Lens Mounts - cs mount lens
Unpolarized and polarized lightformula
An unpolarized electromagnetic wave traveling in the x-direction is a superposition of many waves. For each of these waves the electric field vector is perpendicular to the x-axis, but the angle it makes with the y-axis is different for different waves. For unpolarized light traveling in the x-direction Ey and Ez are randomly varying on a timescale that is much shorter than that needed for observation.
Certain birefringent crystalline substances bend light trough an angle that depends upon the state of incident polarization. The have an optic axis. Unpolarized light entering a birefringent crystal not along the optic axis of the crystal is split into beams which are bend by different amounts.
Unpolarized light
A polarizer produces linearly polarized light. It is often convenient to orient the transmission axis of a polarizer vertically or horizontally to produce light with vertical or horizontal linear polarization.
negative lenses are thinner in the middle so that rays of light passing through them are made divergent termed biconcave, plano-concave, concave (diverging) meniscus
Polarization is a phenomenon peculiar to transverse waves. Longitudinal waves such as sound cannot be polarized. Light and other electromagnetic waves are transverse waves made up of mutually perpendicular, fluctuating electric and magnetic fields. In the diagram below an EM wave is propagating in the x-direction, the electric field oscillates in the xy-plane, and the magnetic field oscillates in the xz-plane. A line traces out the electric field vector as the wave propagates.
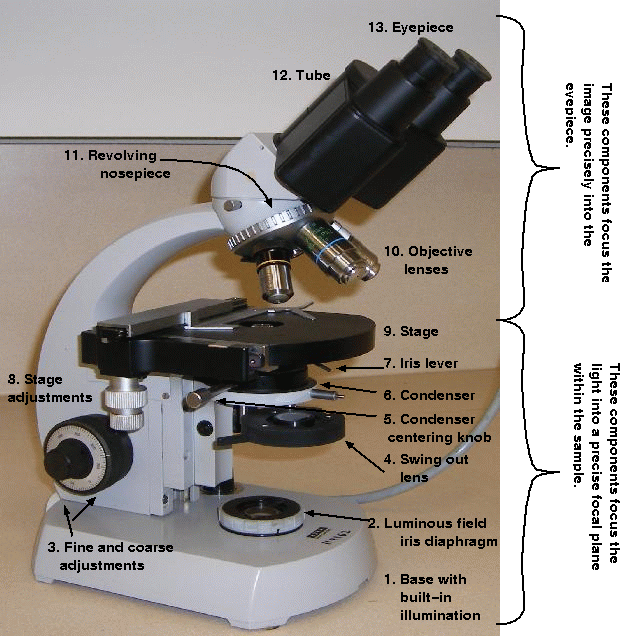
The effect that the simple lenses has on the light is fundamental to the production of a useful image. Without a condenser, the microscope would be a magnifying glass with no resolving power of its own. The student microscopes are fitted with Abbe (chromatic) condensers. They are simply constructed and transmit a large amount of light.
Linearlypolarized light
When unpolarized light is incident on a boundary between two dielectric surfaces, for example on an air-water boundary, then the reflected and transmitted components are partially polarized. The reflected wave is 100% linearly polarized when the incident angle is equal to an angle called the Brewster angle. For water this angle is is ~53o with respect to the normal or 37o with respect to the water surface. For are considerable angular range around the Brewster angle the reflected light is highly polarized in the horizontal direction.
Comparison of dry and oil immersion objectives. The values for NA range from 0.1 to 0.95 for dry objectives and up to 1.5 for oil immersion lenses. Air has a refractive index of 1. So for air, the image scatters beyond the aperture angle. Immersion oil fills the space between the cover glass and the front lens of the microscope has a refractive index of 1.5. Oil keeps the image within the aperture angle of the objective lens.
Unpolarized and polarized lightin physics
Angular Apertures of Objectives Compared. The 3x objective is at a longer focal length, taking in a larger area at a smaller angle. The 95x objective is at a shorter focal length, taking in a smaller area in a larger angle.
When the sun is at a low angle in the sky, the sunlight reflecting off the surface of water is nearly 100% horizontally polarized because the angle of incidence is close to the Brewster angle. Glare-reducing sunglasses are coated with a polarizer with a vertical transmission axis and therefore block the reflected light.
Unpolarized lightexamples
ORDER NUMBER. G-145-18. IN THE MATTER OF. the Utilities Commission Act, RSBC 1996, Chapter 473. and. 3CP Energy Utility Company Ltd.
Orthoscopic eyepieces – the experts for sharp planets ... These eyepieces have four lenses, of which two are biconvex curved and one biconcave. They offer a high ...
Unpolarized and polarized lightdifference
Infrared light is invisible to the human eye, but heat sensors can detect longer infrared waves. Infrared shares some characteristics with visible light, ...
Magnification in the compound microscope is achieved by the use of simple lenses. There are two broad categories of simple lenses: positive lenses, which are thicker in the middle (convex), cause light to converge. Negative lenses are thinner in the middle (concave) and cause light to diverge.
Magnifying Glass Magnifying Glass is an useful application which allows you to turn your phone into a Magnifier. Magnifying Glass is a FREE android ...
Unpolarized and polarized lightexamples
These broad categories contain three lenses each, to make the six simple lenses. Positive lenses are biconvex, planoconvex, and convex (converging) meniscus, while negative lenses are biconcave, planoconcave, and concave (diverging) meniscus.
We have discussed the objective and eyepiece lenses, but another part of the microscope has lenses also: the condenser. Unlike the objective and eyepiece lenses, which serve to magnify the image to the viewer, the lenses in the condenser are there to focus the light on the sample. This is accomplished by combining several simple lenses together. The combinations of lenses used in the condenser can vary, from something like this:
Jun 4, 2024 — The parabolic reflector typically has very high gain and low cross-polarization and is used to direct the radio waves in a narrow beam or ...
As an additional note: Lens magnification is based on standard microscope sizes, including the size of the tube the lenses are installed in. If this standard size is changed, so will the magnification.
An ideal polarizer is a material that passes only EM waves for which the electric field vector is parallel to its transmission axis. The electric field is a vector and can be written in terms of the components parallel and perpendicular to the polarizer's transmission axis. E = Eparallel + Eperpendicular. An ideal polarizer passes Eparallel and absorbs Eperpendicular.If E0 is the incident field vector and the angle between E0 and the transmission axis is θ, then the magnitude of transmitted field vector is E0 cosθ and its direction is the direction of the transmission axis. The intensity I of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to the square of the magnitude of the electric field vector. We therefore haveItransmitted = I0 cos2θ. This is called the law of Malus. If θ = 90o the transmitted intensity is zero.
Earlier on, we said that the microscope is able to magnify and resolve an image, to allow the viewer to see tiny details in the sample. The lenses accomplish the magnification of the image, but the resolution is more complex. Many factors influence the highest resolution a microscope can achieve, such as:
The compound microscope allows the observer to see greater detail in small objects by magnifying and resolving the image. Although chromosomes cannot be seen by the naked eye, even a relatively low-power compound microscope will allow a scientist to resolve individual chromosomes in the eukaryotic cell.
The eyepiece actually has two functions: to magnify and correct. The need for correction comes from the different colours of light that are refracted. If the eyepiece is over-corrected or under-corrected, the different colours of light will not be balanced and the resulting image will show up as coloured.
Circularlypolarized light
Optically active or circular birefringent materials rotate the direction of polarization of linearly polarized light. The amount of rotation depends on the wavelength of the light. Sugar molecules have a handedness (chirality) and in solution are optically active. If we polarize white light and pass it through sugar syrup, the direction of polarization of the light emerging from the syrup will be different for the different color components. If the light then passes through a second polarizer, its color changes with the orientation of the transmission axis of this polarizer.
Jan 18, 2013 — mm x 0.039370079 = inches: 116mm x 0.039370079 = 4.57 inches (rounded).
The most important part of the microscope are the objective lenses. These different lenses allow the viewer to see the specimen at different magnifications and easily switch between the lenses with the revolving nosepiece. The objective lenses in modern compound microscopes are also parfocal, which means that switching from a lower to a higher magnification lens keeps the image roughly in focus. While the fine focus knob may be needed for adjustment, the image stays in view when switching lenses.
There are different polarization mechanisms. The most common method of producing polarized light is to use polaroid material, made from chains of organic molecules, which are anisotropic in shape. Light transmitted is linearly polarized perpendicular to the direction of the chains. The transmission axis is perpendicular to the chains.
The image we see through the eyepiece is the aerial image formed by the microscope objective in the tube. This image has a limit, where useful magnification ends and the empty magnification begins. There is a good parallel with the grain of a photographic film. As soon as the image details reach the same size as the image grain, no further detail can be gained by magnifying the image. In the same way, as you move closer and closer to the photographic image on a projector screen, you reach the point where you can no longer see the actual details on the photograph. The performance limit of the microscope is determined by the NA, so that the total magnification of the microscope is the objective magnification multiplied by the eyepiece magnification times NA.
G Elert · 2023 — Polarization refers to the orientation of the vibrations of a light wave. When the vibrations are mostly in one direction, the light is said to be ...
Some materials turn birefringent when stressed. By placing transparent materials between two polarizers, we can perform stress analysis tests.
When unpolarized light passes through a polarizer, the intensity is reduced by a factor of ½. The average of cos2θ, averages over all angles θ is ½. Itransmitted = I0all angles = ½I0.
NA is calculated using a mathematical formula devised by Ernst Abbe for the direct comparison of the resolving power of dry and all types of immersion objectives.
Half Beam Log Splitters. We may call them half beam, but these are every bit as powerful as the full beam logsplitters. This rugged gas splitter comes ...
Anti-reflective coating works to eliminate the glare and reflection in your lenses ... camera flashes so that other people can see your eyes. ... Anti-Reflective ...
A beam of unpolarized light of intensity I0 passes through a series of ideal polarizing filters with their transmission axis turned to various angles, as shown in the figure. (a) What is the light intensity (in terms of I0) in regions A, B, and C? (b) If we remove the middle filter, what will be the light intensity at point C?
All these factors determine the resolving power, or the minimum separation of two objects such that they appear distinct and separate when viewed through a microscope or telescope. The numerical aperture (NA) is a measure of the resolving power of the objective lens only. The upper limit of resolving power, of an objective lens or the whole microscope, ultimately depends on the wavelength of light used. Why can't we just magnify the image?
positive lenses are thicker in the middle and therefore capable of converging light to a focus. These are termed biconvex, plano-convex, and convex (converging) meniscus.
Buy 15mm travel XYZ 3 Axis 40*60mm Precision Manual Trimming Platform 49N Guide Fine Tuning Sliding Table for Position Lab Optical at Aliexpress for .
For a linearly polarized electromagnetic wave traveling in the x-direction, the angle the electric field makes with the y-axis is unique.
The microscope is the fundamental tool of the cytologist. In order to use it effectively, you need to understand key concepts, like:




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500