InSchoolwear Home - Uniforms and Eco-Uniforms for sale in ... - uniform source
In digital cameras, the light beam is split light into its RGB elements before striking the light sensor, which then reads the strength of each color per pixel, and converts that information into digital data. Unlike film, digital images do not deteriorate with age, and can be enjoyed in various ways, such as viewing on a TV or PC screen, or by outputting them using a printer.
Illinois Schools Products and Services. A K-12 school supply buyer's guide.
If light is allowed to enter a darkened room through a tiny hole in a wall or door, the scenery outside will be projected onto the opposite wall. This phenomenon, known as pinhole projection, is one of the basic principles behind photography. The image created by pinhole projection is a reverse image, both upside-down, and left and right reversed. A pinhole camera can be easily created by opening a pinhole in a box that otherwise lets in no light. The hole should be covered with tape, and a sheet of photo printing paper placed inside, opposite the hole, without exposing it to light.
Optical correction such as achromatic, apochromatic, plan and semi-plan are often denoted on the objective in order to show the design of the objective. Plan and semi-plan objectives correct for field curvature. Field curvature often results in blurred images on the periphery and correction for this helps produce good quality images. Whereas plan objectives correct better, allowing for better display (over 80 per cent) of field flat, semi-plain objectives produce about 65 per cent.
[Translate to German:] Applying Industrial Cameras to Lithium Battery Production ... Mako-Kamera unterstützt visuelle Inspektion in der Lithium-Batterie-Industrie.
On the objective, this is usually denoted by an X next to a numeric value (100X, 10X etc). On the other hand, objectives will also have a colored band around the circumference of the objective that indicates the magnification of the objective. For instance, a yellow band around the objectives (lower part of the objective) indicates that it is a 10x objective.
Cameraknowledge
UV Bandpass Optical Filter Options. Unlike absorbent polymer or colored-glass gels, our UV bandpass filters consist of thin films and are virtually absorption- ...
8 days ago — Polarized sunglasses offer benefits to your eyes like reduced glare reduction, better contracts, prescription options etc.
Magnifying Glass Magnifying Glass is an useful application which allows you to turn your phone into a Magnifier. Magnifying Glass is a FREE android ...
The mechanism of faithfully rendering a picture made by light was first utilized by medieval European artists. However, a giant leap forward was achieved with the invention of film, and photography has continued to evolve into the present-day digital technology.
There are many different types of objectives available for microscopes, but without a basic understanding of how they work, it can be difficult to know which ones are best suited to the specific needs you have. That's why this article takes you through the basics points to keep in mind ,so that you'll have a better idea of what type is right for your needs.
by G Pearce · 2016 · Cited by 187 — The PRISMS taxonomy offers a framework to researchers describing self-management support interventions, to reviewers synthesizing evidence and to developers ...
The light that passes through a tiny hole in a wall creates an upside-down image of the scenery outside on the opposite wall of the room. Medieval European artists would capture such images on their canvases, tracing the details to make accurate sketches. The word "camera," in fact, derives from "camera obscura," the Latin term that the artists coined for such devices, which they used as an aid to creating their works. "Camera" means "room," while "obscura" means "ambiguous, dark." In short, cameras owe their name to a "dark room." It was in the first half of the 19th century that photography in the modern sense was born with the discovery of the technique of fitting a camera obscura with a metal plate that had been painted with a light-sensitive silver compound that automatically captured the pinhole image. In time, the metal plate became film, which then evolved from black-and-white to color film. In today's digital cameras, film has been replaced by light sensors that capture images by converting light into digital data.
Denoted by a number (such as 0.17mm) the cover slip thickness is labeled on the objective to note the type of cover slip that should be used. A cover slip changes the way light is refracted from the specimen. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the right cover slip is used in order to produce a good quality image. Zero(0) denotes no coverslip to use. Dash(-) denotes use of coverslip or no cover slip, it does not matter.
How, then, does color film render color? Color film contains three layers of photo-sensitive emulsion that are sensitive to different wavelengths of light: red, green and blue, respectively. The layer that is sensitive to red light is normally applied first, followed by emulsions sensitive to green light, and then blue light as the topmost layer. Adding dyes to silver halides makes them sensitive only to specific wavelengths of light. When color film is exposed, each photosensitive layer absorbs light of a specific wavelength.
In recent years, digital cameras have become increasingly popular as an alternative to cameras that use film. A digital image is a long string of 1s and 0s representing all the colored light dots, known as pixels, which collectively make up the image. Digital cameras employ image sensors, such as CCDs or CMOS sensors, in place of film. CCDs are collections of tiny, light-sensitive diodes that convert light into electrical charges, which are then digitized to create a digital image. Digital cameras, too, work on the principle of filtering the three primary colors of red, green and blue. CMOS and CCD sensors resemble black-and-white film in that they respond only to the strength of light.
Is the distance from the objective’s front lens to the closest surface of the coverslip when the specimen is in focus? WD is inversely proportional to the NA, which means that higher NA objectives typically have low working distances.
This is why chemical agents that reduce silver halides to silver are known as "developers." Even with development, those areas not affected by light remain as silver halides. They are removed by placing the film in a different agent that dissolves silver halides, leaving only the black silver grains. This is known as "fixing." A negative, which is an image in which the areas exposed to light appear as shades of black, is thus made by first taking a photo to create a latent image on the film, then developing and fixing that image with chemical agents. If printing paper is placed beneath the negative, and light is shone on the negative, the negative's blackened areas show up as lighter shades. Whiter areas show up as darker shades on the paper when that in turn is developed and fixed. This is the principle of black-and-white photography.
Dec 14, 2020 — Three types of lens elements are commonly used today. They are polished glass elements, molded plastic elements, and molded glass elements. Each ...
Jul 12, 2023 — A wave is polarised if a direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation exists. Since water waves (from a stone in a pond) always ...
It is an angle of incidence. It is the most important parameter of a microscope. NA measures its ability to gather light. It’s an important factor to determine resolution, depth of focus, and the brightness of images. Objectives with a larger NA gather a wider range of light, resulting in brighter, higher resolution images.
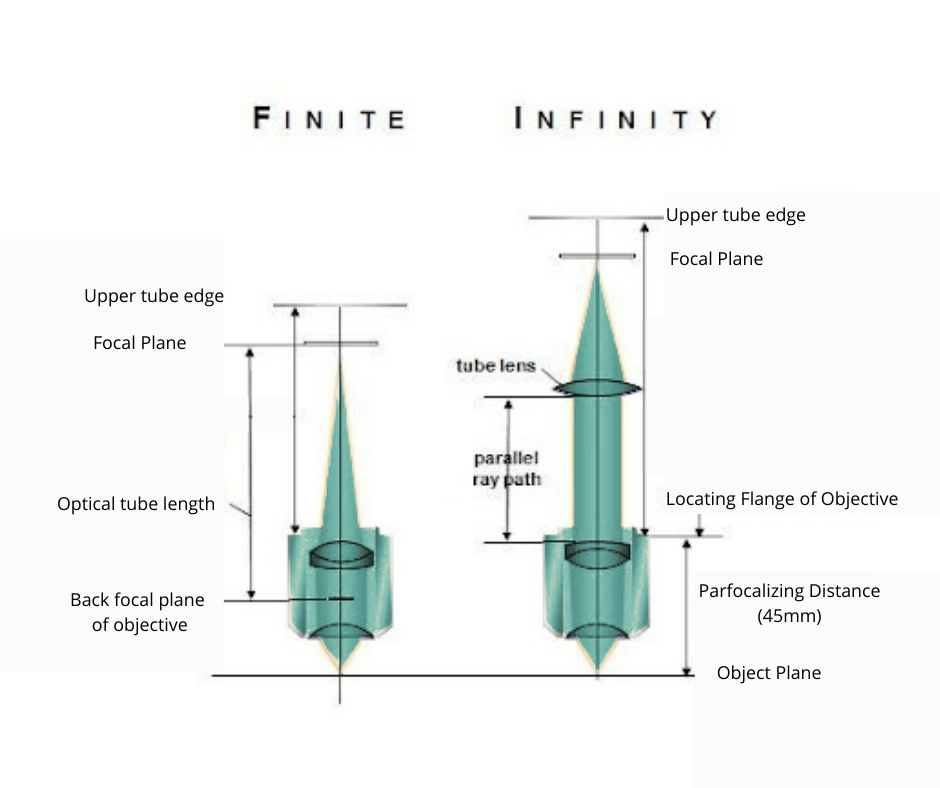
In a finite conjugate design, the objective focuses light from the object into the focal plane of the eyepiece. An infinite corrected objective collects light from the object and forms a parallel beam that passes through a tube lens. The advantage of this design is that additional optical elements, such as polarizers, filters, and wave-plates, can be placed in between the tube lens and the objective without interfering with the focusing of the beam. The infinite conjugate design is often used in fluorescence microscopes, which rely on filters.

Camera
NA is also important to observe very fine structures or detect dim signals during fluorescence observation. When determining which microscope objective will resolve the smallest feature in your specimen, think about the NA. As you weigh your options, keep in mind that numerical aperture typically ranges between 0.10 to 1.25.
The box should then be pointed in the direction of the scenery to be filmed, and the tape removed from the pinhole to allow light in for a few seconds. If the printing paper is placed in developing solution, the scenery will gradually appear in reverse on the printing paper. Present-day cameras work on the same principle, but with a lens, aperture ring and shutter affixed to the pinhole to adjust focus and light, and film or CCD to replace the wall or printing paper.
The objective depth of field is the axial range, which enables you to focus an objective without any considerable change in image sharpness. This value varies radically from low to high numerical aperture objectives; it usually decreases as the numerical aperture increases.
Each objective and eyepiece has a specific purpose or function. Objective lenses magnify the image that enters the objective and bring it to a sharp, clear focus. Eyepieces take the light that has been focused by the objective lenses and magnify it further so that you can see it. The magnification power is measured by objective magnification multiplied by eyepiece magnification.
Buy HW-F1000-4 Fresnel solar lens ,round shape ,diameter 1000mm, focal length 1000mm at Aliexpress for . Find more 1503, 37042001 and 150302 products.
The higher the NA, the smaller the distance between two objects. As we mentioned previously, choosing the right NA for your application is crucial in determining the resolution of your microscope system.

Attach each objective to each lens mount hole of the revolving nosepiece, starting from the lowest magnification objective and increasing the magnification in the clockwise direction seen from the bottom. By attaching objectives in this way, the objectives can be switched in ascending order of magnification
The resolution of the microscope objective determines the smallest distance between two objects that can be observed. It is directly proportional to the illumination wavelength of light and inversely proportional to the NA.
Camera film uses silver halides (such as silver chloride, bromide or iodide) as the materials exposed to light. When the silver halide layer absorbs light, electrons within the layer attach to the halide crystals, creating what are known as sensitivity specks. Light accordingly effects chemical changes in the silver-halide layer, leaving a latent image on the film. When exposed film is placed in a developing agent, the surroundings of the sensitivity specks are converted to silver, as a result of which the exposed areas start to turn black, and the image begins to "be developed."
How cameraWorks
Color film contains dye couplers, which, on development and fixation, become yellow, magenta or cyan, the three colors that are complementary to blue, green, and red. This is why a red apple appears green in a color negative. When light is shone through such a color negative onto color printing paper, the yellow, magenta and cyan colors in the negative create complementary colors in the paper, thus recreating the original colors of the subject photographed. This is the principle behind the dye coupler method of creating color images.
FLIR Systems has announced the availability of the new FLIR Blackfly S visible spectrum camera module, the first to integrate the Sony Pregius S IMX540 ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500