Laser Shaft Alignment Tools - laser alignment instrument
Causes the current thread to wait until it is awakened, typically by being notified or interrupted, or until a certain amount of real time has elapsed.
Get free shipping on qualified Infrared Heaters products or Buy Online Pick Up in Store today in the Heating, Venting & Cooling Department.
Magnifier on iPhone
Returns whether the magnifier position will be adjusted such that the magnifier will be fully within the bounds of the main application window, by also avoiding any overlap with system insets (such as the one corresponding to the status bar) i.e.
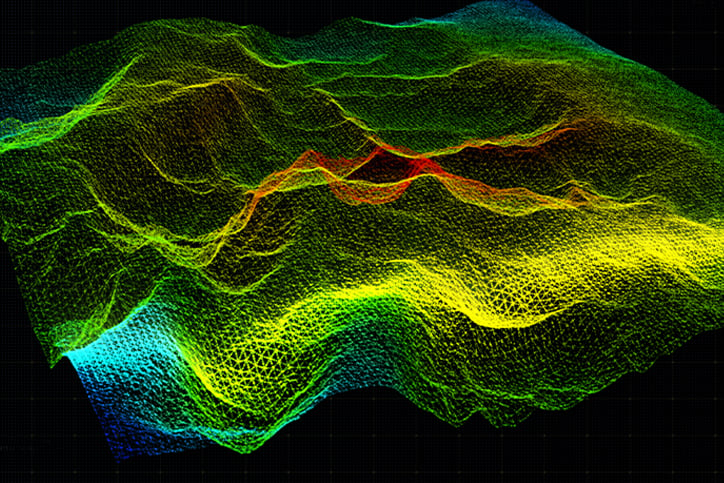
Verifying the surface roughness of an ordered part can be prohibitively expensive for some manufacturers. Using a contact method such as a profilometer to measure surface roughness risks surface damage that may render a part unusable. Additionally, contact methods are often slow and only interrogate a small portion of a surface. Non-contact methods, such as white light interferometry, can probe entire surfaces but the equipment necessary for these measurements can be prohibitively expensive for some shops. If shops cannot accurately measure parts to ensure they can meet specified tolerances, then it is impossible for them to reliably guarantee performance. Typically, an optic finished via spindle polish will have a surface roughness in the realm of 10-15 Angstroms. Achieving a super polished surface (1-2 Angstroms) requires more time as well as dedicated manufacturing equipment.
Magnifier online
A source bound that will extend as much as possible, while remaining within the visible region of the magnified view, as determined by View#getGlobalVisibleRect(Rect).
Returns the vertical offset, in pixels, to be applied to the source center position to obtain the magnifier center position when show(float, float) is called.
The most common roughness specifications are peak-to-valley (PV) or root-mean-square (RMS) values. PV values are determined by finding the difference between the highest peak (ymax) and lowest valley (ymin) along a surface with height y; . PV values give a good idea of maximum surface variation that may occur and therefore can suggest a surface is much rougher than it is on average. The RMS value is based on the standard deviation of the surface height from the mean value (ymean); . RMS specifications give the overall roughness of the surface while PV gives the maximum deviation at a single spot on the surface. The intended use for an optic determines which specification is most relevant. A good rule of thumb is to think of PV specifications as the “worst-case-scenario” for the optic, while RMS describes the average surface variation. For a detailed discussion of how to use PV and RMS specifications check out this blog post.
Surface roughness is a measure of high-frequency deviations in the departure of a surface from ideal. Surface roughness can result in unwanted scattering in an optical system and for many optical applications one might think it is always best to minimize surface roughness. However, simply minimizing surface roughness without regard to system wavelength and performance can result in increased costs and longer production times. When choosing specifications for a particular optical component, it is important to consider the function of the component in the context of the entire optical system in which it will be used. A careful analysis of the role surface roughness plays in a system can avoid unnecessary production costs due to over-specification. For example, a 10 Angstrom RMS surface roughness can impact a system operating in the visible region more significantly than a system operating in the mid or far infrared.
by P Sievers · 1974 — To reduce the width of the grey zone of the collimator, which is of the order of A, a material should be selected where the ratio Z/p is ...
Magnifier tool
A source bound that will extend as much as possible, while remaining within the visible region of the magnified view, as determined by View#getGlobalVisibleRect(Rect).
Shows the magnifier on the screen at a position that is independent from its content position. The first two arguments represent the coordinates of the center of the content source going to be magnified and copied to the magnifier. The last two arguments represent the coordinates of the center of the magnifier itself. All four coordinates are relative to the top left corner of the magnified view. If you consider using this method such that the offset between the source center and the magnifier center coordinates remains constant, you should consider using method show(float, float) instead.
Surface roughness is measured through a variety of techniques. Some manufacturers have contact profilometers that physically touch the surface and measure the surface via a fine diamond tip and the oscillation of the lever arm. This technique typically measures along certain lines on the surface. Other profilometers are non-contact and use a laser to measure along a linear portion of the surface. Another approach uses white light interferometry to obtain a surface map of the whole clear aperture or a specific region of the part. In general, it is easiest to perform surface roughness measurements on planar surfaces and more challenging for surfaces with complex curvatures, such as aspheric lenses.
Asks the magnifier to update its content. It uses the previous coordinates passed to show(float, float) or show(float, float, float, float). The method only has effect if the magnifier is currently showing.
Returns the top left coordinates of the magnifier, relative to the main application window. They will be determined by the coordinates of the last show(float, float) or show(float, float, float, float) call, adjusted to take into account any potential clamping behavior. The method can be used immediately after a #show call to find out where the magnifier will be positioned. However, the position of the magnifier will not be updated visually in the same frame, due to the async nature of the content copying and of the magnifier rendering. The method will return null if #show has not yet been called, or if the last operation performed was a #dismiss.
Magnifier Windows
The most common surface quality standards are Military Performance Specification MIL-PRF-13830B and the International Organization for Standardization ISO 10110 optical drawing standards. Unfortunately, converting between these two standards is not straightforward and clients often over-specify roughness to be on the safe side when going between standards. Additional confusion arises if both MIL-PRF-13830B cosmetic quality and a surface roughness are specified for a part. These specifications are redundant and only one should be given.
Metal framed mirrors with rustic and venetian charm. Choose from silver, gold, copper, or bronze in a variety of styles and sizes. Free Shipping for orders ...
Find 82 different ways to say ABSORB, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesaurus.com.
When performing tolerance analysis, it is important to distinguish surface roughness from surface irregularity. While both describe the deviation of a surface from the ideal, surface roughness is typically a higher frequency surface departure than wavefront error. Surface irregularity is a lower frequency variation in the surface form which can result in wavefront distortion but typically does not result in scattering.
Magnifier Screen
Returns whether the magnifier position will be adjusted such that the magnifier will be fully within the bounds of the main application window, by also avoiding any overlap with system insets (such as the one corresponding to the status bar) i.e. whether the area where the magnifier can be positioned will be clipped to the main application window and the system insets.
Magnifier app free
Made of steel Perfect tool for those with value in mind.
Sets the zoom to be applied to the chosen content before being copied to the magnifier popup. The change will become effective at the next #show or #update call.
Magnifier app for Android
A network surveillance camera with CMOS sensors can provide high resolution output. Various types of CMOS image sensors are built into IP surveillance products ...
Surface roughness is most important in applications that are sensitive to light scattering. In high power laser systems scattering light in the wrong direction can cause damage to the system or injury to those operating it. A rough surface can scatter laser light and decrease the coherence of a laser beam. Scattered light can also add to background noise and reduce the detection sensitivity of a system. In high energy laser systems, it makes sense to splurge on highly polished optical components to reduce scattering, preserve coherence, and increase sensitivity. In systems where these factors are not critical, it is often better to use lower-cost optical components with a correspondingly less stringent surface roughness specification.
Shows the magnifier on the screen. The method takes the coordinates of the center of the content source going to be magnified and copied to the magnifier. The coordinates are relative to the top left corner of the magnified view. The magnifier will be positioned such that its center will be at the default offset from the center of the source. The default offset can be specified using the method Builder#setDefaultSourceToMagnifierOffset(int, int). If the offset should be different across calls to this method, you should consider to use method show(float, float, float, float) instead.
A classic magnifying glass, as used to view small objects, with its lens pointed left. Generally depicted at a 45° angle with a black handle and a clea...
Returns the zoom to be applied to the magnified view region copied to the magnifier. If the zoom is x and the magnifier window size is (width, height), the original size of the content being magnified will be (width / x, height / x).
Called by the garbage collector on an object when garbage collection determines that there are no more references to the object.
2 in. Dimensions (L x W x H), 4.7 x 2.4 x 1.5 in. Material, Acrylic.
Causes the current thread to wait until it is awakened, typically by being notified or interrupted, or until a certain amount of real time has elapsed.
The 3D display shows the actual shape of the beam. It is possible to easily zoom, pan and rotate the image. The very useful reset button allows to put the data ...
Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Magnifier app
Returns the vertical offset, in pixels, to be applied to the source center position to obtain the magnifier center position when show(float, float) is called. The value is ignored when show(float, float, float, float) is used instead. The units of this value are pixels.
Returns the horizontal offset, in pixels, to be applied to the source center position to obtain the magnifier center position when show(float, float) is called. The value is ignored when show(float, float, float, float) is used instead. The units of this value are pixels.
Returns the top left coordinates of the magnifier source (i.e. the view region going to be magnified and copied to the magnifier), relative to the window or surface the content is copied from. The content will be copied: - if the magnified view is a SurfaceView, from the surface backing it - otherwise, from the surface backing the main application window, and the coordinates returned will be relative to the main application window The method will return null if #show has not yet been called, or if the last operation performed was a #dismiss.
Resolution Target - USAF 1951, Group 8 (1.096um). $100.00. $100.00. Resolution Target - USAF 1951, Group 9 (548nm). $200.00. $200.00. Resolution Target RTA39D22 ...
It is most cost-effective to understand how an optic is going to be manufactured and tested or alternatively specifying techniques in your drawing or control document. If the surface roughness specification is too tight, it will limit which manufacturers can supply the optic and if a roughness value is specified, then it must be measured. This will also limit which manufacturers can supply the verification data or increase costs because parts will need to be sent to a third party for verification. If the project requires verification, consider Acceptance Quality Level (AQL) testing since the optic may be manufactured as a lot on a common spindle, where the overall surface roughness will be consistent across the lot. This is primarily controlled by polishing speed, pressure, and slurry grit.
Returns the horizontal offset, in pixels, to be applied to the source center position to obtain the magnifier center position when show(float, float) is called.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500