Lens Mounts - lens mount
By eliminating reflections, AR coatings also makes your eyeglass lenses look nearly invisible so people can see your eyes and facial expressions more clearly. Anti-reflective glasses also are more attractive, so you can look your best in all lighting conditions.
Anti-reflective coatings (also called AR coating or anti-glare coating) improve both your vision through your lenses and the appearance of your eyeglasses.
Applying anti-reflective coatings to eyeglass lenses is a highly technical process involving vacuum deposition technology.
Ar anti reflection coatingfor glasses
Also, don't attempt to clean AR-coated lenses without wetting them first. Using a dry cloth on a dry lens can cause lens scratches. And because anti-reflective coating eliminates light reflections that can mask lens surface defects, fine scratches often are more visible on AR-coated lenses than on uncoated lenses.
Each AR coating manufacturer has its own proprietary formula, but generally all anti-reflective coatings consist of multiple microscopic layers of metallic oxides of alternating high and low index of refraction. Depending on the AR coating formula, most lenses with anti-reflective coating have a very faint residual color, usually green or blue, that is characteristic of that particular brand of coating.
Ar coating
When cleaning AR-coated lenses, use only products that your optician recommends. Lens cleaners with harsh chemicals may damage the anti-reflective coating.
Some eyeglass lenses have factory-applied AR coating on both lens surfaces. Other lenses, particularly progressive lenses and other multifocal lenses (i.e., bifocals and trifocals), have the coating applied after the lenses have been customized to your eyeglass prescription by an optical lab.
AR glass is optically coated on one or both sides. The anti-reflective coating is usually a di-electric coating and can be applied to the glass in a single layer or multiple layers. When this invisible optical coating is applied to a glass substrate it accomplishes the following:
Anti reflection coatingformula
Anti-Reflective Coatings can be applied to just about any glass substrate including: Gorilla Glass, Borofloat, Ultra Clear Low Iron Float Glass, Ultra Thin Glass (Schott AS-87, Schott D263, AGC EN-A1)
The jargon of the glass industry is not always clear when it comes to anti-reflective glass. The terms anti-reflective glass and non-glare glass are often used interchangeably; but in reality, they are very different types of glass. In this post we will explain how these two different glass types serve a similar purpose and also help you determine which might be best suited for your specific application.
Anti-reflective coatings are incredibly thin. The entire multilayer AR coating stack generally is only about 0.2 to 0.3 microns thick, or about 0.02 percent (two one-hundredths of 1 percent) of the thickness of a standard eyeglass lens.
Antireflectivecoatingmaterial
Typically, a production line includes multiple washing and rinsing baths, including ultrasonic cleaning to remove any traces of surface contaminants. This is followed by air drying and heating of the lenses in special ovens to further remove unwanted moisture and gases from the lens surface.
The visual benefits of lenses with anti-reflective coating include sharper vision with less glare when driving at night and greater comfort during prolonged computer use (compared with wearing eyeglass lenses without AR coating).
AR coatings are especially beneficial when used on high-index lenses, which reflect more light than regular plastic lenses. Generally, the higher the index of refraction of the lens material, the more light that will be reflected from the surface of the lenses.
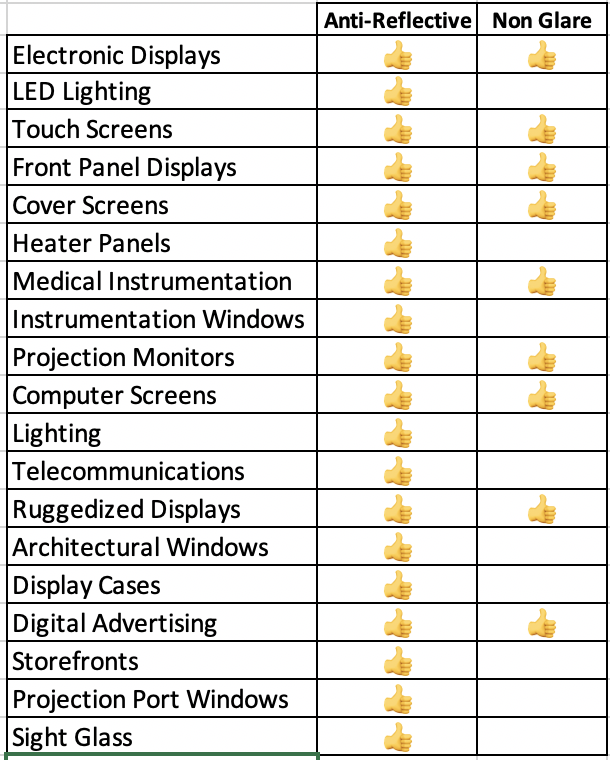
Non Glare Glass. There is an inverse relationship between the amount of diffusion of the non-glare glass and the resolution of the display. Now that we have explored how both Non-Glare and Ant-reflective glass are produced, let’s look at their typical applications. The matrix below can help steer you in the right direction when deciding between Anti-Reflective and Non-Glare Glass.
AntiReflectivecoatingPhysics
Most premium anti-reflective coatings include a "hydrophobic" surface layer that prevents water spots from forming and makes the lenses easier to clean. Some AR coatings also include an "oleophobic" surface layer that repels skin oils and makes it easier to remove smudges from the lenses.
Let’s start with a detailed description of both anti-reflective glass and non-glare glass. After defining both glass types we will list how each is used.
Both benefits are due to AR coating's ability to eliminate reflections of light from the front and back surface of eyeglass lenses.
Antireflectivecoatingspray
The lenses are then loaded into special metal racks with spring-loaded openings so the lenses are held securely but with virtually all lens surfaces exposed for the coating application. The racks are then loaded into the coating chamber. The door of the chamber is sealed, and the air is pumped out of the chamber to create a vacuum.
Anti reflection coatingprinciple PDF
While the lens racks are rotating in the coating chamber, a power source within the machine focuses a beam of electrons onto a small crucible that contains a series of metal oxides in separate compartments. When bombarded by the beam of this electron "gun" in succession, the metal oxides are transformed into vapors that fill the coating chamber and adhere to the lenses in a specific order to form a precise multilayer AR coating.
Non-Glare Glass is produced by etching (via acid bath) one or both surfaces of the glass. The etching process is very precise and leaves the glass with an incredibly consistent etched finish across the entire surface. This etched surface disperses light as it hits the surface of the glass, virtually eliminating glare. This allows the end user to see transmitted images and videos very clearly – even in direct sunlight. Non-Glare Glass works best with high resolution displays.
A differentiator of Anti-Reflective glass – when compared to Non-Glare glass – is the ability to customize the coating for specific wavelengths of light. AR coatings can be customized for visible light, UV and or NIR spectral bands.
Antireflectivecoatingdisadvantages
Today's modern anti-reflective coatings can virtually eliminate the reflection of light from eyeglass lenses, allowing 99.5 percent of available light to pass through the lenses and enter the eye for good vision.
The first step in the AR coating process is to meticulously clean the lenses and inspect them for visible and microscopic surface defects. Even a tiny smudge, piece of lint or hairline scratch on a lens during the coating process can cause a defective AR coating.
Non-Glare is measured in gloss units and is available in numerous gloss (etching) levels. The gloss levels range from 60 to 140. Non-Glare Glass is available in both Low Iron a Soda Lime gloat glass. The challenge with finding the right gloss level is balancing the amount of glare reduction (diffusion) with the resolution of the display behind the glass. The environment of the application, ambient light, thickness of the glass and brightness of the underlying display all play a part in the performance of the
Now that we have explored how both Non-Glare and Ant-reflective glass are produced, let’s look at their typical applications. The matrix below can help steer you in the right direction when deciding between Anti-Reflective and Non-Glare Glass.
For example, regular plastic lenses reflect roughly 8 percent of light hitting the lenses, so only 92 percent of available light enters the eye for vision. High index plastic lenses can reflect up to 50 percent more light than regular plastic lenses (approximately 12 percent of available light), so even less light is available to the eye for vision. This can be particularly troublesome in low-light conditions, such as when driving at night.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500