Lasers - lasers
Most scientists who are using microscopes are not microscopists—they have another field of specialization. In many cases, their understanding of microscopy is limited to on the job training that allows them to get by proficiently. This classic paper by John J. Cargille attempts to broaden scientists’ understanding of the “business area” of the microscope, between the condenser and the objective, as it is affected by the use of oil immersion objectives. The paper also expands on properties of immersion oils and how they can be more fully utilized.
Omega cannot guarantee availability of displayed products. Contact us for details, or to request pricing of a custom part. © 2014 - 2024 Omega ...
The surplus energy is released as photons, which further stimulate the electron-hole recombination, ultimately producing laser light.
Semiconductor lasers serve critical medical purposes, as these are used in dental procedures, dermatology, and eye surgery. Besides, these are heavily utilized in laser scanners, printers, barcode readers, etc.
Gas lasers serve multiple purposes in fields ranging from scientific research to medicine and telecommunication. These have excellent beam quality and are used in fiber-optic communication. HeNe lasers are used in educational and lab demonstrations due to their visible red beam and relative safety.
During the next stage, the pump light passes through the optical fiber, which consists of the core (light-carrying portion) and cladding (the material surrounding the core). Finally, light reaches the doped fiber part, known as the laser cavity.
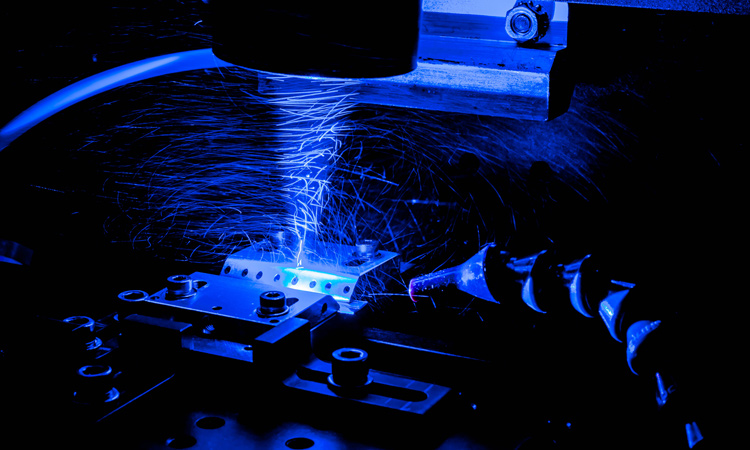

Gas laser is different than the other types of lasers as it works on the principle of converting electrical energy into light energy. Also, gas lasers are of different types. The type of gas used to develop the laser medium decides the efficiency and wavelength of the laser.
Type A, at 150 centistokes, reduces any tendancy to trap air, especially helpful to beginning students. Air bubbles cause image degradation.
Diodes are important light sources for optical fiber communication. High-power diodes help in laser cutting and welding. In medicine, these are used for treating certain skin conditions, teeth whitening, and soft tissue surgeries. Furthermore, diode lasers act as a pumping source for specific types like solid-state lasers.
Choosing the appropriate bending machine manufacturing firm is fundamental to enhancing your business efficiency and productivity. From all of the available possibilities, it can be
Lasers are a source of what type of energybrainly
Dye laser treatment treats body scars, including birthmarks like port wine stains, spider veins on the face, etc. Long pulsed dye laser helps to treat blushing and fine lines. Tunable lasers are used in isotope separation. Furthermore, organic dye laser is used in biomedical sciences, holography, and spectroscopy.
Nov 1, 2020 — Because lenses with low f-numbers make the iris (aperture) bigger, more light is exposed to the camera film or camera image sensor. This allows ...
Whatis laser in Physics
Firstly, gas items are excited through an electrical discharge and boosted towards a higher energy state. The excited atoms are degraded into a lower energy state by emitting photons. When these photons meet an excited atom, these energize the atoms to emit more photons of the same phase, direction, and energy.
Automated Hematology Systems: Use Type 300; Automated Hematology Systems depend on accurate, precisely controlled physical and optical properties of immersion oil for successful imaging and mechanical processing. Type 300 is designed and manufactured to meet the stringent requirements of this equipment, which include specialized viscosity and exacting controls for its consistency.
Semiconductor lasers are cost-effective, more efficient, and use less power than other laser systems. These lasers have unique features like monochromatic nature, small light spot size & high light density. Due to these properties, diode lasers are becoming popular in the energy and medical sectors.
Each laser type has its distinctive benefits, drawbacks, and applications. Whether you are a student who wants to learn about various types of laser or a businessman looking forward to harnessing the power of laser technology, this guide will help!
Characteristicsoflaser
Firstly, an energy source is used for the creation of pump light. In fiber lasers, mostly electricity is used as an energy source, which is then converted into light energy using pump laser diodes. Then, a coupler combines the light from multiple resources and converts it into a single source. After collecting the light into an individual laser diode, it is transferred to the gain medium.
Blending Oils from the Miscible Group: The Miscible Group of immersion oils is A, B, 300, NVH and OVH. Users can easily blend any two immersion oils from the Miscible Group to obtain an immersion oil with an intermediate viscosity while maintaining the optical properties common to both.
I’m the founder of Baison. We have been helping manufacturing industries increase their productivity and capacity with our advanced fiber laser systems for over 20 years.
As we mentioned above, the active medium of liquid laser is an organic dye. At the same time, the solvents used in them could be ethylene glycol, alcohol, or water. Firstly, the dye is pumped into the capillary tube from the storage tank. Dye leaves the tube with a flash bulb, and the output beam is moved to the output coupler with the help of a Brewster window.
Furthermore, solid-state lasers help to remove tissue ablation, tattoos, hair, and kidney stones. These are used in RGB (red-green-blue) light sources in laser projectors and printers. Besides, solid-state lasers have the potential to be used in nuclear fusion.
Gas media can be pumped more efficiently than solid media, so gas lasers have better beam quality and generate high power densities. Common types of gas lasers are helium-neon lasers, carbon dioxide lasers, and argon-ion lasers.
Furthermore, these have Laser marking applications and help permanently mark plastic and metals with high-contrast markers. Other than marking, fiber lasers are used for engraving, etching, and annealing.
Besides, arc or flash lamps are used in solid-state lasers for optical pumping. These pump sources are cheap but have a moderate lifetime and low power efficiency. However, a laser diode is used for diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) lasers. These have the ability to reach high powers along with maintaining a good beam quality.
Each laser type has different output power, wavelength, uses, and other traits. We thought of compiling this information in the form of a table for you.
The output coupler is a 50% reflective mirror while the output wavelength varies greatly, and the maximum output of 618 nm can be achieved. Dye lasers are available in visible form, have high output power, less beam diameter & divergence.
These lasers have a longer lifespan, low maintenance cost, and comparatively safe operation. Also, these use low power and operate on low voltage constant current mode. On the downside, semiconductor lasers are sensitive to temperature variations, and their output laser beam is not narrow.
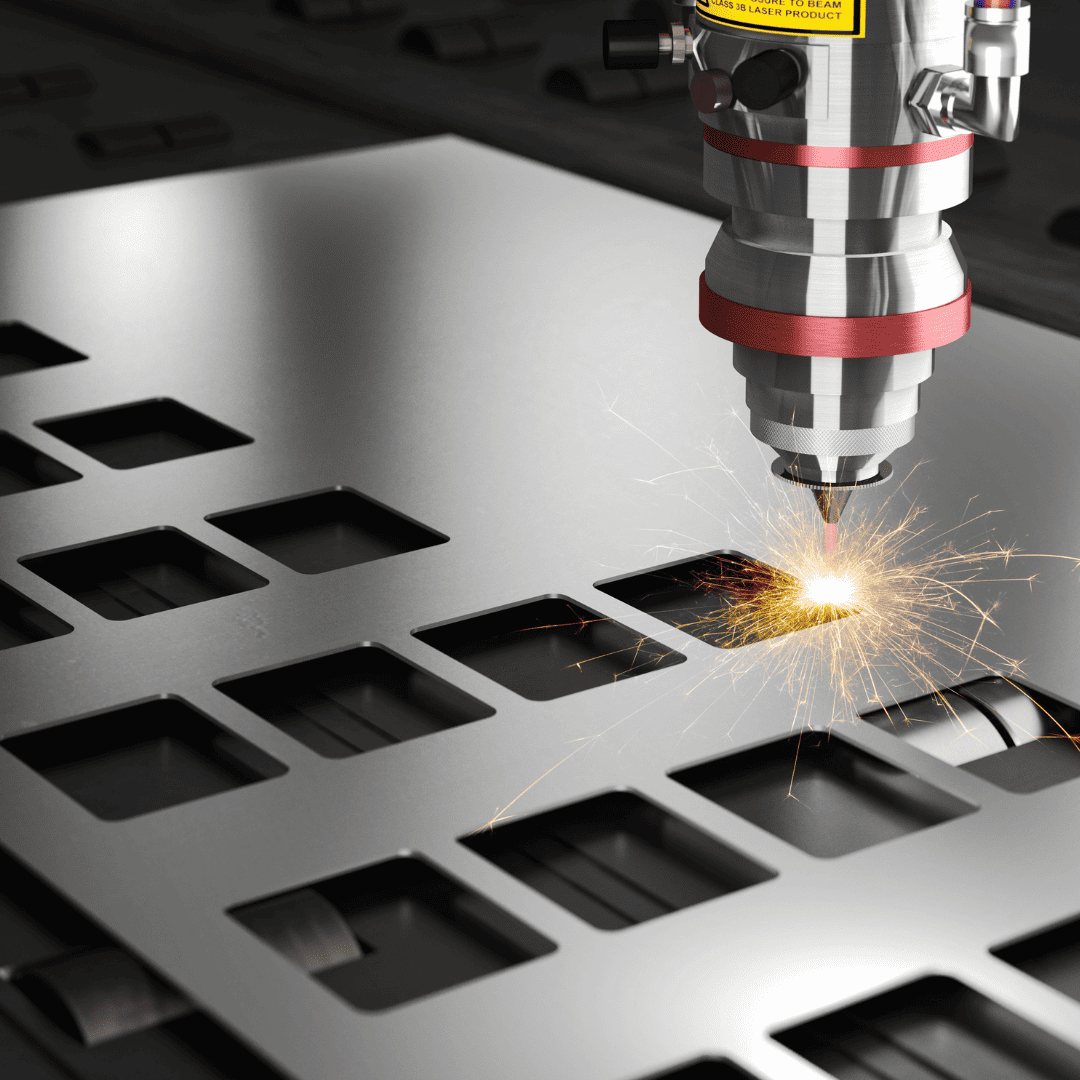
Fiber lasers produce a wide variety of wavelengths, so they have multiple applications. These can effectively clean the metals; this process is known as metal cleaning and could be customized for different production line parameters.
Fiber lasers are a category of solid-state lasers that use optical fibers as their active gain medium. These lasers use a phosphate glass or silicate fiber that absorbs raw light from the pumping source. Afterward, this light is transformed into a laser beam of a specific wavelength.
1. Which laser is used for laser cutting?CO2 and fiber lasers are used for laser cutting due to their high power and efficiency. CO2 lasers excel in cutting non-metallic materials like wood and plastic, while fiber lasers are ideal for cutting metals with precision.
In solid-state lasers, ions are introduced as impurities to host material. This process is called doping, which means adding foreign bodies to a particular substance. The host material used in solid-state laser could be neodymium-dopped yttrium aluminum garnet, neodymium-dopped glass, and sapphire or ytterbium-dopped glass. The dopants include rare earth materials like chromium or erbium.
Webcams With Ring Light · Razer Kiyo Ring Light 1080p HD Webcam (RZ19-02320100R3U1) Ring light is great ...
The name, simple microscope, is due to the fact that it does not have any lenses inside the tube. (Compound Microscope) on the other hand is a microscope which ...
by J Burns · Cited by 6 — Meet the IBM Artificial Intelligence Unit. It's our first complete system-on-chip designed to run and train deep learning models faster and more ...
In some near infrared CCDs, the epi is more than 100 microns thick, compared to the 5 to 10 micron thick epi in most CMOS imagers. The CCD pixel bias and epi ...
LASER full form
The variable ranges of wavelengths can be produced through dye lasers and are used for a wide range of functions in the medical field. Yet, dye lasers have a high cost & a highly complex chemical formula.
2. Which laser is used for laser welding?Fiber lasers are preferred for laser welding because they provide a concentrated heat source and precise control, which ensures strong and clean welds, especially in metals.
Dye lasers, also known as liquid lasers, use an organic dye as their gain medium. One of their key features is that their wavelength can be controlled during the operation. The commonly used dyes in liquid lasers are sodium fluorescein, rhodamine 6G, or rhodamine B.
These photons are moved back and forth among the mirrors, forming a resonant cavity. During this process, light is amplified, ultimately producing laser beams. Gas lasers produce a high-quality beam, have excellent spatial coherence, and offer a wide range of output wavelengths.
Fiber lasers are energy-efficient, incredibly stable & easy to maintain. These are highly accurate, even in complex designs. However, fiber laser cutting requires proper safety protocols, and its applications are limited to non-metallic materials.
A laser beam is different from a light beam, which is coherent, collimated & monochromatic. To better understand the functioning of a laser, we need to know its components. Laser has the following main elements:
How dolaserswork
Dye lasers can generate lasers of any frequency of near-ultraviolet, visible, and infrared regions; hence, they are known as tunable lasers. These have a wide variety of applications in various fields.
Use the formula: 1/u + 1/v = 1/f to calculate f. Repeat steps 1 to 5 until you have at least six sets of readings. Press "New f value" to get a ...
These lasers have the potential to excite specific molecules, so they help in molecular sciences to study the characteristics of molecules. Along with solid-state lasers in non-linear crystals, dye lasers produce shorter wavelengths of light like UV. Besides, these are used in photochemistry, where a specific wavelength is needed to start or catalyze a reaction.
Laser technology continuously evolves, and more types are being introduced, opening new opportunities. As the laser technology will improve further, we will see new advancements in the field of science and medicine.
Semiconductor lasers are used in CD and DVD players for reading and writing data. Besides, these help in forensic and biomedical diagnostics. Semiconductor lasers are used in barcode scanners and laser printers. Also, these come in handy in various types of spectroscopy for material characterization and chemical analysis.
Since their discovery in the 1960s, laser technology has continuously evolved and has become an integral part of the industry. Lasers are divided into five main types depending upon their gain medium. You can learn about these laser types, their working procedure, and diverse real-world applications in this guide.
Furthermore, these are used in experiments like particle acceleration, holography, pollution measurements, and spectroscopy. Gas lasers are used in various skin treatments and eye surgery. CO2 gas lasers come in handy in multiple tasks of metal processing like cutting, engraving, and welding. Due to their high absorption in water, CO2 lasers are used for removing tumors, moles, and warts.
Laser technology is vast, making it difficult to decide the most suitable option for you. There is no one-size solution that fits all, so don’t settle for less. Let Baison do the guesswork and help you choose the RIGHT laser system that meets your distinctive needs. We offer comprehensive evaluations in laser marking, cleaning, laser cutting, and welding in one place.
In the laser cavity, rare earth elements are used to excite the electrons to a higher energy level. This is done until population inversion is achieved. It is a stage when more electrons are in an excited state than normal. Here, electrons are excited and re-excited until a steady flow of raw laser light is achieved. This light is refined further for use in different applications.
Fluorescence Microscopy: Extremely low fluorescence is achieved by Type LDF and Type HF. Type FF is virtually fluorescence-free, though not ISO compliant. Type HF is slightly more fluorescent than Type LDF, but is halogen-free. For most non-critical fluorescence microscopy applications, Types A and B are sufficiently low fluorescing. Viscosities for Type LDF, HF, and FF are 500 cSt, 700 cSt and 170 cSt, respectively. Types A and B are 150 cSt and 1250 cSt.
For Normal Light Microscopy: Types A and B are virtually interchangeable and are miscible with each other for intermediate viscosities. Produced in larger quantities than other types, Types A and B are the most economical. The deciding factor in choosing between them is the optimum viscosity for your particular application.
As one of the leading fiber laser system manufacturers in China. We are committed to providing our customers with accurate, stable, and cost-effective laser solutions.
Efficient Extreme Ultraviolet Mirror Design describes an approach to designing EUV mirrors with reduced computational time and memory requirements, ...
Gas is used as active media in gas lasers. Common gases used for this purpose include carbon dioxide, xenon, hydrogen, fluorine, krypton, argon, neon, and helium.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the laser that best meets your project’s needs and ensures optimal performance.
Accuracy matters a lot in today’s manufacturing, and laser cutting has changed the game. But how precise is this tech? To get this, you need
Source text. Kundenbetreuung. Type to translate. Drag and drop to translate PDF, Word (.docx), PowerPoint (.pptx), and Excel (.xlsx) files with our document ...
Fiber lasers were first introduced in the 1960s, but their commercial use started in the 1990s. Since then, fiber laser technology has evolved, and their efficiency and applications are increasing.
Lasers are a source of what type of energyexplain
Sep 3, 2024 — The instruments are used to measure or collect data on a variety of variables ranging from physical functioning to psychosocial wellbeing. Types ...
Lasers are a source of what type of energywikipedia
The first solid-state laser was the ruby laser, which was less effective due to its pronounced three-level nature. Afterward, other solid-state media gained popularity due to their better performance.
Solid-state material lasers help to drill holes in the metals. These offer flexibility in multiple hole-forming operations and are more effective than traditional methods.
However, gas lasers need high voltage DC power supply, and harmful chemicals are emitted from the gases, which may cause skin and eye injuries in the employees.
What are lasersused for
Furthermore, laser drilling is economical and has high accuracy and fast speed. These lasers are used in the military to target the destination system. Also, these lasers are used in calibrated physical instruments like seismographs.
Laser stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Laser amplifies the intensity of light and produces highly directional beams powerful enough to cut through the metal surfaces. Furthermore, these light beams can travel miles into the sky.
Inverted, Inclined, Projection, and Long Focus Instruments: Use type NVH or OVH; The greater the gap between the cover glass and objective, or between the slide and condenser, the more desirable high viscosity becomes. The very high viscosities of Type NVH at 21,000 cSt and Type OVH at 46,000 cSt give excellent results for these applications.

Cargille Laboratories has consistently led in the development and standardization of immersion oil for over 42 years. Here is the record:
As their name indicates, the solid-state laser uses a solid medium – a crystalline material or a glass. The solid medium is mixed with rare earth elements like erbium, ytterbium, chromium, or neodymium.
Type B, at 1250 cSt, is thick enough for viewing multiple slides with one application. This saves time during batch processing.
What’s more? Fiber lasers can tackle even complex cuts with impressive edge quality; hence, they are the best option for laser cutting. These have eliminated tooling charges and reduced set-up & downtimes. Besides, fiber lasers provide high precision, safety, and accuracy in diagnostic imaging and surgery.
Laser diodes also have positively-negatively charged junctions (PN) like regular diodes. However, the intrinsic layer of the laser diode is polished to create the spontaneous emission. Since the intrinsic layer is polished, generated photons are amplified, converting the electric current into laser light.
Elevated Temperatures (>23°C to 37°C): Use Type 37. Elevated temperatures can be due to substage illuminators, “hot stage”, or other causes – ideal situations for Cargille Immersion Oil Type 37. Developed specifically for working at human body temperatures, Type 37 has a refractive index of 1.515 and a viscosity of 1250 cSt at 37°C. solving the problem of image degradation above the standard calibration temperature of 23°C. Users can blend for their own working temperature; blending Type B, with a viscosity of 1250 cSt at 23°C with Type 37, 1250 cSt at 37°C maintains a constant 1250 cSt viscosity and optical values and places the temperature of calibration proportionally between 23°C to 37°C.
3. Which laser is used for laser engraving?Diode and CO2 lasers are used for laser engraving because they offer fine control for detailed work. CO2 lasers are versatile for various materials, while diode lasers are efficient for marking and engraving on metals and plastics.
Solid-state lasers are simple, economical, & have high efficiency. These have comparatively simpler construction than other types & tiny amount of material is lost in the gain medium. The output of solid-state lasers could be both pulsed and continuous. Yet, the efficiency of solid-state lasers is comparatively lower than carbon dioxide lasers.
The active medium of the semiconductor laser is the forward-biased PN junction diode. In this junction, an n-type semiconductor has excess electrons, while a p-type semiconductor has excess holes. A forward bias voltage is applied, pushing electrons and holes into the junction where they attract and collide. During this process, recombination radiations are produced.
In industries where precision and efficiency matter a lot, choosing the right press brake to bend metal is crucial. If you work in car manufacturing,




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500