KONG Laser Pointer Cat Toy - lazor pointer
Dispersion in optical fibers In an optical medium, such as fiber, there are three types of dispersion, chromatic, modal, and material.
Throughout the last year, Antmicro has been heavily involved with Allied Vision in developing support for their innovative Alvium camera series. As a first step on a path towards a broader, cross-platform software support for the plug-and-play, ISP cameras, the community recently saw the open source release of the Linux drivers for Alvium cameras on the NVIDIA Jetson TX2 platform.
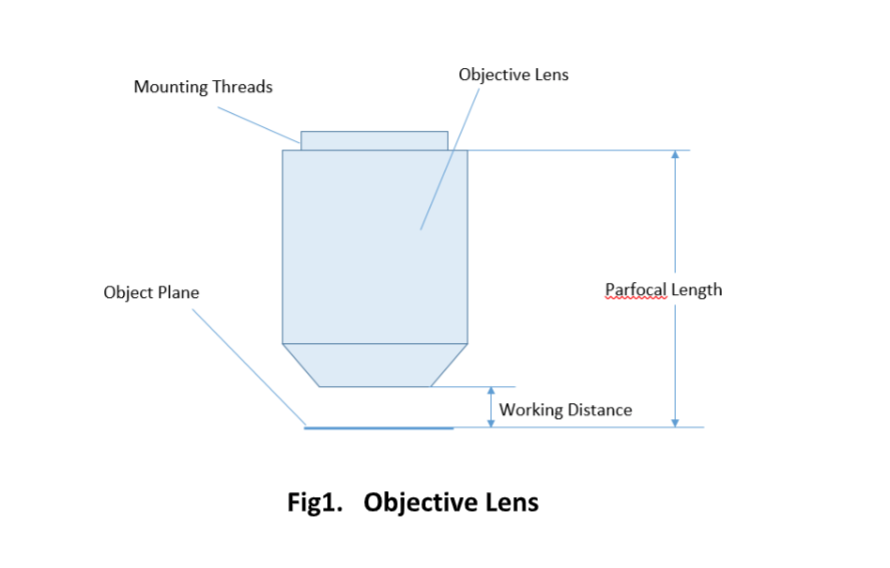
For keeping the objective at the proper position, there are mounting threads on almost all objectives. Commonly used mounting threads include RMS, M25 x 0.75, M26X 0.706, M32 x 0.75.
The Cinegon 1.4/8mm Compact C-Mount Lens covers a 2/3 format sensor with an 11mm image circle. It is broadband coated and corrected for uninterrupted imaging ...
AlviumFlex
The driver created by Antmicro for Allied Vision for the Jetson TX2 platform supports all of the cameras released so far in the Alvium series. The code, together with setup instructions, can be found on Allied Visionâs Github repository.
Important specifications are marked on the barrel of the objective, so students or researchers can easily identify the properties of an objective and determine the optical performance and working conditions for proper use. Figure 1 shows a diagram of an objective lens. A detailed discussion of the objection specifications is provided below.
Two major lens components—the objective lens and the ocular lens, or eyepiece—work together to project the image of the specimen onto a sensor. This may be the human eye or a digital sensor, depending on the microscope setup.
Most objectives are designed to image specimens with air as the medium between the objective and the cover glass. However, for achieving higher working numerical apertures, some objectives are designed to image the specimen through another medium such as special oil with a refractive index of 1.51.
If there is a need to access camera controls remotely, or in a headless system, we have created a useful CLI utility for exactly this use case, called pyvidctrl.
Gaming Slang for Newbies. If you're new to gaming, then there is more to learn than just a game's moves and strategy. Gamers should also be familiar with ...
Based on popular demand, early Jetson Nano support is also available - opening up a way towards inexpensive, smart camera-enabled solutions that weâd been helping our customers build for many years now.
Field-of-view (also known as FOV) ; 45mm. 43.6. 29.9 ; 50mm. 39.6. 27.0 ; 55mm. 36.2. 24.6 ; 60mm. 33.4. 22.6.
The optical aberration correction determines the optical performance of an objective lens and plays a central role in the image quality and measurement accuracy of imaging or microscopy systems. According to the degrees of the aberration corrections, objective lenses are generally classified into five basic types: Achromat, Plan Achromat, Plan Fluorite (Plan Semi-Apochromat), Plan Apochromat, and Super Apochromat.
Frames from the camera can also be obtained using the v4l2-ctl CLI tool - below is an example command that will capture 10 frames from the camera and save them into a file called frames.raw:
Oscillating patterns of light aren't strictly quantum but can help with quantum information. · Up and down or side to side? · Waves can be linearly polarized (up ...
Room 609, 6/F, Global Gateway Tower, No.63 Wing Hong Street, Cheung Sha Wan, Kowloon, Hong Kong +852-54993705 info@shanghai-optics.com
Apr 15, 2016 — The colors you see represent the different colors being reflected based on how deep the oxidation which is based on how hot the metal got at ...
The parfocal length is the distance between the objective mounting plane and the specimen / object. This is another specification that can often vary by manufacturer.
Allied VisionAlvium
The model MI-LED fiber optic illuminator offers long life LED illumination for microscopy and numerous other cold light applications.The MI-LED is available ...

where θ is the maximum 1/2 acceptance ray angle of the objective, and n is the index of refraction of the immersion medium. Figure 2 shows the ray angle θ of an infinity-corrected objective.
The ocular lens, or eyepiece, is also an optical assembly rather than a single lens, but it is typically more simple than the objective. Often it is composed of two lenses: a field lens and an eye lens. The design of the ocular lens determines the field of view of the microscope, as well as contributing to the total magnification of the system.
Alviumprice
Field of View is the area of the object that can be imaged by a microscopy system. The size of the field of view is determined by the objective magnification or focal length of the tube lens for an infinite-corrected objective. In a camera system, the field of view of the objective is related to the sensor size.
Thanks to this modularity aspect, it was possible to create a single, robust driver that supports all current (and future!) Alvium-based cameras and which is able to dynamically obtain a cameraâs properties and capabilities, and present them to the user in a unified manner.
Since the objective is closest to the specimen being examined, it will relay a real image to the ocular lens. While doing so, it contributes a base magnification of anywhere from 4x (for a scanning objective lens, typically used to provide an overview of a sample) to 100x (for oil immersion objectives).
Discover Schneider-Kreuznach C-Mount lenses for precise, durable machine vision in industrial settings. Compact, robust, and ideal for 3D measurement, ...
Alviumcamera
Another useful tool for video processing is gstreamer - video can be streamed using gstreamer with the v4l2src element, and processed further using its powerful plugin system. Here is an example of redirecting the video to the xvimagesink element, which simply displays the stream in a window:
The ocular lens, located at the top of a standard microscope and close to the sensor (receiving eye) receives the real image from the ocular lens, magnifies the image received and relays a virtual image to the sensor. While most eyepieces magnify 10x, there are some which provide no magnification and others which magnify as much as 30x. The magnification power of the microscope can be calculated by multiplying the magnification power of the eyepiece, or ocular lens, by the magnification power of the objective lens. For example, an objective lens with a magnification of 10x used in combination with a standard eyepiece (magnification 10x) would project an image of the specimen magnified 100x.
Objective lenses can be classified based on the objective construction, field of use, microscopy method, performance (optical aberration corrections), and magnification. Many microscope objective manufacturers offer a wide range of objective designs, which provide various degrees of optical aberration corrections for supporting different needs. Mirrors or reflective elements are used in objective lenses for the applications that requires chromatic aberration over board spectral ranges. Most traditional microscopy systems use refractive objectives such as achromatic objectives (the cheaper objectives) for laboratory microscope applications and plan apochromats (expensive objectives) for biological and science research microscope applications.
REFLECTION GRATING · Sodium lamp (269 shelf 46) (nearly monochromatic) gives one diffraction pattern. · Mercury lamp (270 shelf 46) clearly resolves green and ...
Alpha Industrial Park, Tu Thon Village, Ly Thuong Kiet Commune, Yen My District, Hung Yen Province Vietnam 17721 +84 221-730-8668 rfqvn@shanghai-optics.com
As the camera is available as a v4l2 interface, it can be easily used with any application that supports this standard. Here is an example of displaying the video stream using the qv4l2 GUI:
Alvium1800
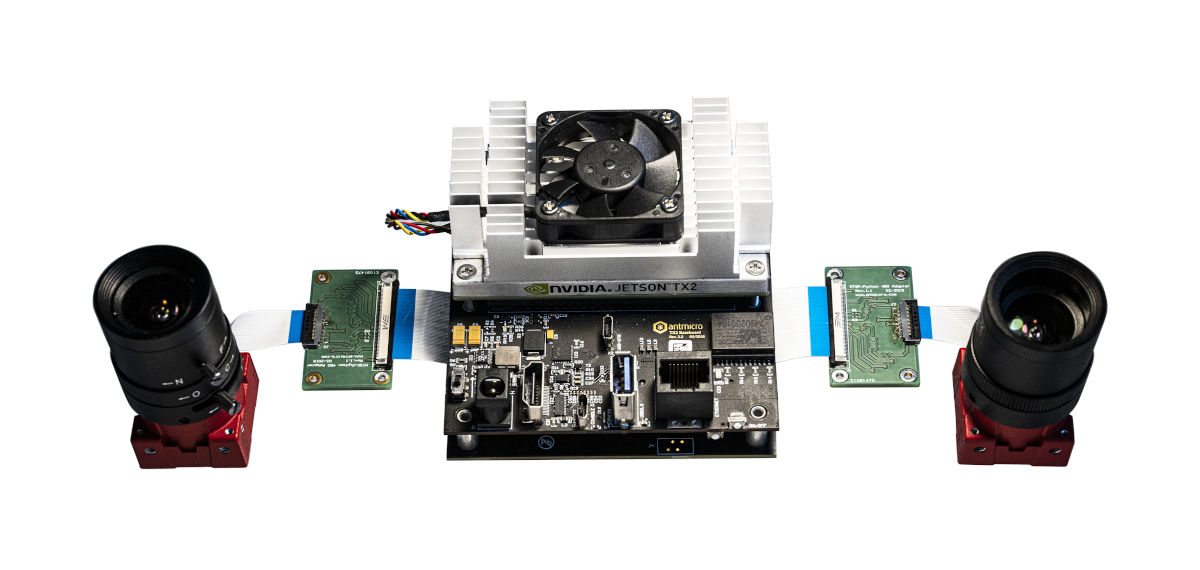
As released, the driver is configured to support Allied Visionâs adapter board for the TX2 devkit, but other adapters can be used, with adjustments to the configuration in the device tree files. Naturally, we have also been using AVâs cameras in our own projects and with our own hardware kits which feature our 2x4 lane MIPI CSI-2 connectors (as seen in the picture) for which we also have adapters.
A great match for creating edge computing vision systems is the powerful NVIDIA Jetson TX2 platform - the widely used and less power-hungry/expensive predecessor of the current Jetson Xavier (now in both the original and Jetson Nano-compatible form factor). The Jetson TX2 is able to drive up to 6 CSI-2 cameras, and is equipped with a powerful GPU that can be used for image processing.
At Shanghai Optics, we design and manufacture custom objectives and imaging systems to support our customers’ needs in many industries, including medical, biomedical, machine version, scientific research, and metrology, etc. Taking the client’s budget and precision requirements into consideration, our experienced engineering team ensure that each design can be manufactured at a reasonable cost and the optical performance is being met based on fabrication, assembly, and alignment tolerance analysis.
Many objectives are designed to be used with a cover glass. Using an incorrect coverslip thickness can greatly reduce the optical performance of a microscopy system.
Objectives are complex multi-element lenses. For any given application, careful consideration of the optical parameters and specifications is necessary. In many cases, custom-designed objective assemblies provide the best-fit solution for meeting all the requirements of a specialized application. Custom parameters may include antireflection coatings, chromatic focus shift, working distance, image quality (MTF and spot size), lens mount, glass window thickness, and field of view, among others.
Antmicro had successfully helped its customers build a plethora of products using the TX2 - but varying degrees of support for different camera sensors, and their differing capabilities and interfaces have always been pain points. Working with Allied Vision to create a unified, open source solution has therefore been a very welcome project where we can fill an important gap.
AlviumG1
Microscope Objectives or Objective lenses are in many ways the heart of the microscope, and are typically mounted on a rotating nosepiece or turret to enable easy selection. Many microscopes will be equipped with a scanning objective (4x), a low power objective (10x), a high power objective (40x), and perhaps even an oil immersion objective lens.
While the simplest of microscopes is simply a magnifying glass with a single lens, compound microscopes used today are highly complex devices with a carefully designed series of lenses, filters, polarizers, beamsplitters, sensors, and perhaps even illumination sources. The exact combination of optical components used will depend on the application of the microscope; the wavelength of light with which it is intended to be used, and the resolution and magnification required in the final image.
Diving in deeper into the drivers, they provide the user with a standard video4linux2 device. Available video formats are obtained dynamically from the camera, and the driver supports all of the possible formats (including Bayer, RGB and YUV). The CSI lane count can be configured to the desired value - from 1x up to 4x CSI lanes. The configurable camera parameters are available to the user as custom video4linux2 controls.
AlviumG5
An extensive line-up of anti-reflectivon film (AR) with excellent anti-smudge, abrasion resistance and not to impaire a touch panel operation, and moth-eye ...
Each microscope objective is itself a complex assembly of lenses, and besides contributing to the magnification, it is the objective lens which determines the resolution power of the microscope. An objective lens can also provide optical aberration corrections. A reflective objective, for instance, includes two mirrors within the assembly. These mirrors can focus laser light as well as provide chromatic corrections.
Alviumai
Since indirect backlight illumination is generally more effective than direct illumination, most microscopes do not include an internal light source. Instead, they rely on daylight or on background illumination such as a lightbulb. In brightfield illumination, also known as Koehler illumination, two convex lenses saturate the specimen with external light admitted from behind. These two lenses, the collector lens and condenser lens, work together to provide a bright, even, and constant light throughout the system: on the image plane as well as on the object plane. This system of illumination is used in many compound microscopes, including student microscopes and those found in many research labs.
Magnification is one important parameter. Magnification is usually denoted by an X next to a numeric value. Objectives are available in a range of magnifications from 2X to 200X.
A microscope is a special optical device designed to magnify the image of an object. Depending on the type of microscope, it may project the image either onto a human eye or onto a recording or video device. As an example, consider the photographs of cells that can be found in a science textbook. These photographs have all been taken by a specialized microscope, and may be called micrographs.
A microscope objective is an important component of a microscopy or imaging system for a range of science research, biological, industrial, and general lab applications.. An objective lens determines the basic performance of an optical microscope or imaging systems and is designed for various performance needs and applications. It is located closest to the object and is an important component in imaging an object onto the human eye or an image sensor.
Alvium is a brand-new series of cameras by Allied Vision targeting embedded platforms. They are equipped with a custom-made Alvium System-on-Chip that controls the image sensor. The Alvium SoC provides a unified interface for controlling the camera, independent of what sensor it is equipped with. This creates an abstraction layer which takes away the differences in handling various image sensors from the software that controls it.
A simple magnifier (magnifying glass), works when the object to be examined is situated within focal length of the magnifier lens, enabling larger virtual image is produced. This type of magnifier is very limited in both resolution and magnification. A compound microscope, on the other hand, uses a relay lens system instead of the single lens, and since each lens component can contribute magnifying power, the result is greatly increased capability.
Weâre currently working with Allied Vision to produce Linux drivers supporting Alvium for a broad range of edge AI platforms - next up is the NXP i.MX 8. If youâre interested to get your cameras working in an elegant, scalable fashion for a new embedded device, Antmicro offers expertise in the NVIDIA Jetson Xavier, Xavier NX, Nano, the NXP i.MX series and many other platforms. Find out more at contact@antmicro.com.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500