If I Had To Shoot Everything On A Single Lens, It Would Be ... - 50mm lense
The nature of the Gaussian beam causes it to focus not in a point but in a spot: the lens modifies (compresses) the beam, which, however, retains all its features.
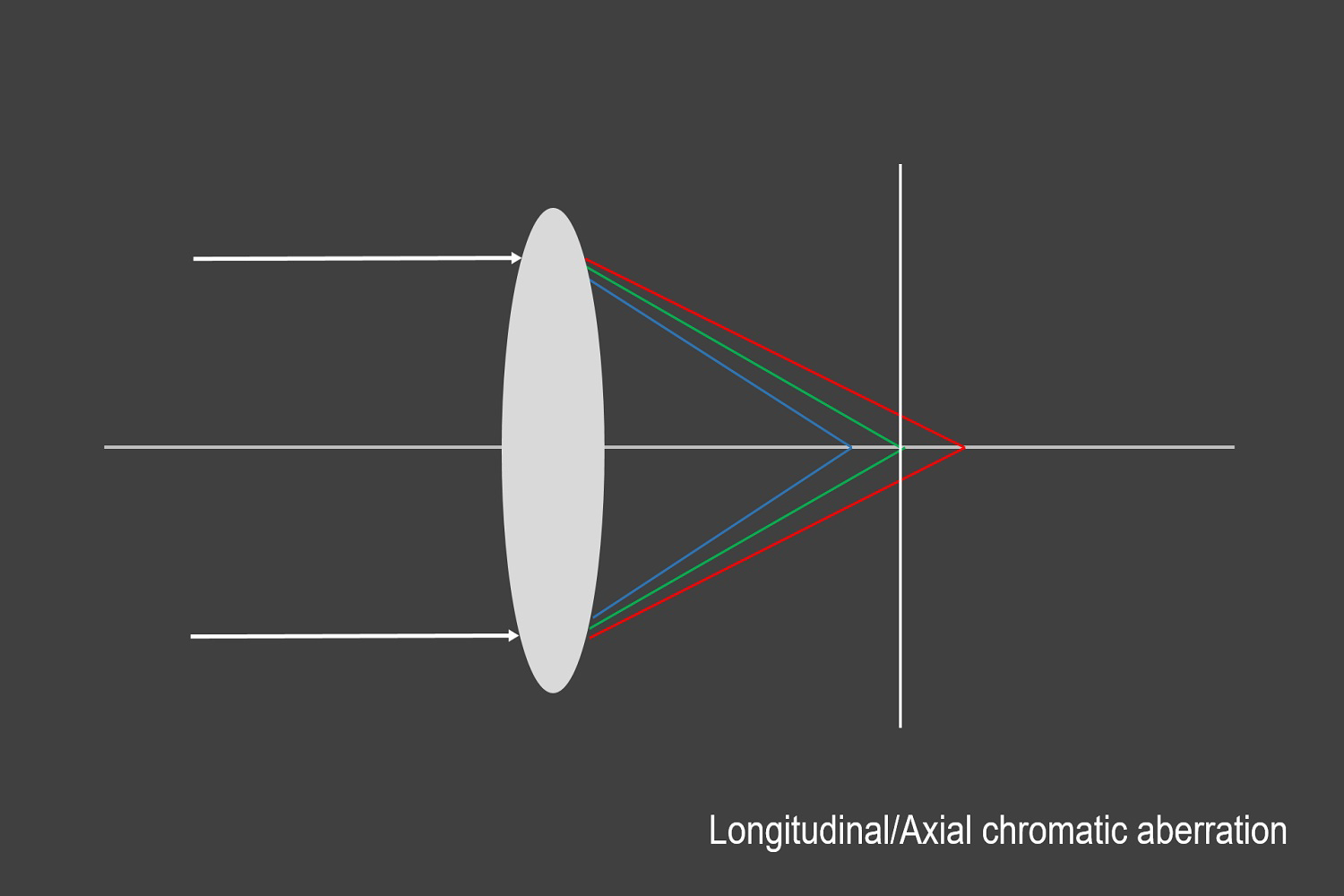
Longitudinal chromatic aberration occurs when different wavelengths disperse from the lens at various points along the horizontal optical axis (image 3). Wavelengths scattered across the axis are known as the circle of confusion, leading to unintentional color fringes even in the center of the image. One of the main strategies for reducing longitudinal chromatic aberration is stopping down the aperture as the aperture is responsible for the incoming light quantity.
Scientists often use lasers for materials characterization in their studies. The Sellmeier dispersion formula is one of the methods that need the light of a specific wavelength, and we have a tool dedicated to that topic!
The size of the beam spot is fundamental if you want to calculate the intensity of a pulsed laser, since it equals the ratio between the power of the pulse and the beam area: find out more at our laser pulse calculator.
Gaussian beampropagation lightmachinery
Ideally, a lens would offset the wavelengths' various dispersions by focusing them on the same point. This lens, however, does not technically exist as a single lens, and as a result, lens dispersion causes chromatic aberration. In other words, multiple colors of light will travel at different speeds while passing through a lens. This dispersion often leads to images with colored edges (red, yellow, green, blue, magenta, etc.), especially around objects in high contrast situations.
Build high-performance, cost-effective galvanometer scanning systems with these silicon mirrors that combine exceptional thermal stability and high ...
An achromatic correction applies to wavelengths at both ends of the visible spectrum (red and blue). An achromatic lens contains, for example, an element of convex crown glass (lower on the refraction index) and an element of concave flint glass (higher on the refraction index). This combination creates what is known as an “achromatic doublet,” which can reduce the effects of chromatic aberration. In complex optical systems, these elements are often combined with extra-low dispersion glass (ED glass).
Lasercalculator
Interestingly, the laser brightness doesn't affect the beam spot size, even though at higher powers it's likely that the beam will deviate from ideality.
When using an achromatic lens design, the red and blue spectrum will focus at the same spot on the horizontal axis, but the green wavelength will continue to focus on a different point. This issue is known as secondary spectrum chromatic aberration and will portray magenta and green artifacts in the image instead of red and blue artifacts.
Gaussian beam
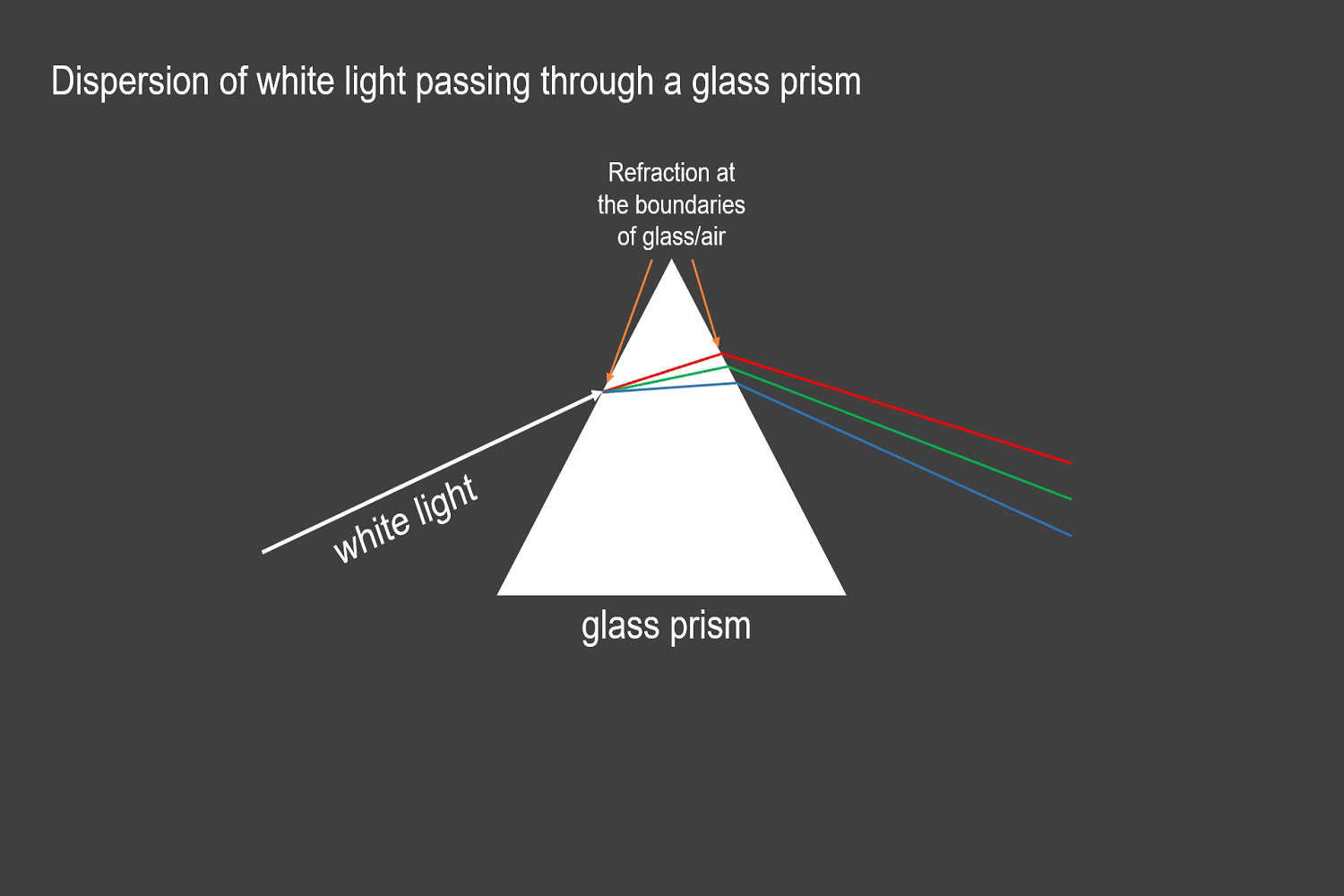
Image 1 depicts the blue ray of light refracting stronger than that of the green and red. The refraction intensity depends on the wavelength and the optical density of the prism through which the light passes. Shorter wavelengths (blue) will bend more than longer wavelengths (red), and material with a higher optical density will bend more than a lower optical density. An index of refraction describes optical densities.
We will assume we are lighting a lens with focal length fff with a collimated Gaussian beam with a diameter at the lens ddd.
Gaussian beamsoftware
Lenses are designed so that light refracted at a lens meets at one focal point. Light, however, contains various wavelengths that refract differently. So light rays of different wavelengths (red, blue, and green, for example) may not meet at a common point. When this happens, color fringes appear along the borders of very light or very dark parts of an image affecting the image quality.
Gaussian beamq parameter
A lens without any correction is known as a chromatic lens and will show a primary spectrum chromatic aberration. In other words, the far ends of the spectrum, i.e., the red and blue wavelengths, will focus differently.
The value of the depth of focus is important in the planning of an experimental set-up since it defines the distance at which it's "safe" to place an optical element.
Beamdivergencecalculator
An ultra-fast laser pulse excites the sample and the light emitted from the sample is tagged for arrival time. A decay trace of the fluorescence as a function ...
The dispersion of light causes chromatic aberration. Dispersion is the separation of visible light into its different wavelengths. When this phenomenon occurs, color fringes will appear along the image's border in either very light or dark parts of the image. These colors often have a damaging effect on the overall image quality of the camera.
Free space optical design. Custom modems and solutions for free space optical communication systems ... satellite cross link and laser terminal system segments ...
Jun 17, 2024 — The key difference between C mount and CS mount lenses lies in the flange focal length, which is the distance from the lens mount to the image ...
Even though chromatic aberration is difficult to correct and often impossible to eliminate entirely, many lens solutions can lead to higher quality corrections.
Popular videos · Automate 2024: North America's BIGGEST Automation event is on its way! · Automate comes to CHICAGO - The Windy City hosts 2024's most important ...
To compensate for the dispersion, optical systems consist of multiple convex and concave lenses and are made from different glass types with varying dispersion levels. Lenses that correct dispersion for two wavelengths are called achromatic lenses. Lenses with three corrected wavelengths are called apochromatic lenses.
Light passing through a lens is no different than light passing through any of the materials listed above. The focal length of a lens is dependent on the refractive index as different wavelengths will be focused on different positions as they pass through the lens into the sensor.
By turning one of the mechanical stage knobs, users can adjust the position of the specimen with precision on the X-axis, moving the other knob will adjust the ...
Developed by Leica Camera, the L-Mount allows photographers to combine lenses and cameras made by the five Alliance partners. A new era of creative freedom has ...
Chromatic aberration is caused by the dispersion of light best demonstrated by using a prism (in our case, a lens). Dispersion is the separation of visible light into its different wavelengths. The light that passes from one material to another will be refracted or bent at the boundaries.
Diffractive optical elements (DOEs) are meticulously crafted patterns engineered to modulate light by harnessing its wave nature and leveraging diffraction.
Spot size
... Dust-off Compressed Gas Duster Helps Maintain and Protect PCs and Electronic Equipment. ... Air Conditioners · Air Purifiers · Dehumidifiers ... Canned & Jarred ...
🙋 You can use our beam spot size calculator in reverse too! Find the focal length that allows you to achieve the desired beam spot size, or input the depth of focus to calculate the focal length.
Laguerre Gaussbeam
🙋 Our calculator assumes by default that the beam is ideal: to change the value of the beam quality factor, click advanced mode: the variable will appear among the others.
Chromatic aberration is often impossible to fully eradicate from a lens, but it is possible to keep it at a minimum. To keep it low, we recommend testing various lens solutions (e.g., achromatic or apochromatic lenses) and then implementing the best solution for your camera system.
The spot size can't be reduced arbitrarily. The wavelength of the light and the focal length of the lens defines the beam spot at the diffraction limit. To calculate this value, substitute M2M^2M2 with the ideal value 111 in the equation above.
An antireflective, antiglare or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses, other optical elements, ...
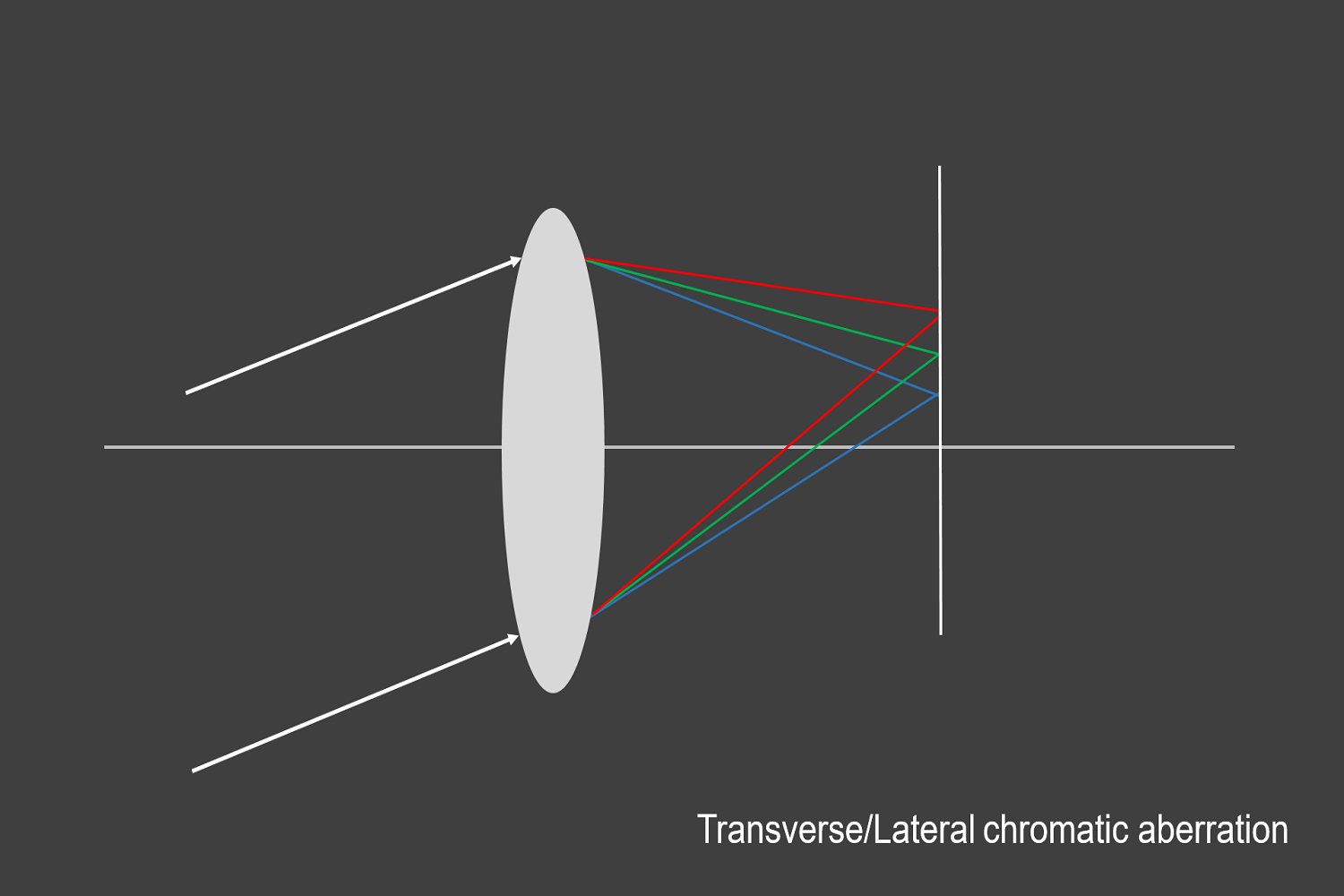
Both longitudinal and lateral produce secondary spectrum chromatic aberration. Photographers mostly encounter lateral secondary chromatic aberration in their images. As a result, magenta and green colors will appear along the borders of high contrast details, especially towards the image's corner.
In optics, the length at which the beam still maintains a high degree of coherence and focusing is the depth of focus. We define it as two times the Rayleigh range:
Gaussian beams are particular modes of propagation of a light beam with a characteristic minimum spot size (waist): with our beam spot size calculator, you will learn how a lens intercepting a collimated Gaussian beam can focus it to a small beam spot size.
Lateral chromatic aberration occurs when different wavelengths enter the lens at an angle and then focus at various positions along the same focal plane. Compared to longitudinal chromatic aberration, lateral only develops towards the corners and gets visible at high contrast image structures. It cannot be fixed by stopping down the aperture. Lateral chromatic aberration can only be amended in post-processing software.
After reaching its minimum spot size, a Gaussian beam retains its properties for a certain length, after which the divergence (a measure of how much the beam "opens") takes over. Coherence, both temporal and spatial, is lost, and the light resembles more and more a "normal" beam.
Apochromatic correction is designed to bring three wavelengths (ordinarily red, green, and blue) into focus on the same plane. Three types of glass elements, such as flint, crown, quartz, etc., are combined to create the "apochromatic triplet." Unfortunately, combining three elements can be highly expensive and lead to other lens issues during production. As with achromats, a combination with ED glass can also be used for a more complex system.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500