Image Sensors Explained: The Heart of Digital Cameras - cameras sensor
OCTeye test results
Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCT-A) has emerged as a non-invasive technique for imaging the microvasculature of the retina and the choroid. The first clinical studies using this innovative technology were published in 2014 .[1]
While clinicians primarily utilize OCT-A to qualitatively assess retinal microvasculature, researchers in recent years have aimed to develop more quantitative approaches.[29] These include the development of several vascular metrics that aim to quantify vascular features such as density and morphology. Though not exhaustive, below are several commonly used metrics.
Fleet Optics Inc, Mississauga, Ontario. 162 likes. Transport + Logistics, Redefined. FleetOptics provides Dedicated Fleet Customers with Final-Mile...
World-class Nikon objectives, including renowned CFI60 infinity optics, deliver brilliant images of breathtaking sharpness and clarity, from ultra-low to the highest magnifications.
Francesco Pichi and collaborators recently reviewed the uses and importance of OCT-A in uveitis.[8] For the sake of this article, only a brief summary will be reported.
It has been reported as a useful tool for evaluating optic disc perfusion in glaucomatous eyes, since attenuated peripapillary and macular vessel density was detectable in pre-perimetric glaucoma patients. Therefore, there is enthusiasm about the role of OCT-A in early detection of glaucomatous damage. Moreover, the quantitative data from these retinal vessels may prove useful in analysing metabolic activity from the inner layers of the retina and thus provide further advances in monitoring function and progression in this disease.[14][24]
OCTmachine
Les caractéristiques UV 400 et anti-buée renvoient aux qualités protectrices contre le rayonnement UV intense des écrans HEAD et à leur capacité à minimiser ...
It may also prove useful as a tool for ocular blood flow research and thus to help uncover non-IOP related mechanisms in this disease.
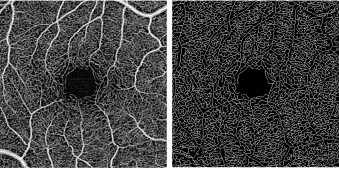
Light is emitted through either a spectral domain OCT (SD-OCT), with a wavelength of near 800nm; or a swept-source OCT (SS-OCT), which utilizes a longer wavelength, close to 1050nm. Longer wavelengths have a deeper tissue penetrance, but a slightly lower axial resolution. OCT-A employs two methods for motion detection: amplitude decorrelation or phase variance. The former detects differences in amplitude between two different OCT B-scans. Phase variance is related to the emitted light wave properties, and the variation of phase when it intercepts moving objects. To improve visualization and reduce background noise from normal small eye movements, two averaging methods - split spectrum amplitude decorrelation technique and volume averaging - were developed.[4][5] These OCT-A algorithms produce an image (3mm2 to 12mm2) that is segmented, by standard, into four zones: the superficial retinal plexus, the deep retinal plexus, the outer retina and the choriocapillaris. Applied to the optic disc it includes its full depth.[6][7]
Don't think these lenses are made anymore, the website does kinda look dodgy but they do have a cool selection of old lenses, i'd wait, if you ...
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
Vessel Area Density – a unitless measure that reflects the proportion of the OCT angiogram that is occupied by vessels of all caliber. This is typically accomplished by first binarizing the image such that the area occupied by vessels is comprised of white pixels and the avascular area is comprised of black pixels. A proportion of the white pixels divided by the total pixels in the image provides a measure of vessel density.
OCTppt
Enhanced single vision lenses that provide sharper vision than ordinary single vision lenses and are available to all ages. ... No-line multifocal for distance, ...
Extravascular signal from exudative edema - macular edema may appear as hypo- or hyper-reflective on structural OCTs. Hyper-reflective fluid, a form of exudate, is thought to be caused by suspended particles. OCT-A devices may capture the motion of these particles, leading to extravascular artifact. Transudative macular edema, in contrast, will not appear on OCT angiograms.
This interactive tutorial demonstrates the change in numerical aperture light cones displayed by a microscope objective with corresponding changes in the angular aperture (and numerical aperture) of an objective. To operate this tutorial, use the mouse cursor to adjust the position of the Angular Aperture slider. As the angular aperture is varied with the slider, the size and shape of the illumination cone entering the objective front lens is altered. The adjustable numerical aperture range for this tutorial is from 0.13 to 0.95, and an approximate objective magnification factor has been assigned to each numerical aperture value.
Flexible Fiber Optic Light Guides made of high transmission glass fibers sheathes in PVC-covered monocoil are available at Edmund Optics.
OCTprinciple
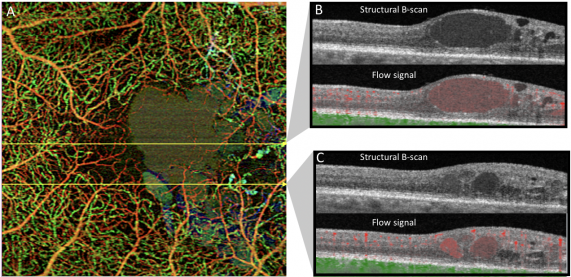
The detection and evaluation of choroidal vascular membranes may be similarly achieved with OCT-A in uveitis, as in the other causes referred above.[28]Specifically in inflammatory conditions, OCT-A has the advantage of acquiring three-dimensional data, and potentially improving our understanding of the pathophysiology of these diseases as well as their follow-up and management. However, multimodal imaging is still the option of choice in the diagnosis and management of uveitis.[8]
Projection Artifact - Projection artifact is inevitable and is related to light that traverses blood vessels and is reflected back by deeper layers (e.g. pigment retinal epithelium), which will appear in the final deep image with a similar vascular pattern as the overlying superficial vessels.[30]
The brightness of an image formed by an objective at a fixed magnification increases with the diameter of the angular aperture (the angle of the cone of light collected by the objective). Light rays emanating from the specimen proceed through air (or an immersion medium) that lies between the cover glass and the objective front lens. The angular aperture is expressed as the angle between the microscope optical axis and the direction of the most oblique light rays captured by the objective (see the tutorial figure). Mathematically, the numerical aperture is expressed as:
Optical coherence tomography
where n is the refractive index of the media in the object space (between the cover glass and the objective front lens) and θ is one-half the angular aperture. The value of n varies between 1.0 for air and 1.52 for a majority of immersion oils utilized in optical microscopy. The angular aperture, which varies with the objective focal length, is the maximum angle of image-forming light rays emanating from the specimen that the objective front lens can capture when the specimen is focused. As the objective focal length decreases, the maximum angle between the specimen and the outside diameter of the objective front lens increases, causing a proportionate increase in the angular aperture. From the equation above, it is obvious that numerical aperture increases with both angular aperture and the refractive index of the imaging medium.
This model supersedes RRT-ICG-ST01-QUEL02. To read more about the design changes, download this document. USAF 1951 Resolution target Group 0 through Group ...
OCTeye test price
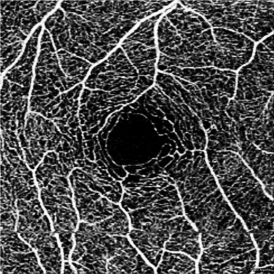
Motion Artifact - OCT-A examination is motion-sensitive and requires patients to be able to reasonably fixate, which may be difficult to obtain for the visually impaired.[11] Excessive motion of the eye can lead to motion artifacts as seen in the image. This can be overcome to some extent with a tracking feature present on most devices.
However, some limitations and artifacts are important to consider in the interpretation of OCT-A images (see section below).
Media Opacities - media opacities such as corneal scarring, cataracts, posterior capsular opacification, and vitreous floaters may lead to signal attenuation and shadowing artifact.[3] These may obscure portions of the OCT angiogram or lead to diffuse reduction in image quality.
Premium 10 degree Focusing Lens Premium 45, Universal, Universal Mini, Double Flange, and Mini Double Flange Extrusions.
Tube Spanner 8 x 10 mm for Classic Fiat 500, 600, 126, Topolino, 850, Panda 141 · No. 1 expert in vintage Fiat parts · More than 6,000 different classic Fiat ...
OCTin Cardiology
Michael W. Davidson - National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310.
One asset of this OCT-based approach is that it provides a quantitative analysis of the retinal vessels (in addition to the qualitative analysis done on standard angiography). Moreover, and contrary to the "2-D" conventional angiograms, OCT-A technology provides "3-D" imaging information of the macula and visualizes peripapillary capillaries that supply the retinal nerve fiber layer.[6]
Therefore, only a brief description of current uses is available in this article and further information should be looked in the available ophthalmology journals.
The main advantages are the shorter acquisition time and that it is a non-invasive process. Fluorescein and indocyanine-green angiography require an injectable dye (which takes time to reach retinal vessels, and may be associated with systemic adverse effects and even anaphylatic reactions[2]).
nanoplus DFB Quantum Cascade Lasers (DFB QCL) are available at any customized wavelength between 6000 nm and 11000 nm. Explore their specifications ...
OCTinterpretation PDF
The light-gathering ability of a microscope objective is quantitatively expressed in terms of the numerical aperture, which is a measure of the number of highly diffracted image-forming light rays captured by the objective. Higher values of numerical aperture allow increasingly oblique rays to enter the objective front lens, producing a more highly resolved image.
OCT-A technology uses laser light reflectance of the surface of moving red blood cells to accurately depict vessels through different segmented areas of the eye, thus eliminating the need for intravascular dyes.[2] The OCT scan of a patient's retina consists of multiple individual A-scans, which when compiled into a B-scan provides cross-sectional structural information. With OCT-A technology, the same tissue area is repeatedly imaged and differences are analyzed between scans (over time), thus allowing one to detect zones containing high flow rates (i.e. with marked changes between scans) and zones with slower, or no flow at all, which will be similar among scans.[3]
Theoretically, the highest angular aperture obtainable with a standard microscope objective would be 180 degrees, resulting in a value of 90 degrees for the half-angle utilized in the numerical aperture equation. The sine of 90 degrees is one, which indicates that numerical aperture is limited not only by the angular aperture, but also by the imaging medium refractive index. A majority of microscope objectives are designed to operate with air (which has a refractive index of 1.0) as the imaging medium between the cover glass and the objective front lens. This yields a theoretical maximum numerical aperture of 1.00, but in actual practice, the highest numerical aperture for a dry objective is about 0.95 (the angular aperture half-angle equals approximately 72 degrees).
As a fast, safe and noninvasive procedure to assess the chorioretinal microvasculature, OCT-A has been increasingly used in retinal diseases. The number of studies reporting new findings and utilities is exponentially growing.
Vessel Skeletal Density – One limitation of vessel area density is the variability of vessel caliber among OCT angiograms in different eyes. For example, one eye may by chance have a greater number of larger vessels than another within a set window, thereby giving a false impression that it has increased density. Vessel skeletal density adjust for this variability by iteratively deleting outer pixels of each vessel such that each individual vessel, regardless of size, is represented by only a single line of pixels.
Segmentation Error - Automated segmentation of a structural abnormal retina is an unavoidable limitation of OCT-A imaging. In cases of pigment epithelial detachments (PED), one should look carefully for segmentation errors and manually edit layers if deemed necessary for a correct interpretation.[31]
Vessel Diameter Index – this value reflects the average vessel diameter within an OCT angiogram and is calculated by dividing vessel area density by vessel skeletal density.
Quickly tighten or loosen fasteners with the help of the Hex Key Set (SAE + Metric). This tool is perfect for DIYers, mechanics, homeowners, and handymen ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500