeable amount of shielded pixel space. These devices typically suffer from reduced optical fill factors because of reduced active pixel area compared to total pixel size.
A typical lenslet placement scheme is illustrated in Figure 1, where a tiny optical lens is strategically placed over the dye layer and metal light shield of a photodiode. The lenslets are either grown in parallel arrays during the CCD fabrication process or manufactured out of a material such as quartz and placed on the array surface during packaging. Each lenslet is a high quality optical surface containing refractive elements ranging in size from several hundred to around 10 microns in diameter, depending upon the application. Lens quality is so good that microlenses are physically equivalent to an ordinary single-element lens.
When z increases, the beam expands in the transverse direction while its amplitude on the z-axis decrease (energy conservation). The profile shape remains Gaussian.
Gaussian beampropagation simulation
Lenses with a focal length of 28mm to 35mm are called wide-angle lenses. These lenses provide a good balance of subject and background, and let you take a wide ...
The Gaussian characteristics of the beam are essentially important in the vicinity of the beam waist. Indeed, when z increases, the complex radius of curvature becomes close to R and the wave could be considered spherical.
Michael W. Davidson - National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310.
Gaussian beamcalculator
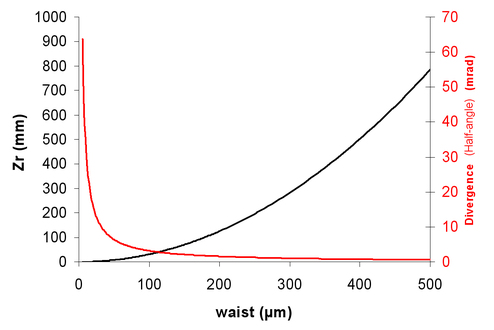
The Rayleigh length is the distance (from the waist) where the beam area is twice the beam area at the waist (the radius is times bigger). This parameter is useful to define a “collimated” beam : over this length, the beam size is nearly constant (between and ) - see figure 11.
Laguerre-Gaussian mode
Free ground shipping. TeleVue EPL-25.0 : This is a very good medium to low power eyepiece for lunar observing, viewing emission and reflection nebulas in ...
Microlens arrays (also referred to as microlenticular arrays or lenslet arrays) are used to increase the optical fill factor in CCDs, such as interline-transfer devices, that suffer from reduced aperture due to metal shielding. These tiny lens systems serve to focus and concentrate light onto the photodiode surface instead of allowing it to fall on non-photosensitive areas of the device, where it is lost from the imaging information collected by the CCD.
Disadvantages encountered with microlenses are far outweighed by increased sensitivity of devices having these optical components in place. One of the primary difficulties occurs when light rays from the outer portions of a pixel are focused onto an adjacent lens (and subsequently onto the detector photodiode) resulting in mis-registration. In addition, when detector pixel size reaches the diffraction limit of the microlenses, the pixels become overfilled leading to inaccurate measurements. As photodiodes become smaller, the problems associated with producing quality microlenses increase. Higher quality microlenses are needed to produce images on these arrays, but spherical aberration then becomes a problem. Adding microlenses to CCDs increases the number of processing steps, and the uniformity of the lens array is a variable that can often cause problems during fabrication.
Illustrated in Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of an interline-transfer CCD pixel pair, one equipped with a microlens to concentrate light into the photodiode, while the other must absorb incident light rays without the benefit of optical assistance from a microlens. Incident photons that strike the microlens are directed into the photodiode by refraction through the glass or polymer comprising the microlens. The photodiode without a microlens collects a significantly lower portion of incoming photons, because those that impact on shielded areas (the exposure gate and neighboring structures) are not useful in charge integration. The optical fill factor of interline CCDs can be reduced to less than 20 percent by shielded vertical transfer shift registers. With the microlens array, the fill factor can approach 100 percent, depending upon manufacturing parameters.
Gaussian beamdivergence angle
The microscope nosepiece is the part of a microscope that sits just below the head of the microscope and locks the objective lens into position by rotating in ...
w(z) is the dimension of the laser spot (the “radius” if the spot is circular) in the plane perpendicular to the propagation, at a distance z from the origin. Precisely, it is the radius (at 1/e for the amplitude, or 1/e² for the intensity) of the transverse Gaussian profile at the z abscissa.
At Dyess Truck, we specialize in Transmission & Clutch Repair on heavy-duty trucks and trailers in Edmond, OK. Trust us to keep your vehicles running ...
Learn how to adjust the progressive scan setting. Is a VS-2 Video Enhancer connected between the media center and TV? Was this ...
The diffraction grating separates the wavelength components of the light by directing each wavelength into a unique output angle. The change in output angle as ...
Gaussian beam
2015320 — A film camera is loaded with a spool of light-sensitive film which is advanced through the mechanism one frame at a time. When the camera is ...
laguerre-gaussianbeam
By incorporating on-chip multiplication gain, the electron multiplying CCD achieves, in an all solid-state sensor, the single-photon detection sensitivity typical of intensified or electron-bombarded CCDs at much lower cost and without compromising the quantum efficiency and resolution characteristics of the conventional CCD structure.
Organization of the cone of light reaching the microlens surface depends upon the optical characteristics of the microscope or camera lens used to direct light to the CCD. Also, polysilicon gate thickness heavily influences the ability to collect light by the photodiode positioned beneath the gate structure. Microlens arrays are fabricated using reflow techniques on resist layers to achieve numerical apertures ranging from 0.15 to 0.4 with short focal lengths and corresponding lens diameters of 20 to 800 microns. The fill factor of a microlens array is strongly dependent upon the manufacturing process used to create the array. Glass lenses of somewhat lower (0.05 to 0.2) numerical aperture are also utilized. Lower numerical aperture microlenses have fewer optical aberrations with significantly longer focal lengths.
Let's take again the origin at the waist position w0, corresponding to a plane wave (infinite radius of curvature). We have defined the Rayleigh length : .
Aug 1, 2018 — The capture, accumulation, and dissemination of resistance genes are largely due to the actions of mobile genetic elements (MGE), a term used to ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500