Image Distortion and How to Fix it? | A Comprehensive Guide - picture of distortion

HEF bushings are recognized worldwide for their excellent frictional and anti-seizure properties, and ability to withstand high loads.
Dlc coatingnear me
Other DLC coatings can be customized based upon the unique combination of wear mode, contact mode and the friction regime under which the component in operating.
In this blog, we break down distortion parameters in lens datasheets and the three ways in which distortion is represented.
We also provide various customization services, including camera enclosures, resolution, frame rate, and sensors of your choice, to ensure our cameras fit perfectly into your embedded vision applications.
DLC coatingmachine
The formula calculates the difference between the expected height of an object based on the sensor size and its actual distorted height based on the distortion values and field of view. This difference is then expressed as a percentage of the vertical sensor size to provide a measure of barrel distortion.
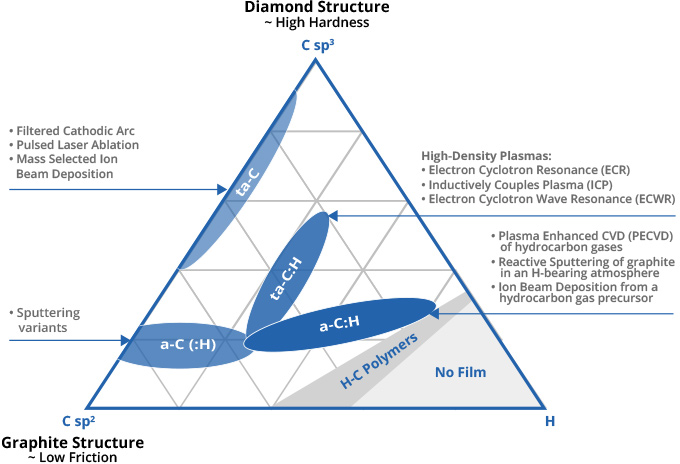
In recent years, a new generation of PVD + PACVD (plasma-assisted CVD) coatings has gained widespread commercial success. As is well known, carbon can exist in three allotropic forms. Carbon, in a diamond crystal structure, is one of the hardest know materials. Carbon, in a graphite crystal structure, is very soft and lubricous. Carbon-based coatings, referred to as Diamond-like-Carbon (DLC) coatings, combine these two different properties of diamond and graphite - hence possess high hardness levels - in the range of conventional tribological PVD coatings (1500 - 3200 HV), coupled with a coefficient of friction which is 200-500% lower than that of conventional PVD coatings.
Both methods can be used to estimate distortion, but they can be more applicable in certain situations. F-Tan (Theta) is preferred when the focus is on object size and magnification changes due to distortion. And the F(Theta) method is used to get the angular relationship of distorted image points without needing magnification information.
DLC coatinghardness
Besides this unique combination of properties, this new generation of coatings has high load-bearing capabilities, making them an ideal choice for improving the performance of engineered components. Moreover, these coatings are usually bio-compatible and hence suitable for food-contact and medical applications. The lubricious surface also has good release properties, making these coatings a good choice for plastic processing applications.
F-Theta lenses are specifically designed to maintain a constant image size (or spot size for lasers) across a scan field. The F-Theta calculation helps ensure the accuracy of this constant size by measuring deviations from the ideal. These lenses are used in various applications like laser marking and engraving, laser cutting, 3D printing and LiDAR.
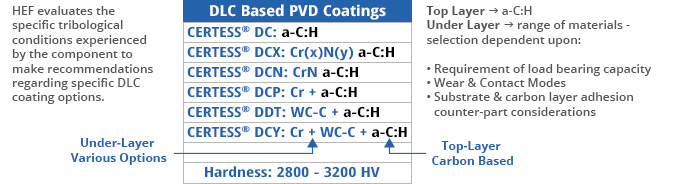
In order to meet the diverse operating conditions encountered by engineered components used for automotive and other generic industrial applications, HEF has developed a family of diamond-like-carbon DLC coatings. These coatings usually include several layers of different materials such as Cr, CrN, W, WC-C, Si with a top layer of amorphous carbon, with hydrogen. The selection of the under-layer is based upon several factors such as: adhesion requirements, wear mode and contact mode, friction regimes encountered during operation, load carrying capacity, and other metallurgical considerations. These coatings have a unique combination of high hardness and low friction coefficient, compared to conventional PVD coating (TiN, CrN, ALTiN etc) and soft coatings (such as solid lubricants like Molybdenum di-sulfide).
F*tan(theta) calculations are used in camera calibration processes, where distortion parameters are estimated for correcting captured images. Lens designers often utilize F*tan(theta) calculations during the design phase to predict and minimize distortion in the final lens. This helps create lenses with minimal image curvature and ensures accurate image reproduction.
DLC coatingthickness
A negative value indicates barrel distortion (objects appear smaller towards the edges). In the above example, the calculation shows a higher barrel distortion (-39.5%) at a larger image distance (10mm). As the image distance decreases (9mm and 5mm), the distortion percentages become less negative, indicating a decrease in the barrel effect.
The properties of DLC coatings in terms of hardness; coefficient of friction; roughness; adhesion level; load carrying capacity; resistance to humidity influenced degradation; fatigue tolerance, etc. can be tailored over a wide range depending upon deposition parameters, deposition technology and the combination of materials constituting the coating. Some of the more common commercial variants of WCC and DLC coatings from HEF are shown below.
PVD coatings involve the deposition of thin (2-10 microns; 0.0001" – 0.0004") films on the surface of tools and components.
Prabu is the Chief Technology Officer and Head of Camera Products at e-con Systems, and comes with a rich experience of more than 15 years in the embedded vision space. He brings to the table a deep knowledge in USB cameras, embedded vision cameras, vision algorithms and FPGAs. He has built 50+ camera solutions spanning various domains such as medical, industrial, agriculture, retail, biometrics, and more. He also comes with expertise in device driver development and BSP development. Currently, Prabu’s focus is to build smart camera solutions that power new age AI based applications.
DLC coatingat home
Optical distortion represents the overall distortion parameter of the optical system. F-Tan theta or optical distortion can be calculated using the following formula.
The F*tan(theta) method is a more general approach to calculating distortion. It’s often used for initial distortion assessment in various lenses, including photographic lenses. This method helps understand how straight lines deviate from their ideal positions due to distortion.
TV Distortion, as the name suggests, originated in the context of television applications. It can be calculated using the following formula:
DLC coatingapplication
Mathematically, distortion can be represented in three different ways in the lens datasheet; let us look at each of them in detail.
F-Tan (Theta) method uses the tan(theta) relationship to calculate a reference height based on magnification, and the F(Theta) method uses F*theta (radians) to represent the ideal image point location based on its angular position.
DLC coatingwatch
Lens datasheets often include distortion information to help photographers and engineers understand how the lens behaves. Lens distortion refers to the phenomenon where straight lines in a scene appear curved in the final image. This happens because lenses don’t perfectly focus light from all parts of the field of view.
Imagine a scene with a square grid. In barrel distortion, the grid would bulge outwards, making the squares appear wider on the edges. Meanwhile, in pincushion distortion, the grid would sink inwards, making the squares appear narrower on the edges. Mustache distortion would cause the grid lines to become wavy.
DLC coatingprice
Diagonal Field of View (FOV) at a Specific Image Distance: Values provided at different image distances (e.g., 124° @ 10mm)
Liquid nitriding is a subcritical surface enhancement process with one of the longest track records of success of any case hardening technology.
As shown below, DLC coatings can be deposited using a diverse range of technologies and alloyed with elements such as hydrogen and metals such as chromium. These constituent elements and deposition technique can have a significant impact on the properties and structure of the DLC coating.
F(Theta) method focuses on the angular relationship between the ideal undistorted image point and the actual distorted image point without needing magnification information.
The F-Tan (Theta) method uses the tangent function to relate the angle to object size and magnification. Whereas the F(Theta) method focuses on the angular position of the image point relative to the centre. Both the methods require the focal length (F) and the diagonal FOV (degrees). But in the F(Theta) method the FOV in degrees is converted to radians.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500