Kolari Pro UV IR Dual Flashlight (Ultraviolet/Infrared) - infrared flashlight filter
Spherometermeasures


Spherometerphysics
Figure 3.1 is a schematic diagram of a single disk spherometer. It consists of a central leg OS, which can be raised or lowered through a threaded hole V (nut) at the centre of the frame F. The metallic triangular frame F supported on three legs of equal length A, B and C. The lower tips of the legs form three corners of an equilateral triangle ABC and lie on the periphery of a base circle of known radius, r. The lower tip of the central screw, when lowered to the plane (formed by the tips of legs A, B and C) touches the centre of triangle ABC. A circular scale (disc) D is attached to the screw. The circular scale may have 50 or 100 divisions engraved on it. A vertical scale P marked in millimetres or half-millimetres, called main scale or pitch scale P is also fixed parallel to the central screw, at one end of the frame F. This scale is kept very close to the rim of disc D but it does not touch the disc D. This scale reads the vertical distance when the central leg moves through the hole V.
Definition noun (general) The condition of polarity (biology) The process or act of producing positive and negative electric charge values to opposite ends, such as the electrical charge inside a (nerve) cell relative to the surrounding environment Supplement Polarization in general context refers to the state or condition of polarity. In biology, polarization pertains to..Read More
Spherometeris used to measure
The Least count (LC) is the distance moved by the spherometer screw, when the screw is turned through 1 division on the circular. We are using a spherometer which has 100 divisions (N) on the disc. The least count can be calculated using the formula,
Definition noun (general) The condition of polarity (biology) The process or act of producing positive and negative electric charge values to opposite ends, such as the electrical charge inside a (nerve) cell relative to the surrounding environment Supplement Polarization in general context refers to the state or condition of polarity. In biology, polarization pertains to the act or process of producing a positive electrical charge and a negative electrical charge such that between a nerve cell internal electrical charge, which is negative, and the surrounding environment of a nerve cell, which is positive. The cell is able to regulate the differing electrical charge relative to its surrounding via the plasma membrane. A closer look at the plasma membrane reveals transmembrane proteins and pumps that act as ion channels. These proteins that are embedded in the plasma membrane are selective, which means they allow certain molecules to move in and out of the cell while prevent or control the efflux and influx of others (in this regard, ions). There are move negative ions (e.g. Cl–) inside the cell, which results in a cell that is negative relative to the outside. In general, a nerve cell has a resting potential of approximately -70 mV.1 Word origin: French polarisation Variant(s):
Spherometerleast count
Now, let l be the distance between any two legs of the spherometer or the side of the equilateral triangle ABC (Fig. 3.4), then from geometry we have, a = l/√3. Thus the radius of curvature of the spherical surface can be given by,
Spherometerformula
The content on this website is for information only. It is not intended to provide medical, legal, or any other professional advice. Any information here should not be considered absolutely correct, complete, and up-to-date. Views expressed here do not necessarily reflect those of Biology Online, its staff, or its partners. Before using our website, please read our Privacy Policy.
Now, let l be the distance between any two legs of the spherometer as shown in figure 3.6, then from geometry we have, a = . Thus the radius of curvature of the spherical surface can be given by,
Photosynthesis is the process that plants undertake to create organic materials from carbon dioxide and water, with the ..
Spherometerexperiment
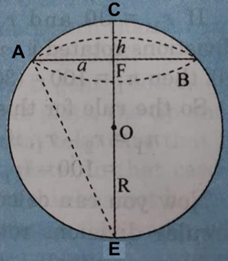
From the figure 3.3, O is the centre of the circle. OE = OA = R, radius of the circle. F is the tip of the screw at the same plane with A, B and C. EF = h, AF = a and ∠AFO =
From the figure 3.4, the circle is passing through A and C. O is the centre of the circle. OE =R, radius of the circle. F is the tip of the screw at the same plane with A, B and C. CF = h, AF = a ∠EAC = 900.
This tutorial digs into the past to investigate the origins of life. The section is split into geological periods in the..
Spherometerdiagram
This tutorial investigates perception as two people can interpret the same thing differently. Know more about human perc..
A spherometer is a measuring instrument used to measure the radius of curvature of a spherical surface and a very small thickness.
Digitalspherometer
We are a School laboratory furniture and Lab equipment manufacturer and supplier. In laboratory furniture for school, we first design the entire laboratory room keeping in mind the requirements as per affiliation CBSE Bye-Laws. Also, we take care of the complete designing and installation of laboratory furniture.
The vertical distance moved by the screw S in one complete rotation of the circular Scale/Disc D is called the pitch (p) of the spherometer. To find the pitch, give full rotation to the screw (say 4 times) and note the distance (d) advanced over the pitch scale.
In the lab equipment section, we have a wide range of glassware, chemicals, equipment and other lab accessories. Most of them are available for order online on our website but some of them can be procured on demand.
A running water environment offers numerous microhabitats for many types of animals. Similar to plants, animals in lotic..
Ferns and their relatives are vascular plants, meaning they have xylem and phloem tissues. Because of the presence of va..
Plants, like animals, produce hormones to regulate plant activities, including growth. They need these hormones to respo..




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500